A Tapestry of Conflict: Major Battles of the American Civil War
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Conflict: Major Battles of the American Civil War
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Conflict: Major Battles of the American Civil War. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Conflict: Major Battles of the American Civil War
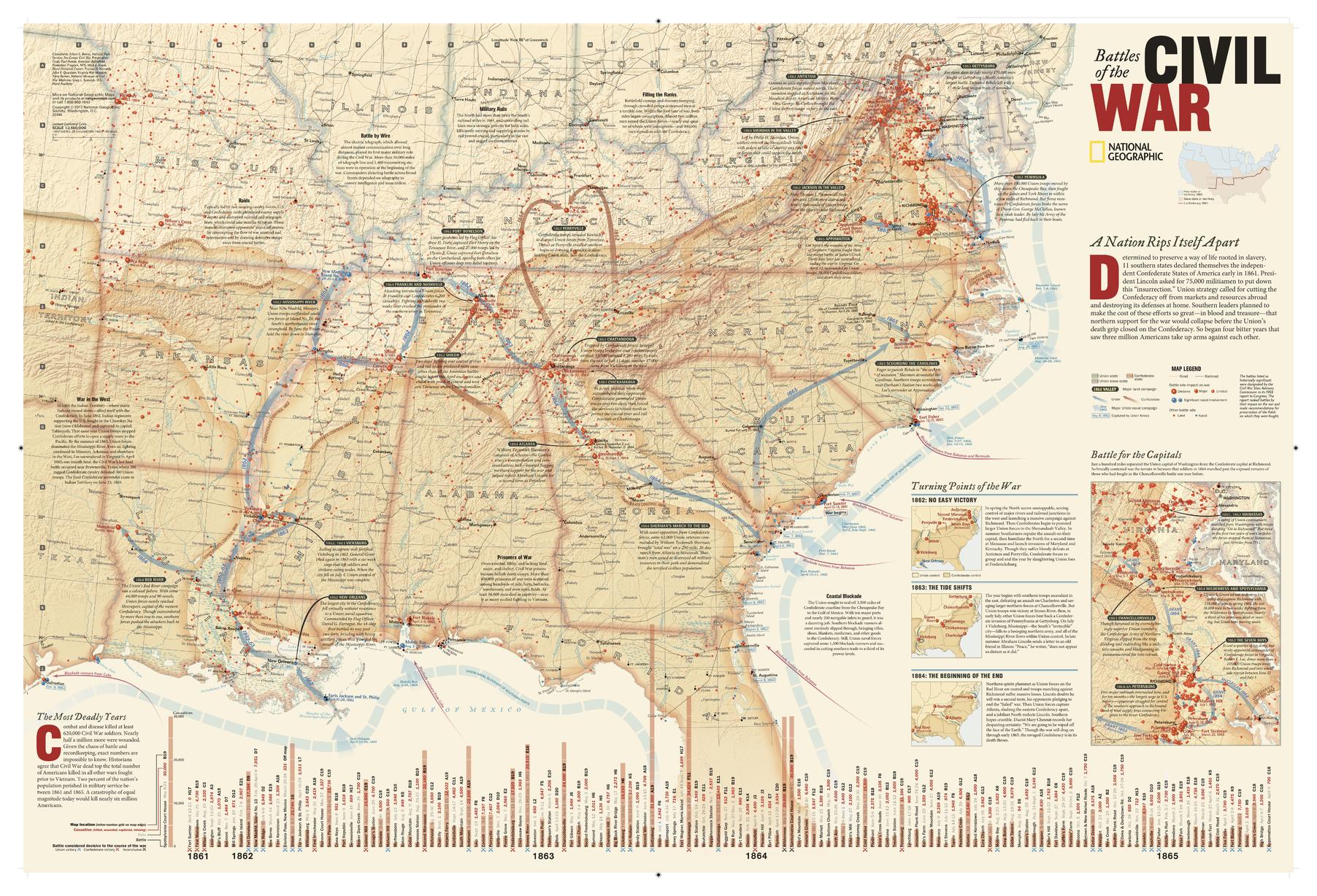
The American Civil War, a tumultuous period in American history, was fought over the issue of slavery and the fundamental principles of the Union. This brutal conflict spanned four years, from 1861 to 1865, leaving an indelible mark on the nation’s landscape and psyche. The war’s narrative is woven through a tapestry of major battles, each a pivotal moment in the struggle for freedom and unity.
The Early Battles: Setting the Stage
The first shots of the war were fired at Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, on April 12, 1861. The Confederate forces, led by Brigadier General P.G.T. Beauregard, bombarded the fort, forcing its surrender. This act ignited the flames of war, and the Union mobilized its troops to confront the secessionist South.
One of the first major engagements was the Battle of Bull Run (also known as the First Battle of Manassas), fought on July 21, 1861, near Manassas Junction, Virginia. This battle saw a Confederate victory, shattering the Union’s initial optimism and highlighting the long and arduous road ahead.
The Western Front: A Struggle for Control
The Western Theater of the war saw a series of battles, primarily in the states of Kentucky, Tennessee, and Mississippi. The Union’s goal was to capture the Mississippi River, cutting off the Confederacy’s vital supply lines.
The Battle of Shiloh (April 6-7, 1862), fought in southwestern Tennessee, was one of the bloodiest engagements of the war. The Confederates, under General Albert Sidney Johnston, launched a surprise attack on Union forces led by Ulysses S. Grant. Despite initial setbacks, Grant ultimately prevailed, solidifying Union control of the crucial Tennessee River.
The Battle of Vicksburg (May 18-July 4, 1863) marked a turning point in the war. Grant’s siege of Vicksburg, a key Confederate stronghold on the Mississippi River, lasted for weeks. The Union forces, under relentless bombardment, finally captured the city on July 4, 1863, giving them complete control of the river.
The Eastern Front: A Grueling Struggle for the Capital
The Eastern Theater was marked by a series of brutal battles, fought primarily in Virginia and Maryland. The Union’s primary objective was to capture the Confederate capital at Richmond.
The Battle of Antietam (September 17, 1862), fought near Sharpsburg, Maryland, was one of the bloodiest single-day battles in American history. The Union forces, led by General George B. McClellan, clashed with the Confederate army under General Robert E. Lee. The battle resulted in a tactical Union victory, preventing Lee’s invasion of the North and allowing President Abraham Lincoln to issue the Emancipation Proclamation.
The Battle of Gettysburg (July 1-3, 1863), fought in Pennsylvania, was a pivotal battle in the war. Lee’s invasion of the North was met with a fierce resistance by Union forces under General George Meade. The Confederates suffered a crushing defeat, marking the turning point of the war in favor of the Union.
The Final Push: The Road to Victory
The final year of the war saw the Union forces gain momentum, pushing towards the Confederacy’s heartland. The Battle of Atlanta (July 22-September 2, 1864), fought in Georgia, was a major victory for the Union forces under General William T. Sherman. The capture of Atlanta, a key Confederate rail hub, dealt a significant blow to the Confederacy’s war effort.
Sherman’s March to the Sea (November 15-December 21, 1864), a devastating campaign through Georgia, further weakened the Confederacy. Sherman’s army destroyed infrastructure and resources, crippling the South’s ability to sustain the war.
The Siege of Petersburg (June 15, 1864-April 2, 1865), a protracted siege of a crucial Confederate supply center in Virginia, marked the final stages of the war. The Union forces, under Ulysses S. Grant, gradually tightened their grip on Petersburg, forcing the Confederates to abandon the city.
The End of the War
The war finally came to an end on April 9, 1865, with the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee to Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House, Virginia. The surrender marked the end of the Confederacy and the beginning of the long process of national reunification.
FAQs by Major Battles of the Civil War
1. What was the significance of the Battle of Bull Run?
The Battle of Bull Run, despite its early stage in the war, demonstrated the Union’s unpreparedness and the strength of the Confederate forces. It shattered the initial belief of a swift victory and highlighted the need for a more strategic approach to the conflict.
2. Why was the Battle of Shiloh so bloody?
The Battle of Shiloh was characterized by intense fighting and a high casualty rate due to the surprise attack launched by the Confederates and the dense terrain where the battle took place. The battle serves as a stark reminder of the brutal realities of war.
3. How did the Battle of Vicksburg impact the war?
The capture of Vicksburg by the Union forces gave them control of the Mississippi River, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two. This strategic victory dealt a significant blow to the South’s ability to supply its troops and hindered their war effort.
4. What was the importance of the Battle of Antietam?
The Battle of Antietam, though a tactical Union victory, was a devastating battle with a high casualty rate. However, its significance lies in preventing Lee’s invasion of the North and providing President Lincoln the opportunity to issue the Emancipation Proclamation, shifting the war’s focus to the abolition of slavery.
5. How did the Battle of Gettysburg change the course of the war?
The Battle of Gettysburg marked a turning point in the war, as the Confederates suffered a decisive defeat, halting their advance into the North and weakening their morale. It also provided a significant boost to Union morale and solidified the Union’s resolve to fight for the preservation of the nation.
6. What was the impact of Sherman’s March to the Sea?
Sherman’s March to the Sea was a devastating campaign that crippled the Confederacy’s infrastructure and resources. It demoralized the Southern population and further weakened their ability to sustain the war.
7. Why was the Siege of Petersburg crucial?
The Siege of Petersburg, a prolonged and bloody battle, ultimately forced the Confederates to abandon the city, a vital supply center for Richmond. This victory significantly weakened the Confederacy’s military capabilities and contributed to their eventual surrender.
Tips by Major Battles of the Civil War
1. Utilize maps and timelines: Visual aids, such as maps and timelines, can help in understanding the geographical context of the battles and the chronology of events.
2. Focus on the key players: Understanding the roles of major military figures like Ulysses S. Grant, Robert E. Lee, and William T. Sherman can provide valuable insights into the strategies and outcomes of the battles.
3. Explore primary sources: Reading diaries, letters, and official reports from the period can offer firsthand accounts of the battles and the human cost of the war.
4. Consider the social and political context: Understanding the political climate, the issues of slavery and states’ rights, and the social impact of the war can provide a more complete understanding of the battles and their significance.
Conclusion by Major Battles of the Civil War
The major battles of the Civil War were not just military engagements but pivotal moments that shaped the course of the nation. They reflected the complexities of the conflict, the sacrifices made by both sides, and the ultimate triumph of the Union cause. These battles continue to serve as reminders of the importance of unity, freedom, and the enduring legacy of the Civil War in American history.

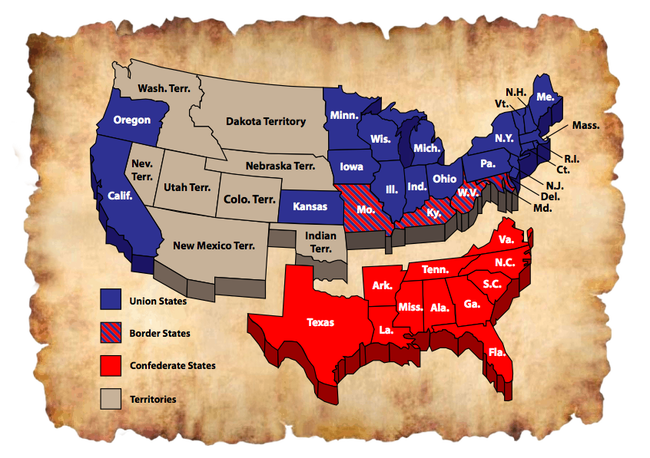
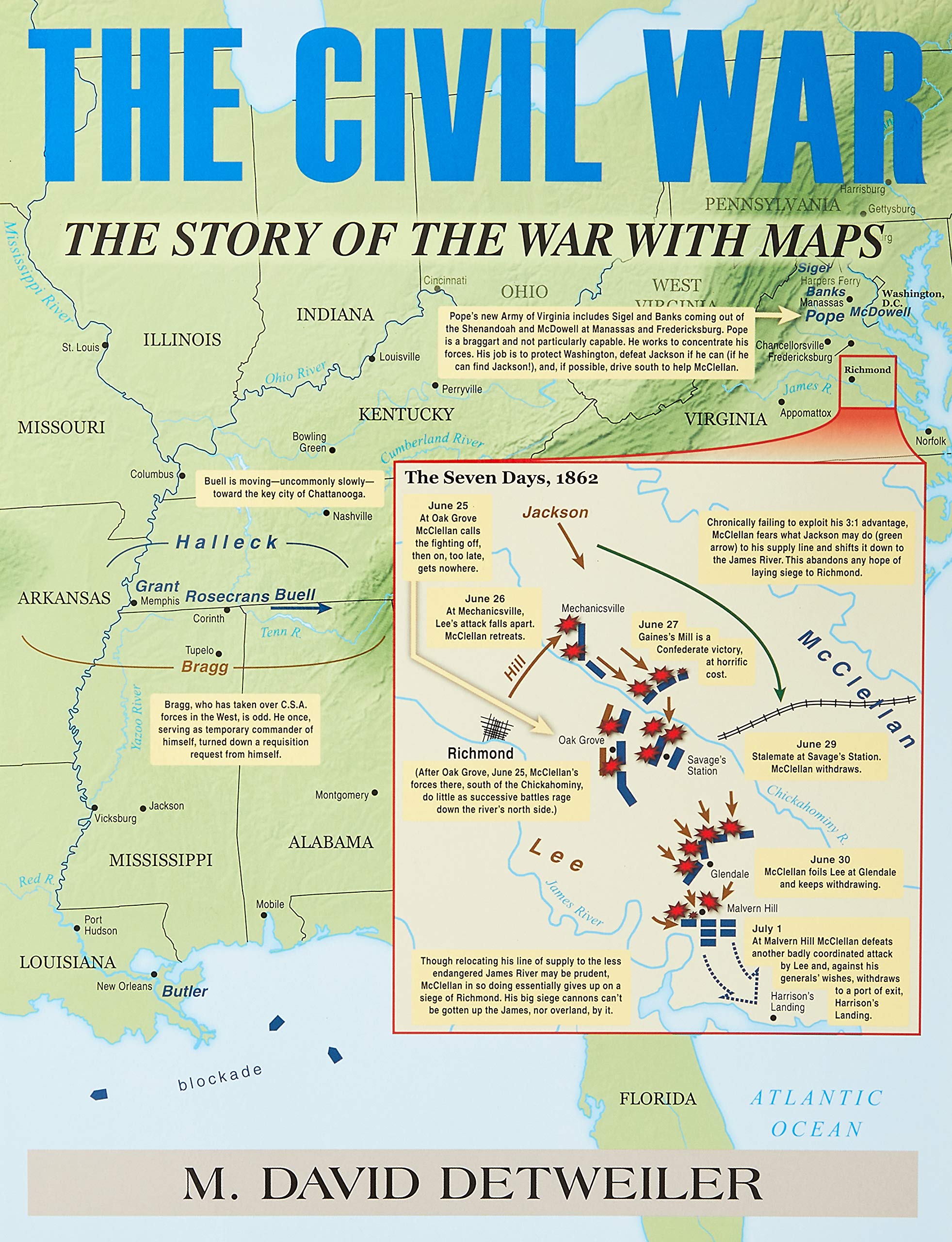
/3204210_HighRes-resize-56a4881b3df78cf77282dc90.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Conflict: Major Battles of the American Civil War. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!