Charting the Future: Understanding Climate Change Map Projections
Related Articles: Charting the Future: Understanding Climate Change Map Projections
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Future: Understanding Climate Change Map Projections. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Future: Understanding Climate Change Map Projections
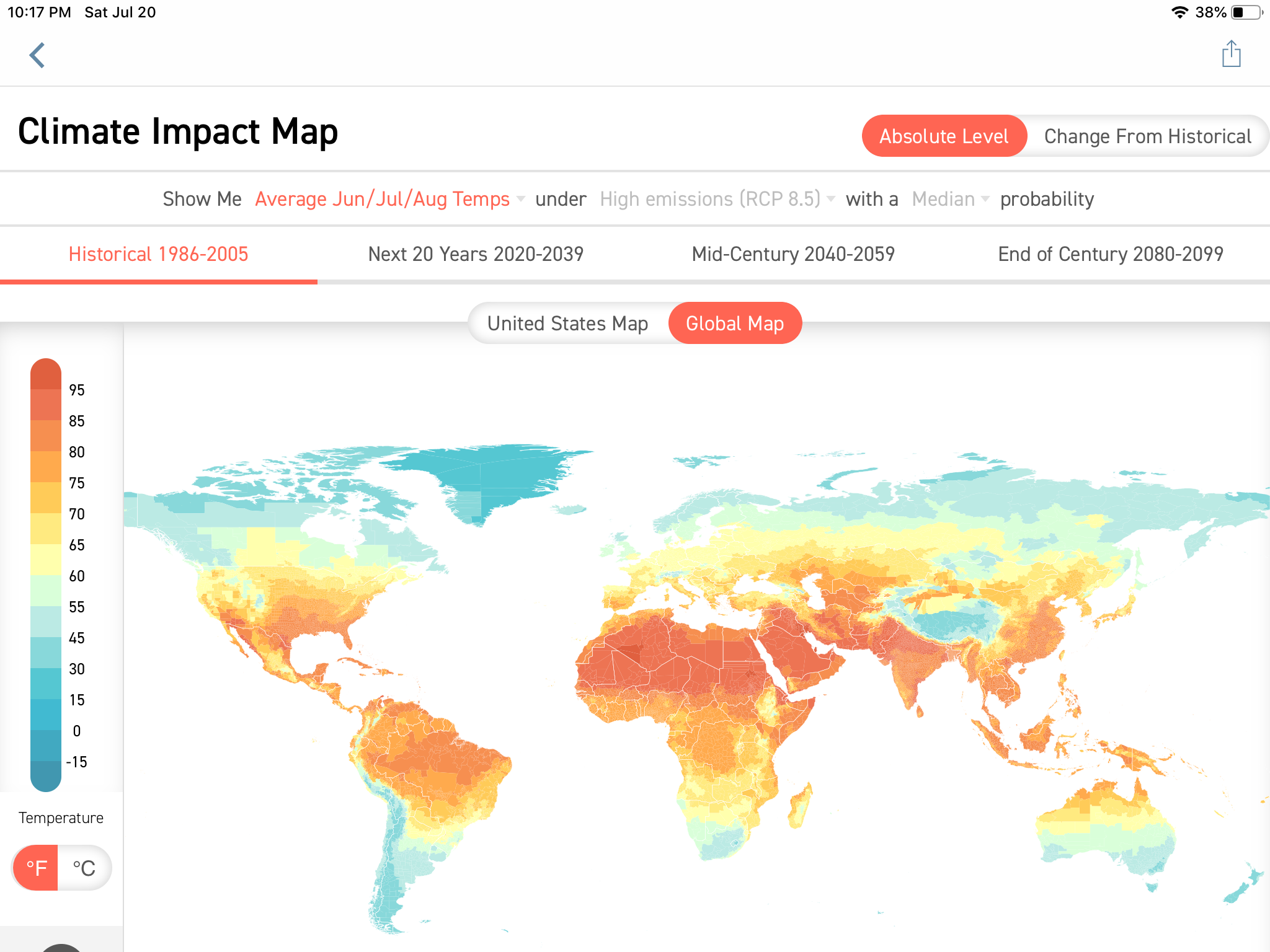
Climate change is a multifaceted and complex challenge, with far-reaching consequences for ecosystems, societies, and economies. To effectively address this issue, we need to understand its potential impacts and develop strategies for mitigation and adaptation. Climate change map projections serve as invaluable tools in this endeavor, providing crucial insights into the future trajectory of our planet under varying climate scenarios.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Climate change map projections are visual representations of projected changes in climate variables, such as temperature, precipitation, and sea level rise, across geographical regions. These projections are generated through sophisticated computer models that simulate the Earth’s climate system, incorporating various factors like greenhouse gas emissions, solar radiation, and ocean currents.
Key Components of Climate Change Map Projections
Several key components contribute to the accuracy and comprehensiveness of climate change map projections:
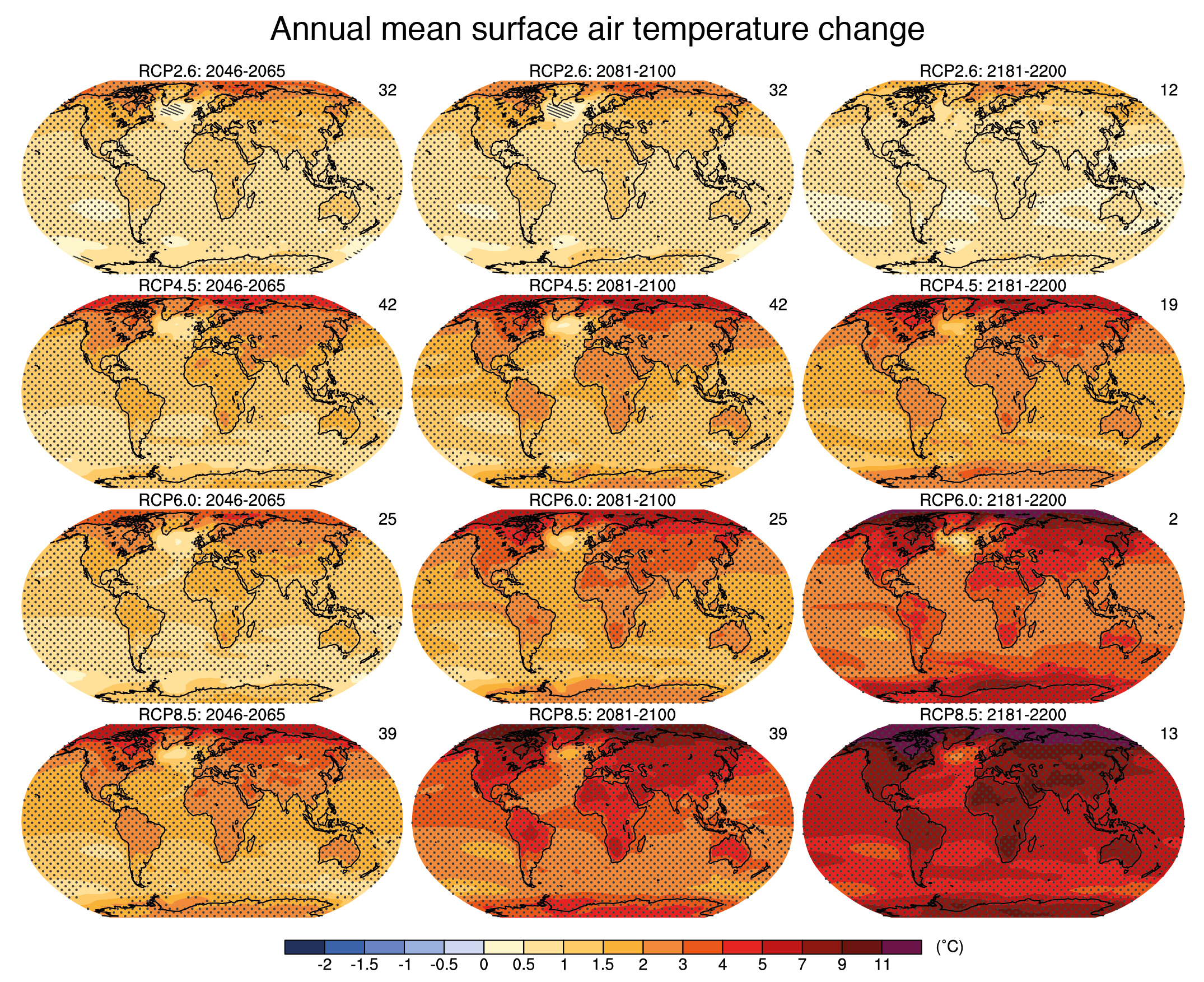
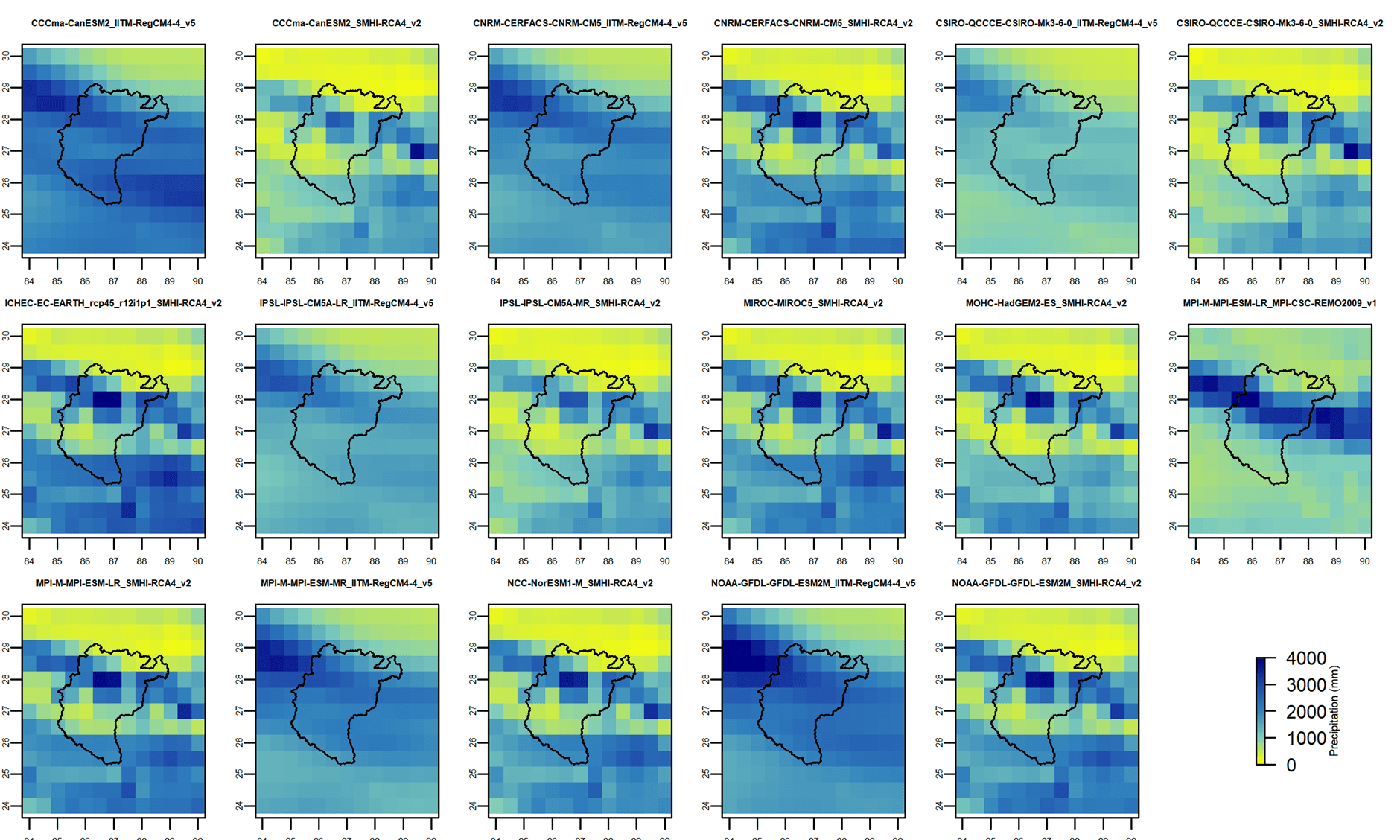
- Climate Models: These models are complex mathematical representations of the Earth’s climate system, incorporating physical laws governing atmospheric, oceanic, and terrestrial processes. They are constantly being refined and improved based on advancements in scientific understanding and computing power.
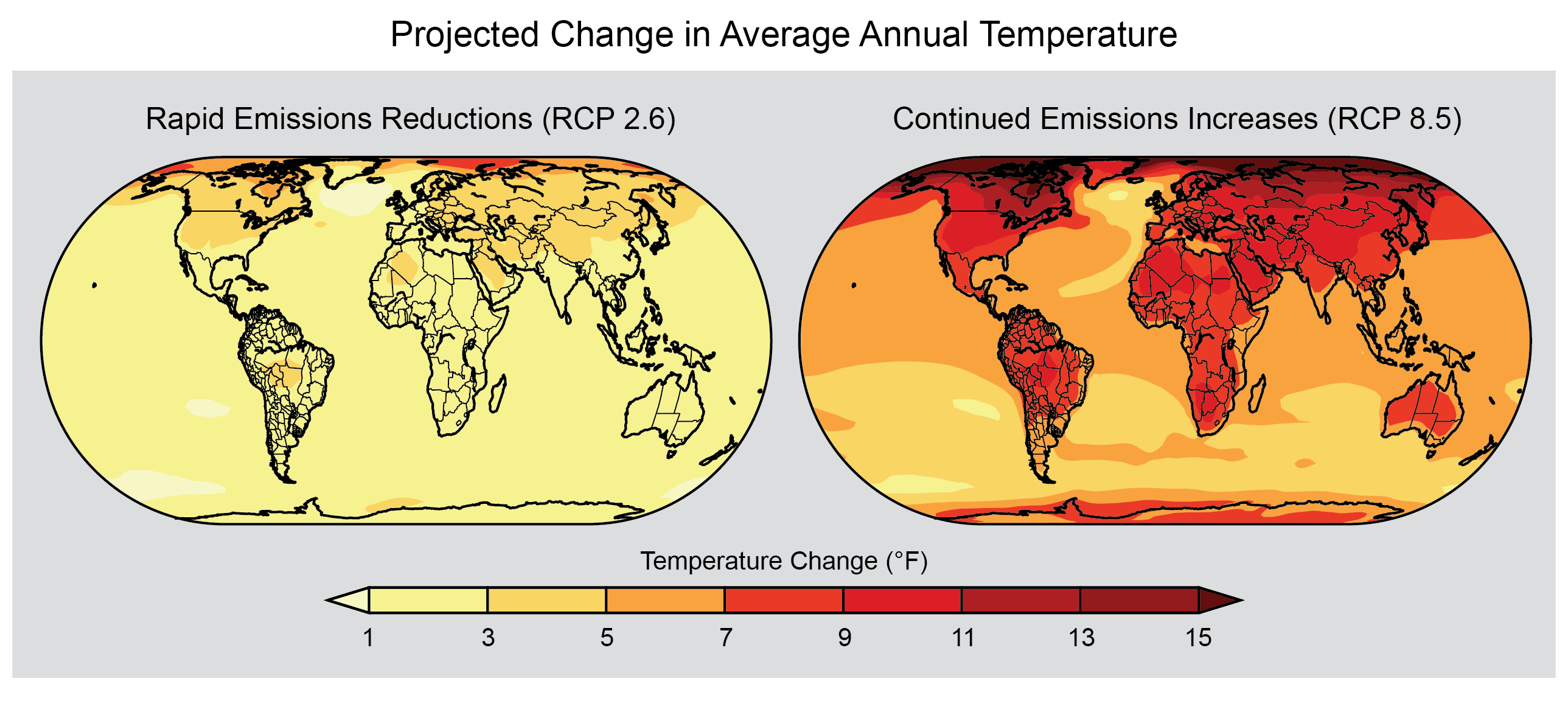
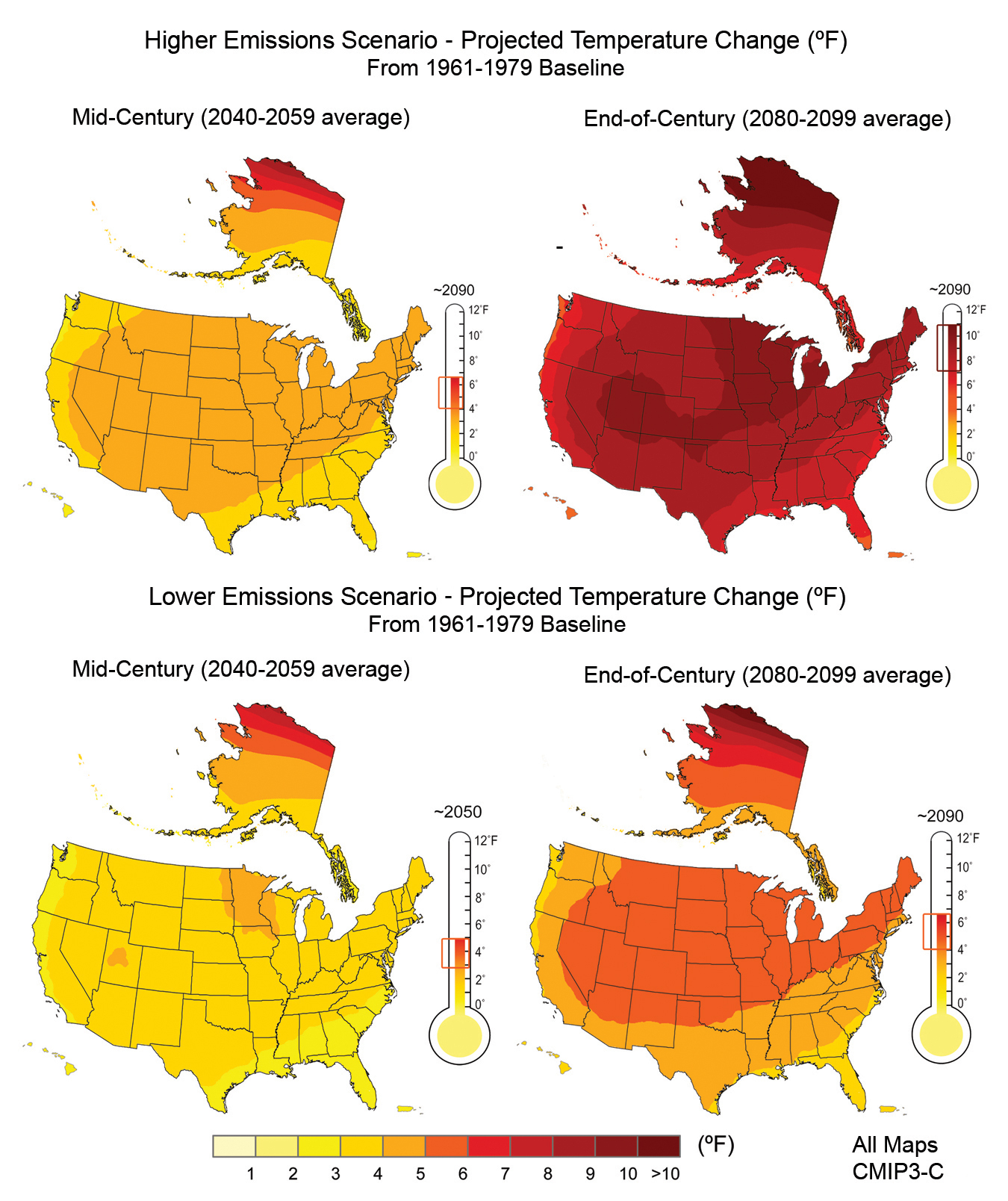
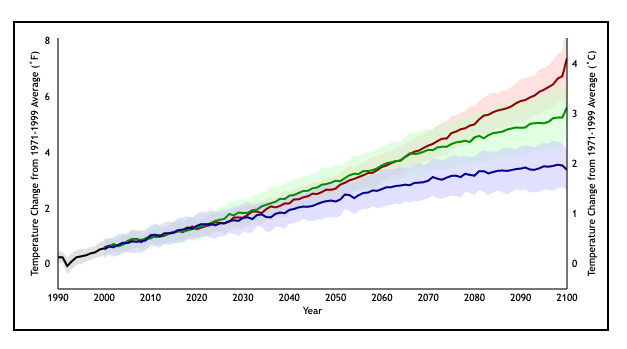
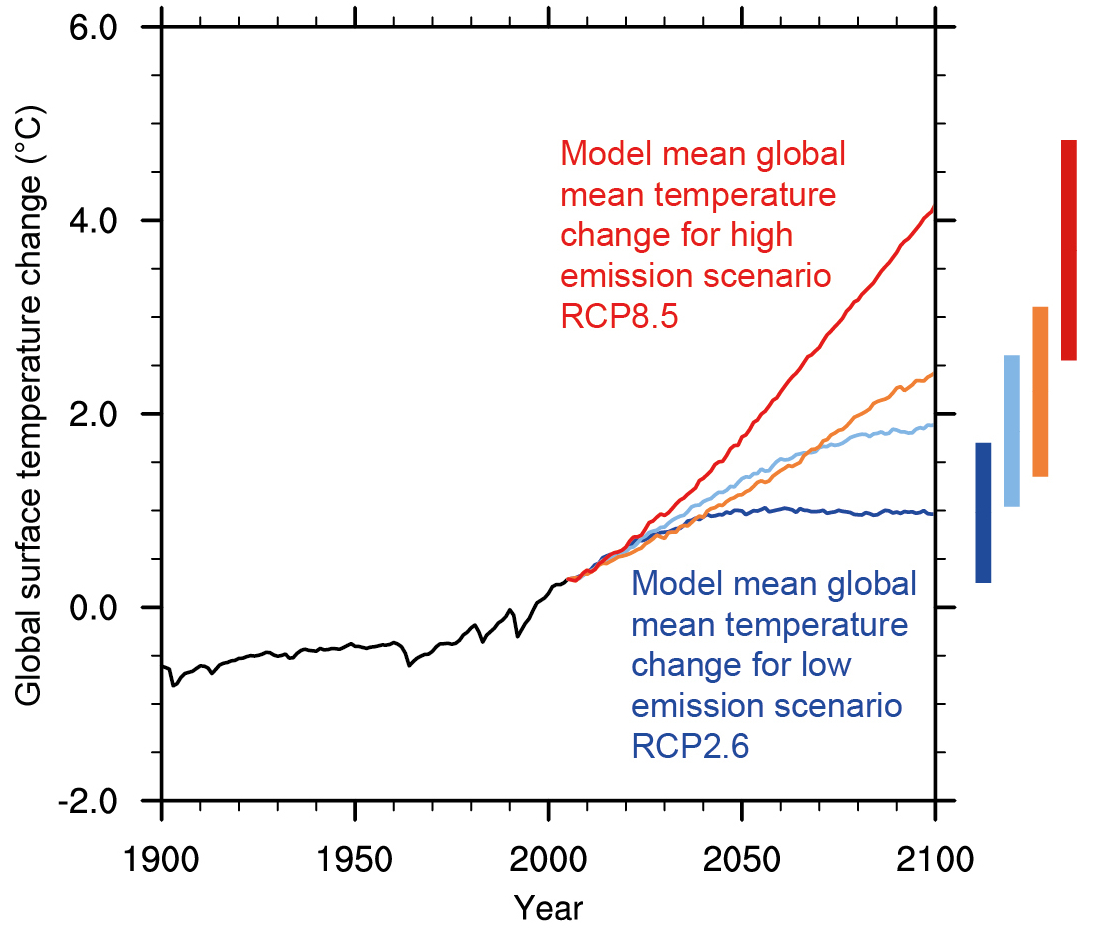
- Emission Scenarios: These scenarios represent different plausible futures for greenhouse gas emissions, ranging from optimistic scenarios with rapid emissions reductions to pessimistic scenarios with continued high emissions. Each scenario leads to distinct climate projections.
- Spatial Resolution: This refers to the level of detail captured in the projections, with higher resolutions providing more localized information. The choice of resolution depends on the intended application, with finer resolutions often required for regional assessments.
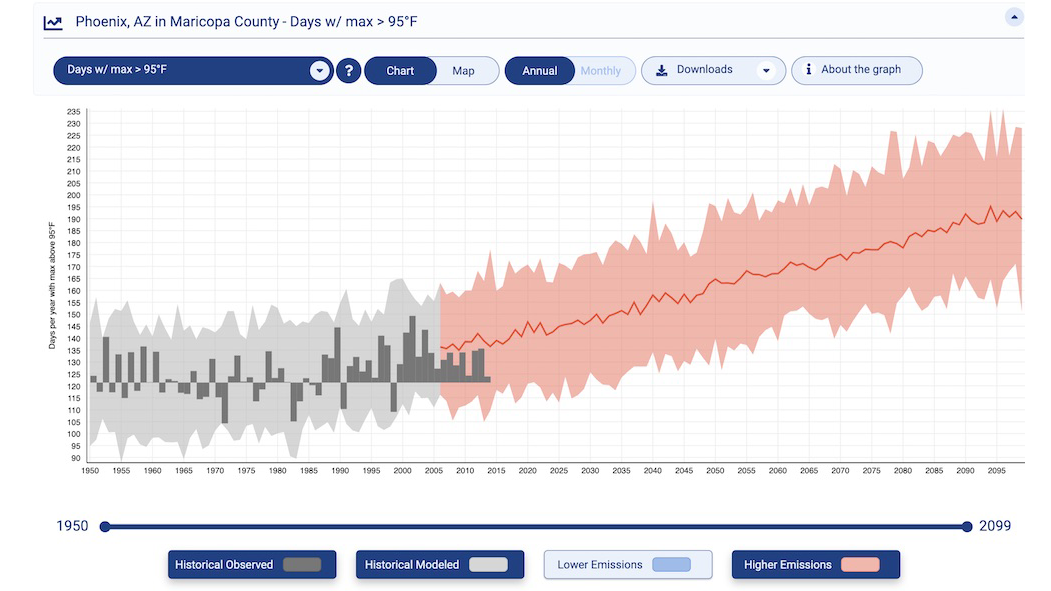
- Time Horizons: Projections are typically generated for different time periods, ranging from decades to centuries, allowing for an assessment of long-term trends and impacts.
- Uncertainty: Climate change projections inherently involve uncertainty, stemming from the complexity of the climate system, limitations in model representations, and the inherent variability of natural processes. This uncertainty is acknowledged and quantified in the projections, providing a range of possible outcomes.
Applications and Benefits of Climate Change Map Projections
Climate change map projections offer a wide range of applications, providing valuable information for decision-making across diverse sectors:
- Resource Management: Projections can inform water resource management, agricultural planning, and ecosystem conservation by highlighting areas vulnerable to drought, flooding, or changes in biodiversity.
- Infrastructure Planning: They aid in designing and adapting infrastructure to withstand extreme weather events, such as heatwaves, floods, and sea level rise, ensuring resilience and minimizing risks.
- Disaster Risk Reduction: Projections help identify areas prone to climate-related disasters, allowing for targeted preparedness and mitigation efforts to minimize human and economic losses.
- Policy Development: Projections provide crucial data for informing climate policies, such as carbon pricing, renewable energy investments, and adaptation strategies.
- Public Awareness: They can effectively communicate the potential impacts of climate change, raising awareness and motivating individuals and communities to take action.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How reliable are climate change map projections?
A: While climate change map projections involve inherent uncertainty, they are based on robust scientific principles and have consistently shown remarkable accuracy in predicting past climate changes. Ongoing research and advancements in modeling techniques continually improve their reliability.
Q: What are the limitations of climate change map projections?
A: Limitations include the complexity of the climate system, which makes it challenging to fully capture all relevant factors. Moreover, projections are based on assumptions about future emissions and societal responses, which can influence outcomes.
Q: How can I access and interpret climate change map projections?
A: Several organizations, including the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), national meteorological agencies, and research institutions, provide publicly accessible climate projections. Online platforms and interactive tools are often available to visualize and interpret these projections.
Q: How can climate change map projections be used to inform decision-making?
A: Projections can be integrated into decision-making processes by:
- Identifying vulnerable areas: Identifying regions most susceptible to climate change impacts allows for targeted adaptation strategies.
- Assessing risks and opportunities: Evaluating potential risks and opportunities associated with climate change can inform investment decisions and policy development.
- Developing adaptation plans: Projections can guide the development of adaptation plans, including infrastructure upgrades, water management strategies, and disaster preparedness measures.
Tips for Using Climate Change Map Projections
- Consider the context: Pay attention to the specific emission scenario, time horizon, and spatial resolution used in the projections.
- Understand the uncertainty: Recognize the inherent uncertainty in projections and consider a range of possible outcomes.
- Integrate with other data: Combine climate projections with other relevant data, such as demographic information, economic indicators, and existing infrastructure.
- Engage with stakeholders: Involve relevant stakeholders in the interpretation and application of climate projections to ensure their relevance and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Climate change map projections are essential tools for understanding and responding to the complex challenges posed by a changing climate. They provide a roadmap for navigating the future, highlighting areas of vulnerability, informing decision-making, and guiding adaptation strategies. By leveraging these projections, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Future: Understanding Climate Change Map Projections. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!