Deciphering California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Diverse Regions
Related Articles: Deciphering California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Diverse Regions
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Diverse Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Diverse Regions
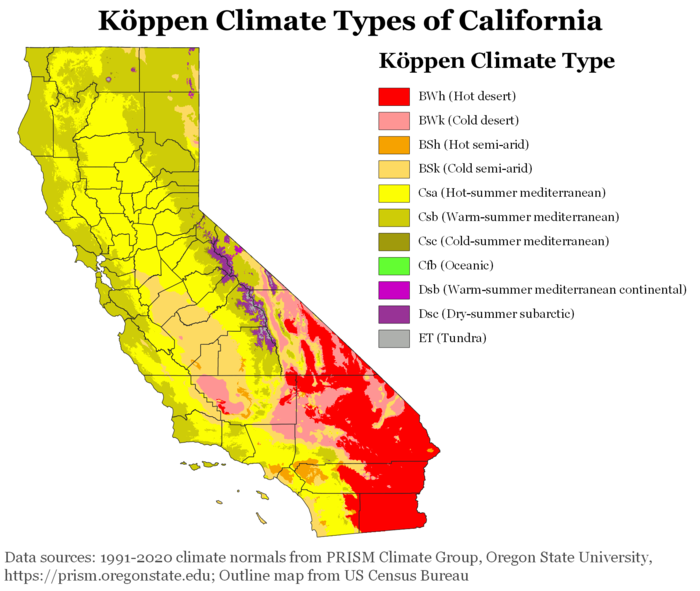
California, renowned for its iconic coastline, sprawling deserts, and towering mountains, boasts an astonishing diversity of climates. Understanding these nuances is crucial for appreciating the state’s unique ecosystems, informing agricultural practices, and planning for the future in the face of climate change.
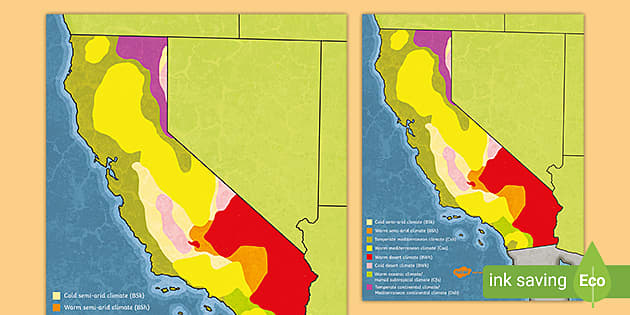
A climate map of California reveals a tapestry of distinct microclimates, shaped by a complex interplay of geographical factors. The Pacific Ocean, the Sierra Nevada mountain range, and the state’s latitude all contribute to the distribution of temperature, precipitation, and other climate variables.
The Coastal Influence: A Tapestry of Moderation
The Pacific Ocean’s vast expanse exerts a significant moderating influence on California’s coastal regions. The cool California Current, flowing southward along the coast, brings relatively cool, moist air, resulting in mild temperatures year-round. This maritime influence creates a Mediterranean climate, characterized by warm, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
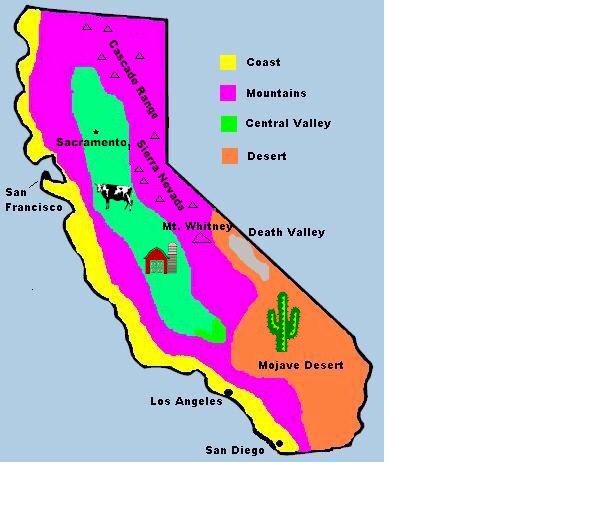
The coastal region, stretching from the northern border to the Mexican border, experiences a diverse range of microclimates. Northern coastal regions, including areas like Humboldt County, receive significant rainfall, supporting lush forests and temperate rainforests. Further south, along the central coast, the climate becomes drier, with milder winters and warmer summers.
The Sierra Nevada’s Shadow: A Gradient of Elevation and Precipitation
The towering Sierra Nevada mountain range acts as a rain shadow, significantly influencing the climate of the state’s interior. As moist air from the Pacific Ocean rises over the mountains, it cools, condenses, and releases precipitation on the western slopes. The eastern slopes, sheltered by the Sierra Nevada, receive significantly less precipitation, creating a rain shadow effect.
This effect results in a dramatic shift in climate as one travels eastward from the coast. The Central Valley, nestled between the Coast Ranges and the Sierra Nevada, experiences a hot, dry climate, with warm summers and mild, wet winters. The eastern slopes of the Sierra Nevada, exposed to the arid air, are characterized by a semi-arid climate, with hot summers and cold winters.
The Desert’s Embrace: A Realm of Extremes
The southeastern corner of California falls within the realm of the Mojave and Sonoran deserts, characterized by extreme temperatures and minimal rainfall. The Mojave Desert, known for its harsh, arid conditions, experiences scorching summers and mild winters. The Sonoran Desert, located in the extreme southeastern corner, is characterized by a slightly wetter climate, with a greater diversity of plant and animal life.
Mapping the Climate: Understanding the Nuances
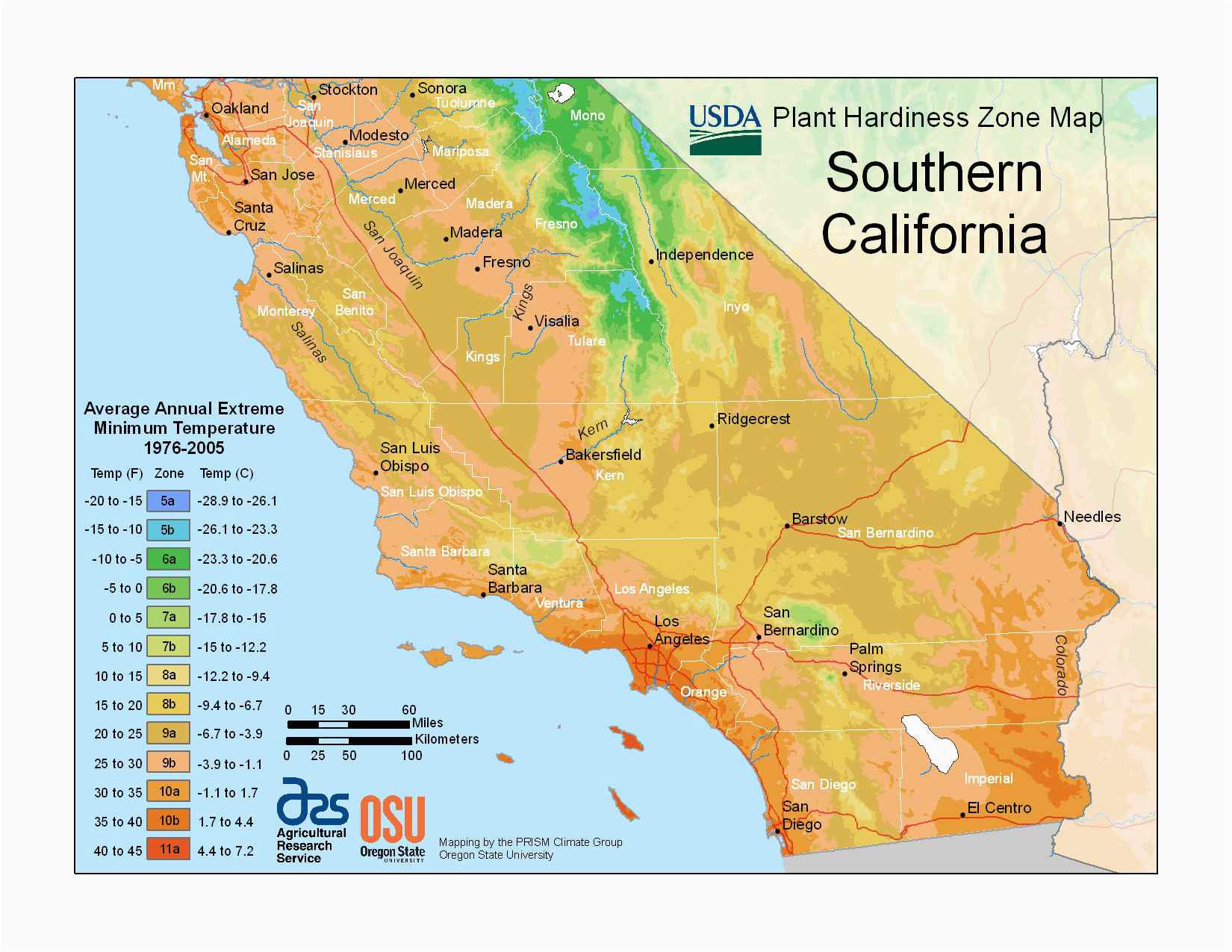
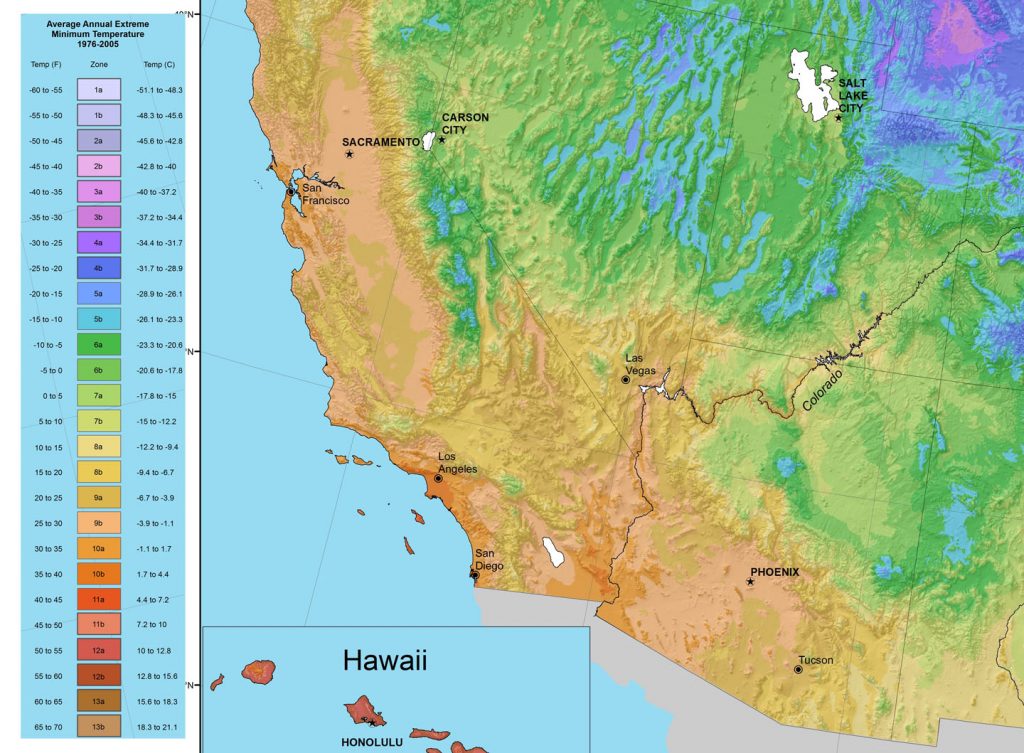
Climate maps of California are essential tools for understanding the state’s diverse climate zones. These maps use color gradients and lines to depict various climate parameters, including temperature, precipitation, and growing season length.
For instance, a temperature map might show a gradient from cool coastal regions to hot desert areas. A precipitation map would highlight the dramatic differences in rainfall between the windward slopes of the Sierra Nevada and the rain shadow regions. These maps provide valuable information for a wide range of applications, including:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely on climate maps to select appropriate crops and irrigation techniques for their specific region.
- Water Management: Water resource managers use climate data to assess water availability and plan for drought mitigation strategies.
- Urban Planning: City planners consider climate factors when designing infrastructure and green spaces to mitigate heat island effects and manage stormwater runoff.
- Ecosystem Management: Ecologists use climate maps to understand the distribution of different plant and animal communities and to predict the potential impacts of climate change.
- Public Health: Public health officials use climate data to monitor heat waves, air quality, and disease outbreaks.
Climate Change and California’s Future
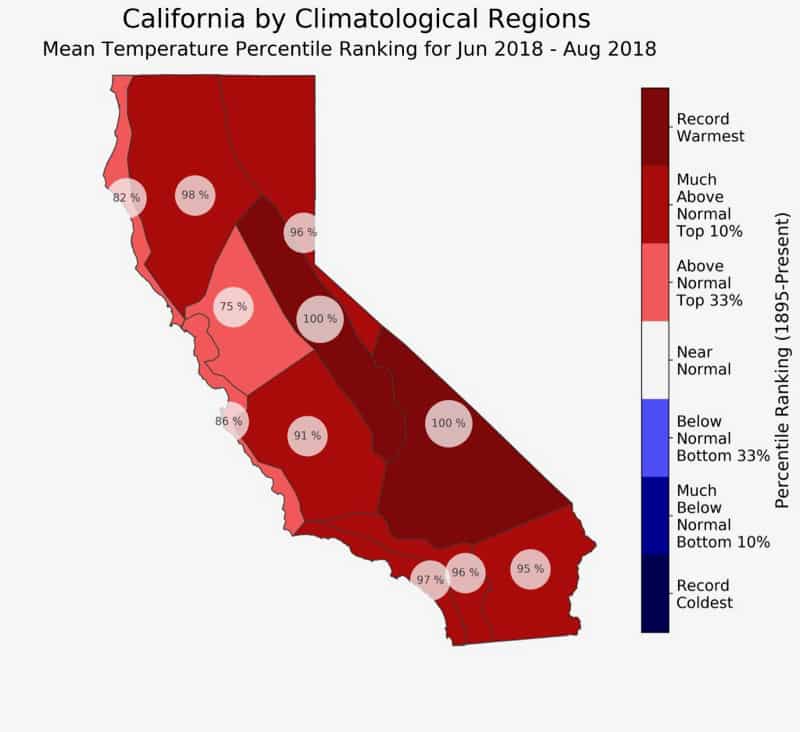
Climate change is already having a significant impact on California’s climate, and these impacts are projected to intensify in the coming decades. Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events are altering California’s ecosystems, water resources, and human communities.
Climate maps are crucial tools for understanding these changes and planning for the future. By analyzing historical climate data and projecting future trends, scientists can assess the potential impacts of climate change on different regions of California and develop strategies for adaptation and mitigation.
FAQs about California’s Climate Map
Q: What are the main climate zones in California?
A: California encompasses a variety of climate zones, including:
- Mediterranean: Coastal regions with warm, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
- Semi-arid: Eastern slopes of the Sierra Nevada with hot summers and cold winters.
- Desert: Southeastern California with extreme temperatures and minimal rainfall.
- Temperate Rainforest: Northern coastal regions with abundant rainfall and lush forests.
Q: How does the Pacific Ocean influence California’s climate?
A: The Pacific Ocean moderates coastal temperatures, creating a mild Mediterranean climate with warm, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
Q: How does the Sierra Nevada mountain range affect California’s climate?
A: The Sierra Nevada acts as a rain shadow, causing the eastern slopes to receive significantly less precipitation than the western slopes.
Q: What are the impacts of climate change on California’s climate?
A: Climate change is causing rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events, affecting ecosystems, water resources, and human communities.
Q: How are climate maps used to address climate change?
A: Climate maps help scientists understand the impacts of climate change, develop adaptation strategies, and plan for the future.
Tips for Utilizing California’s Climate Map
- Consider the scale: Climate maps come in various scales, from regional to local. Choose a map appropriate for your specific needs.
- Understand the data: Familiarize yourself with the parameters depicted on the map, such as temperature, precipitation, and growing season length.
- Interpret the information: Use the map to identify climate trends and potential impacts on specific regions.
- Integrate with other data: Combine climate data with other relevant information, such as soil type, elevation, and land use.
- Stay informed: Climate change is an ongoing process, so stay updated on the latest climate projections and data.
Conclusion
California’s climate map is a powerful tool for understanding the state’s diverse climate zones and the complex interplay of factors that shape them. From the cool, moist coastal regions to the scorching deserts, the state’s climate varies dramatically across its landscape. By understanding these nuances, we can better appreciate the unique ecosystems, inform agricultural practices, and plan for the future in the face of climate change.
![Best Time to Visit California [For Cheap, Best Weather, Months]](https://www.anytraveltips.com/wp-content/uploads/california_climategov-regions_x-768x869.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering California’s Climate: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Diverse Regions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!