Elevating Geometry: A Deep Dive into Displacement Mapping in Blender
Related Articles: Elevating Geometry: A Deep Dive into Displacement Mapping in Blender
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Elevating Geometry: A Deep Dive into Displacement Mapping in Blender. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Elevating Geometry: A Deep Dive into Displacement Mapping in Blender

In the realm of 3D modeling, achieving intricate and realistic surfaces often necessitates meticulous detail. While traditional modeling techniques can be effective, they can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially when dealing with complex geometries. This is where displacement mapping emerges as a powerful tool, enabling artists to add depth and realism to their models without significantly increasing the polygon count.
Displacement mapping, in essence, involves using a grayscale image, known as a displacement map, to manipulate the geometry of a 3D model. This image acts as a blueprint, guiding the displacement of vertices along the model’s surface based on the brightness values within the map. Brighter areas in the map correspond to areas that are pushed outward, while darker areas are pulled inward, creating subtle or dramatic changes in the model’s form.
Understanding the Mechanism:
The process of displacement mapping relies on a combination of image data and mathematical calculations. The displacement map, typically a grayscale image, encodes information about the desired surface detail. Each pixel in the map represents a specific point on the model’s surface, and its grayscale value determines the magnitude of displacement at that point.
Blender, a widely used 3D modeling software, leverages this principle by applying the displacement map to the model’s geometry during rendering. This process involves calculating the displacement vector for each vertex based on the corresponding pixel value in the map. These vectors then push or pull the vertices, effectively modifying the model’s surface.
Benefits of Displacement Mapping:
-
Enhanced Detail and Realism: Displacement mapping allows artists to introduce fine details and surface irregularities that would be impractical or impossible to model manually. This leads to a more realistic and visually appealing final render.
-
Reduced Polygon Count: By using displacement maps, artists can achieve high-fidelity results with significantly fewer polygons compared to traditional modeling methods. This reduces the computational load during rendering, making it more efficient and allowing for larger and more complex scenes.
-
Flexibility and Control: Displacement maps offer artists a high degree of flexibility and control over the surface details. Artists can easily modify the displacement map to adjust the level of detail, create specific patterns, or experiment with different effects.
-
Procedural Generation: Displacement maps can be generated procedurally, allowing for the creation of complex and intricate surface patterns with minimal effort. This eliminates the need for manual sculpting or texturing, streamlining the workflow.
Creating Displacement Maps:
Displacement maps can be created using various methods, including:
-
Sculpting Software: Tools like ZBrush and Mudbox allow artists to sculpt high-resolution details on a model, which can then be exported as a displacement map.
-
Image Editing Software: Programs like Photoshop and GIMP can be used to create custom displacement maps by manipulating grayscale images, applying filters, and adjusting contrast.
-
Procedural Generation: Specialized software and plugins offer the capability to generate displacement maps procedurally, using mathematical algorithms to create intricate patterns and textures.
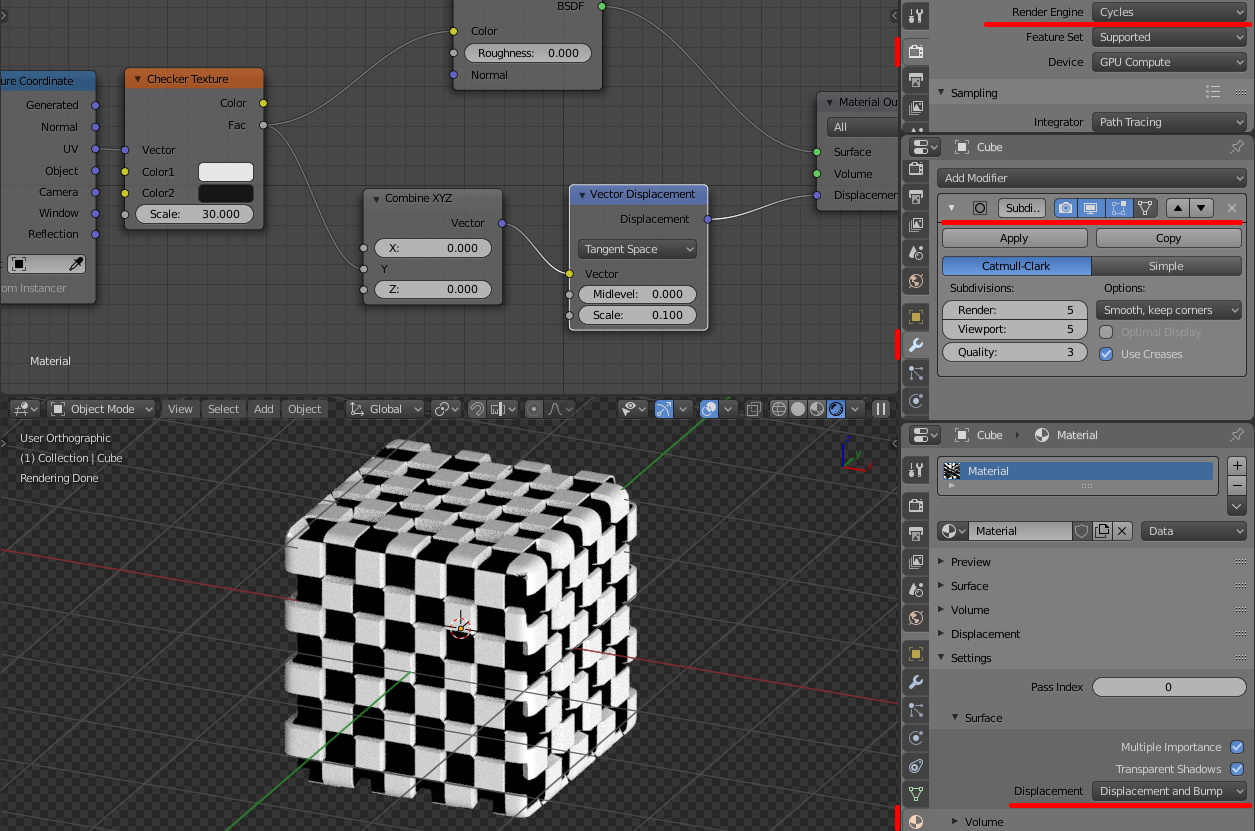
Applying Displacement Maps in Blender:
Blender offers a straightforward workflow for applying displacement maps to models. The process typically involves:
-
Importing the Displacement Map: Import the displacement map image into Blender.
-
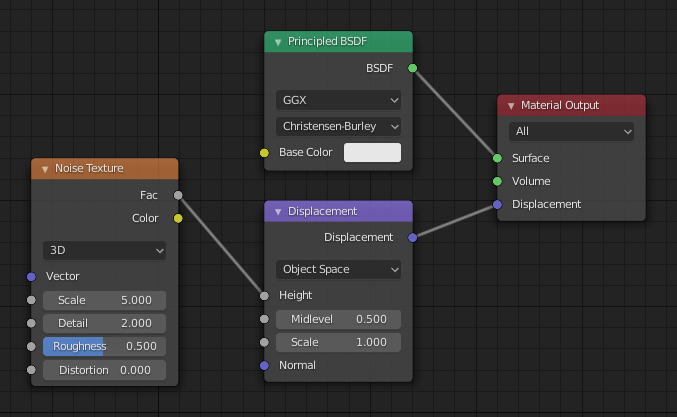
Assigning the Map to the Material: In the material properties panel, select the displacement node and connect it to the displacement input of the material output.
-
Adjusting Settings: Fine-tune the displacement settings, including the strength, scale, and texture coordinates.
-
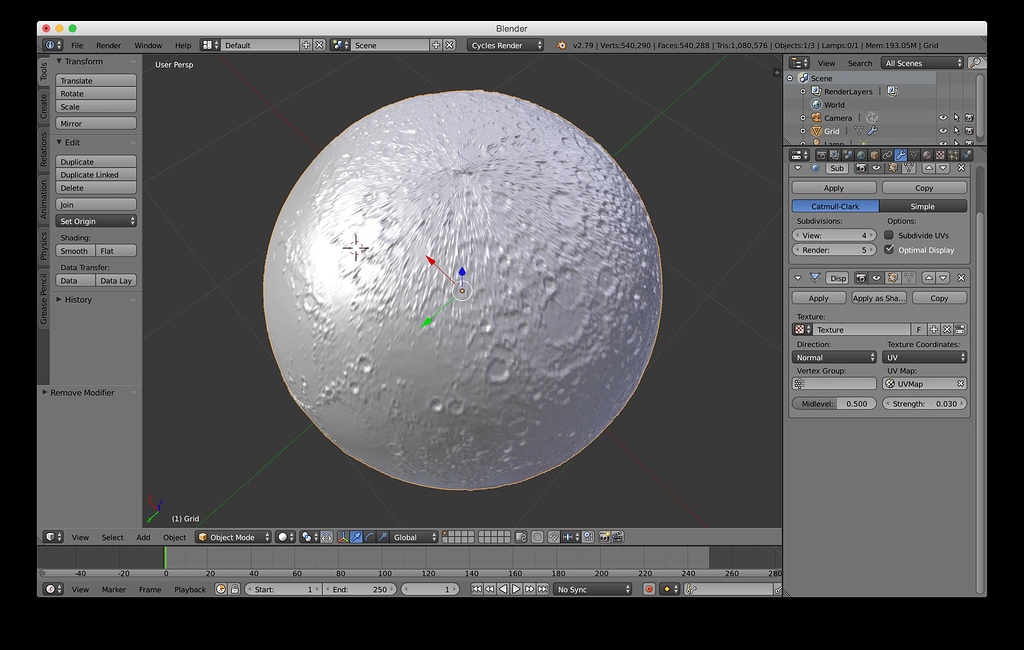
Rendering: Render the scene to visualize the effect of the displacement map on the model’s geometry.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What is the difference between displacement mapping and bump mapping?
A: Both displacement mapping and bump mapping are techniques used to add detail to surfaces. However, they differ in how they achieve this:
- Bump mapping simulates surface detail by manipulating the normals of the model’s surface, giving the illusion of depth. It does not actually alter the geometry.
- Displacement mapping physically modifies the geometry of the model by displacing vertices based on the displacement map. This results in actual changes to the model’s shape.
Q: Can I use any image as a displacement map?
A: While any image can technically be used as a displacement map, grayscale images are generally preferred for their clarity and ease of interpretation. Color images can introduce unwanted artifacts or color variations in the displacement.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate strength for my displacement map?
A: The strength of the displacement map determines how much the model’s geometry is affected. A higher strength value results in more pronounced displacement, while a lower value produces subtler changes. Experiment with different strengths to find the desired level of detail.
Q: What are some common uses of displacement mapping?
A: Displacement mapping is widely used in various 3D modeling applications, including:
- Creating realistic textures: Adding subtle bumps, cracks, and other imperfections to surfaces.
- Simulating organic forms: Modeling detailed skin, fur, and vegetation.
- Generating complex geometries: Creating intricate architectural details, sculpted objects, and terrain features.
Tips for Effective Displacement Mapping:
- Use high-resolution displacement maps: For best results, use high-resolution displacement maps that capture fine details.
- Optimize the displacement map: Reduce noise and artifacts in the map to avoid unwanted distortions in the model.
- Experiment with different settings: Adjust the displacement strength, scale, and texture coordinates to achieve the desired effect.
- Consider the model’s geometry: Ensure that the model’s geometry is suitable for displacement mapping. Avoid excessively high or low polygon counts, as this can lead to issues with displacement.
Conclusion:
Displacement mapping stands as a powerful and versatile tool within the arsenal of 3D artists. It empowers them to elevate the visual fidelity of their models, adding intricate detail and realism without sacrificing performance. By understanding the principles behind displacement mapping, artists can harness its capabilities to create compelling and immersive 3D environments, pushing the boundaries of realism in digital art.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Elevating Geometry: A Deep Dive into Displacement Mapping in Blender. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!