A Continent Unfurled: Exploring the African Map with Names
Related Articles: A Continent Unfurled: Exploring the African Map with Names
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Continent Unfurled: Exploring the African Map with Names. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Continent Unfurled: Exploring the African Map with Names
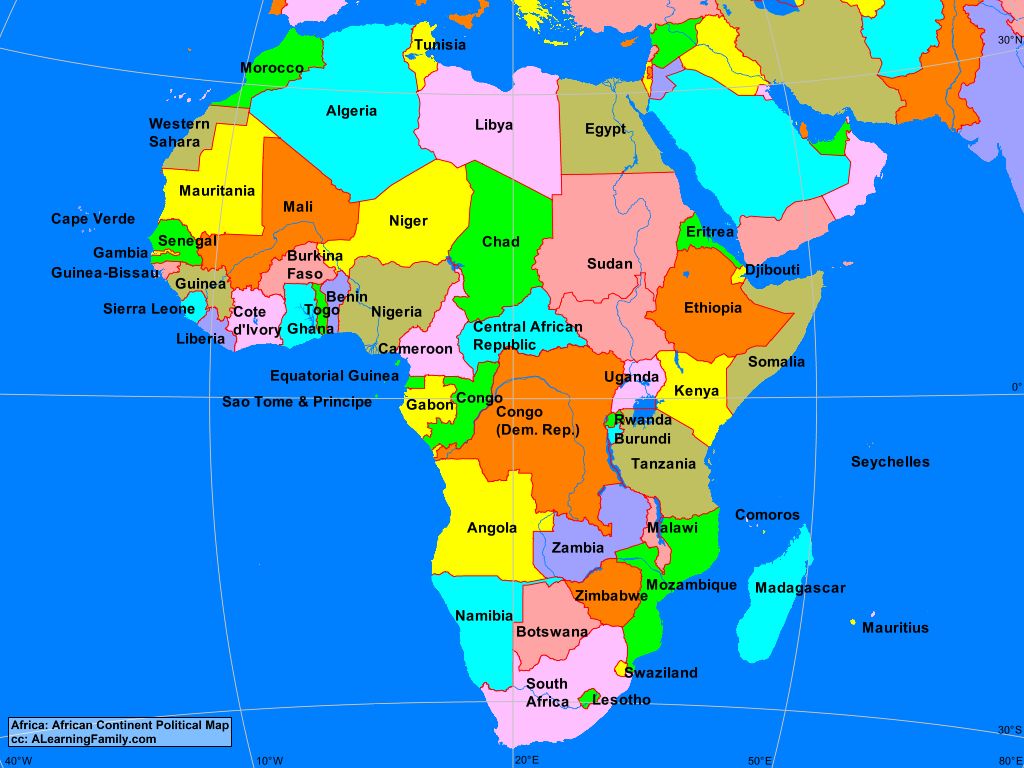
The African continent, the second-largest landmass on Earth, is a tapestry woven with diverse landscapes, vibrant cultures, and a rich history. Its geographic features and political divisions are intricately intertwined, shaping its destiny and influencing its people. Navigating this vast and complex continent requires a comprehensive understanding of its physical geography and political landscape. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the African map with names, highlighting its significance in understanding the continent’s unique character and complexities.
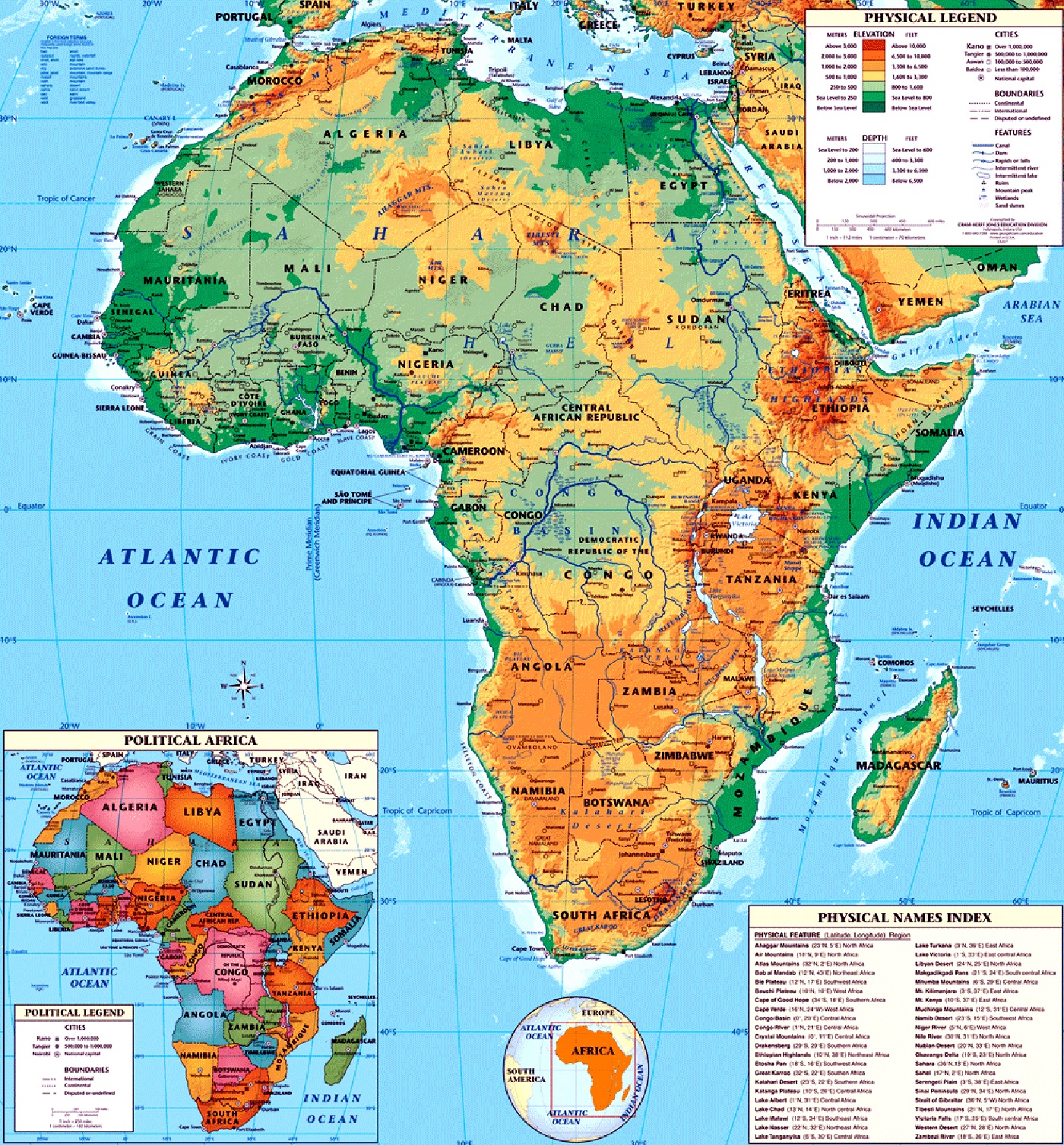
A Geographic Overview
Africa’s physical geography is as diverse as its cultural tapestry. From the snow-capped peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, the continent encompasses a wide array of landscapes.
Landforms and Features:
- Mountains: The Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the Drakensberg Mountains in South Africa are prominent mountain ranges, contributing to the continent’s diverse topography.
- Deserts: The Sahara, the largest hot desert in the world, dominates North Africa. Other significant deserts include the Namib and Kalahari in Southern Africa.
- Plateaus: The African continent is characterized by extensive plateaus, including the East African Plateau, the Congo Basin, and the Highveld in South Africa.
- Rivers and Lakes: The Nile River, the longest river in the world, flows through northeastern Africa. Other major rivers include the Congo, Niger, and Zambezi. Africa is also home to numerous lakes, including Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa, and Lake Tanganyika, the second deepest lake in the world.
Climate Zones:
Africa’s diverse climate zones are shaped by its geographic location, latitude, and altitude.
- Tropical Climates: The equatorial regions experience hot and humid tropical climates with abundant rainfall.
- Arid Climates: North and Southern Africa are dominated by arid climates, characterized by low rainfall and high temperatures.
- Mediterranean Climates: The northern and southern coastal regions experience Mediterranean climates with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
- Subtropical Climates: Coastal areas in the south and east experience subtropical climates with warm temperatures and moderate rainfall.
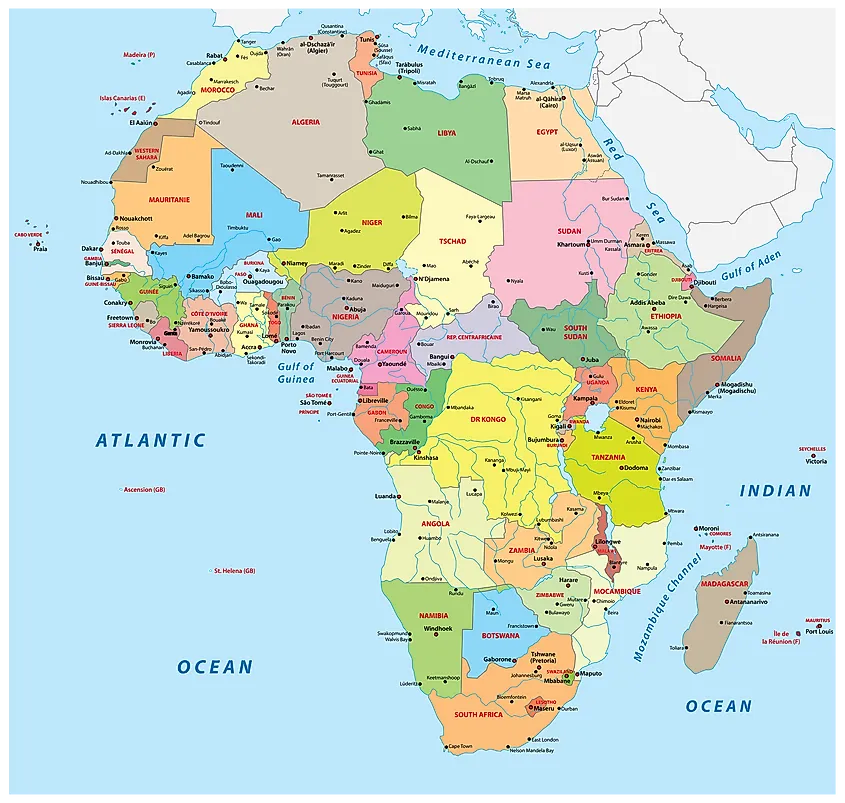
Political Divisions:
The African continent is politically divided into 54 sovereign states, each with its unique history, culture, and political system.
- North Africa: Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara.
- West Africa: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, Côte d’Ivoire, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
- Central Africa: Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe.
- East Africa: Burundi, Comoros, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Rwanda, Seychelles, Somalia, South Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zambia.
- Southern Africa: Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia, South Africa, and Zimbabwe.
The Importance of Understanding the African Map with Names
Understanding the African map with names is crucial for comprehending the continent’s complexities and appreciating its unique characteristics.
- Economic Development: The map provides insights into the distribution of natural resources, infrastructure, and economic activities, facilitating informed decision-making in development initiatives.
- Political Dynamics: The map helps analyze political boundaries, regional alliances, and conflicts, shedding light on the continent’s political landscape.
- Cultural Diversity: The map reflects the diverse cultures, languages, and ethnicities that shape the continent’s rich heritage.
- Environmental Challenges: Understanding the geographic features, climate zones, and ecosystems is essential for addressing environmental challenges such as deforestation, desertification, and climate change.
- Global Connections: The map highlights Africa’s strategic location and its role in global trade, migration, and security.
FAQs about the African Map with Names
1. What are the major geographical features of Africa?
Africa is characterized by diverse landforms, including mountains, deserts, plateaus, rivers, and lakes. The continent’s physical geography significantly impacts its climate, ecosystems, and human activities.
2. What are the main climate zones in Africa?
Africa encompasses a wide range of climate zones, from tropical climates in the equatorial regions to arid climates in the north and south. The continent’s diverse climates influence its vegetation, agriculture, and human settlements.
3. What are the largest countries in Africa by land area?
The largest countries in Africa by land area are Algeria, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sudan, Libya, and Angola. The size of these countries reflects their geographic diversity and potential for natural resources.
4. What are some of the major challenges facing Africa?
Africa faces numerous challenges, including poverty, inequality, conflict, disease, and environmental degradation. Understanding these challenges is crucial for promoting sustainable development and improving the lives of its people.
5. What are some of the opportunities for Africa’s future?
Despite its challenges, Africa holds immense potential for growth and development. The continent’s abundant natural resources, growing population, and emerging markets offer opportunities for economic prosperity and social progress.
Tips for Navigating the African Map with Names
- Use a high-quality map: Choose a map with clear labels, accurate borders, and detailed information about geographical features and political divisions.
- Focus on key regions: Start by familiarizing yourself with the major regions of Africa, such as North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, and Southern Africa.
- Learn about major cities and landmarks: Identify important cities, landmarks, and geographical features to gain a better understanding of the continent’s geography.
- Explore online resources: Utilize online maps, atlases, and educational websites to enhance your knowledge of the African map with names.
- Engage with other learners: Discuss your findings with others and share your insights to deepen your understanding of the continent.
Conclusion
The African map with names is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich diversity, complex history, and unique challenges. By engaging with the map and its intricate details, we gain a deeper appreciation for the continent’s cultural tapestry, its physical geography, and its potential for a brighter future. As we navigate the complexities of the African landscape, the map serves as a compass, guiding us towards a more informed and inclusive understanding of this dynamic and vibrant continent.
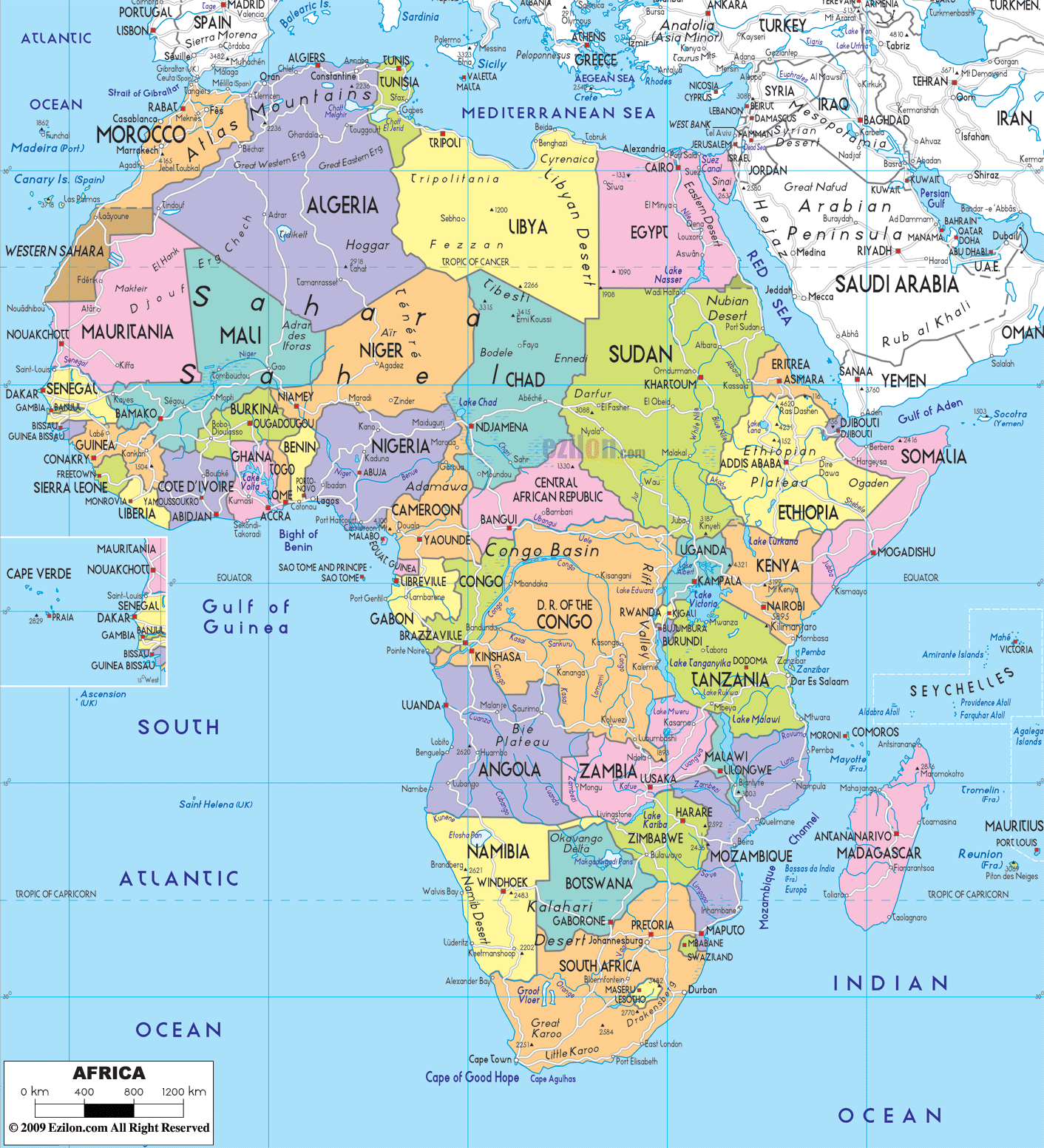
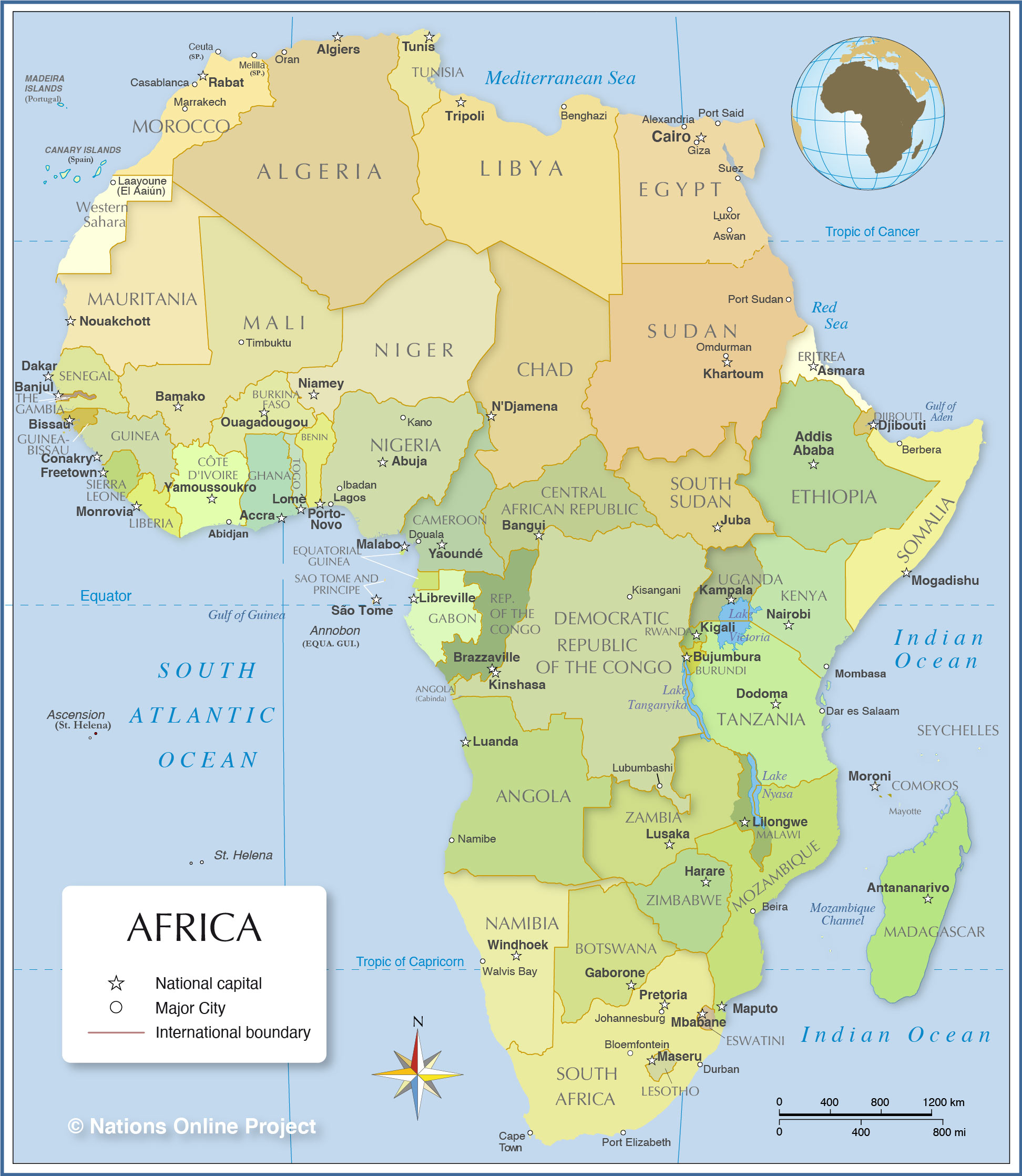
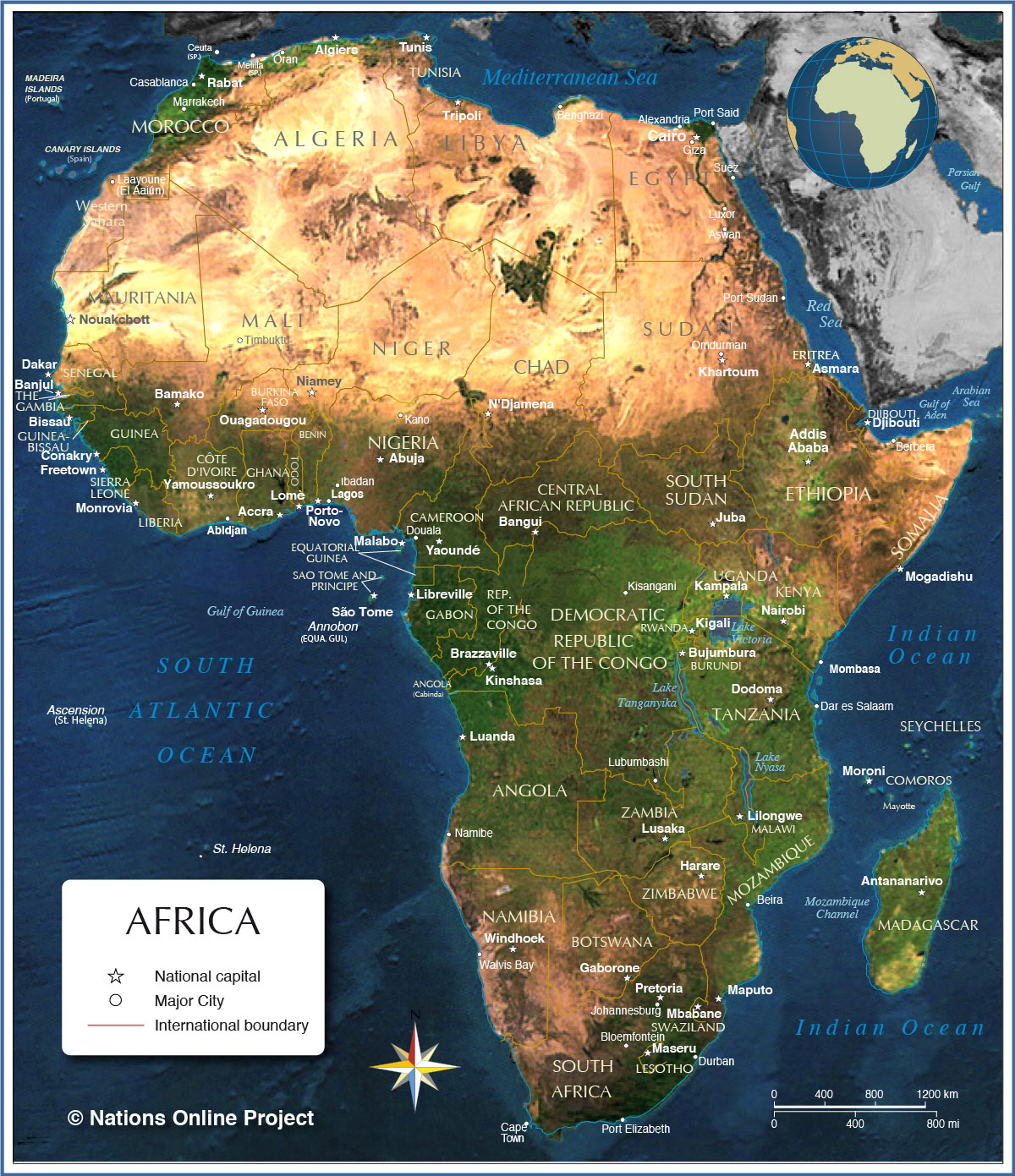



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Continent Unfurled: Exploring the African Map with Names. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!