Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression
Related Articles: Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression

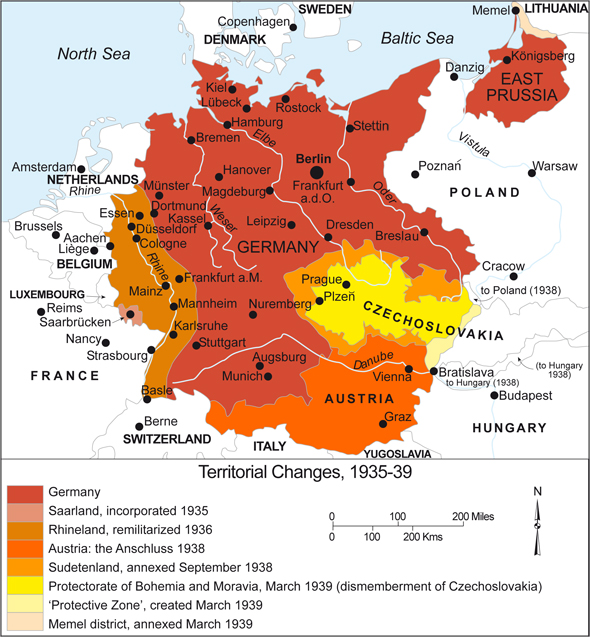
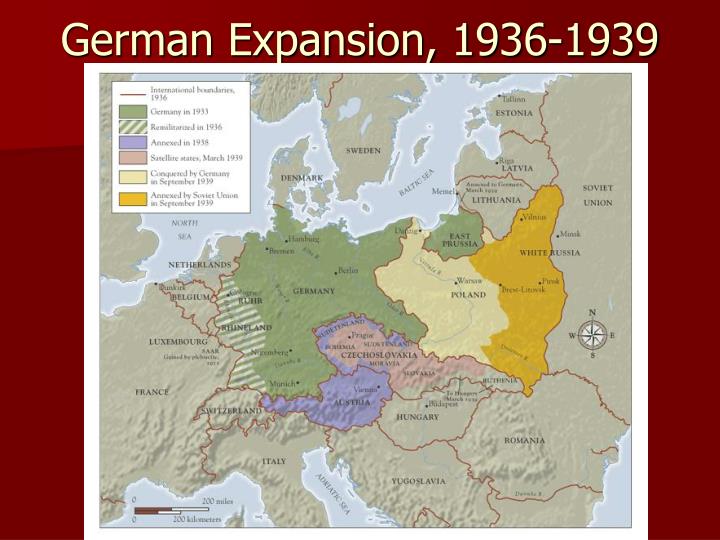
The year 1939 marks a pivotal moment in European history, as the Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler embarked on a campaign of territorial expansion that would culminate in the devastating Second World War. A map of Germany in 1939 reveals a nation transformed, its borders dramatically altered through a series of aggressive annexations and territorial claims.
The Pre-War Landscape:
Prior to the Nazi rise to power, Germany was a republic, its borders established after the First World War. The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, significantly reduced German territory, stripped it of its colonies, and imposed heavy reparations. This treaty, seen as a humiliation by many Germans, fueled nationalist sentiments and paved the way for the rise of the Nazi Party.
The Expansionist Agenda:
Hitler, a fervent nationalist, openly defied the Treaty of Versailles and embarked on a program of territorial expansion. He began with the annexation of Austria in 1938, followed by the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia, a predominantly German-speaking area. This aggressive expansion was facilitated by the appeasement policy adopted by Britain and France, who sought to avoid another major conflict.
The Map of 1939:
By 1939, Germany’s map had been radically reshaped. The country had absorbed Austria and the Sudetenland, effectively swallowing up significant chunks of territory from its neighbors. This expansion was not limited to annexation; it also involved the establishment of protectorates and the creation of puppet states.
- Austria: Incorporated into the German Reich as the "Ostmark," Austria became a key component of Nazi Germany’s territorial ambitions.
- Sudetenland: This German-speaking region of Czechoslovakia was annexed by Germany in October 1938 after a series of diplomatic maneuvers and threats.
- Czech Protectorate: Following the annexation of the Sudetenland, the remaining Czech territories were occupied and turned into a German protectorate.
- Memel Territory: This region, previously part of Lithuania, was annexed by Germany in March 1939.
- Poland: While not formally annexed in 1939, Poland was subject to a German invasion in September 1939, marking the official start of World War II.
The Significance of the 1939 Map:
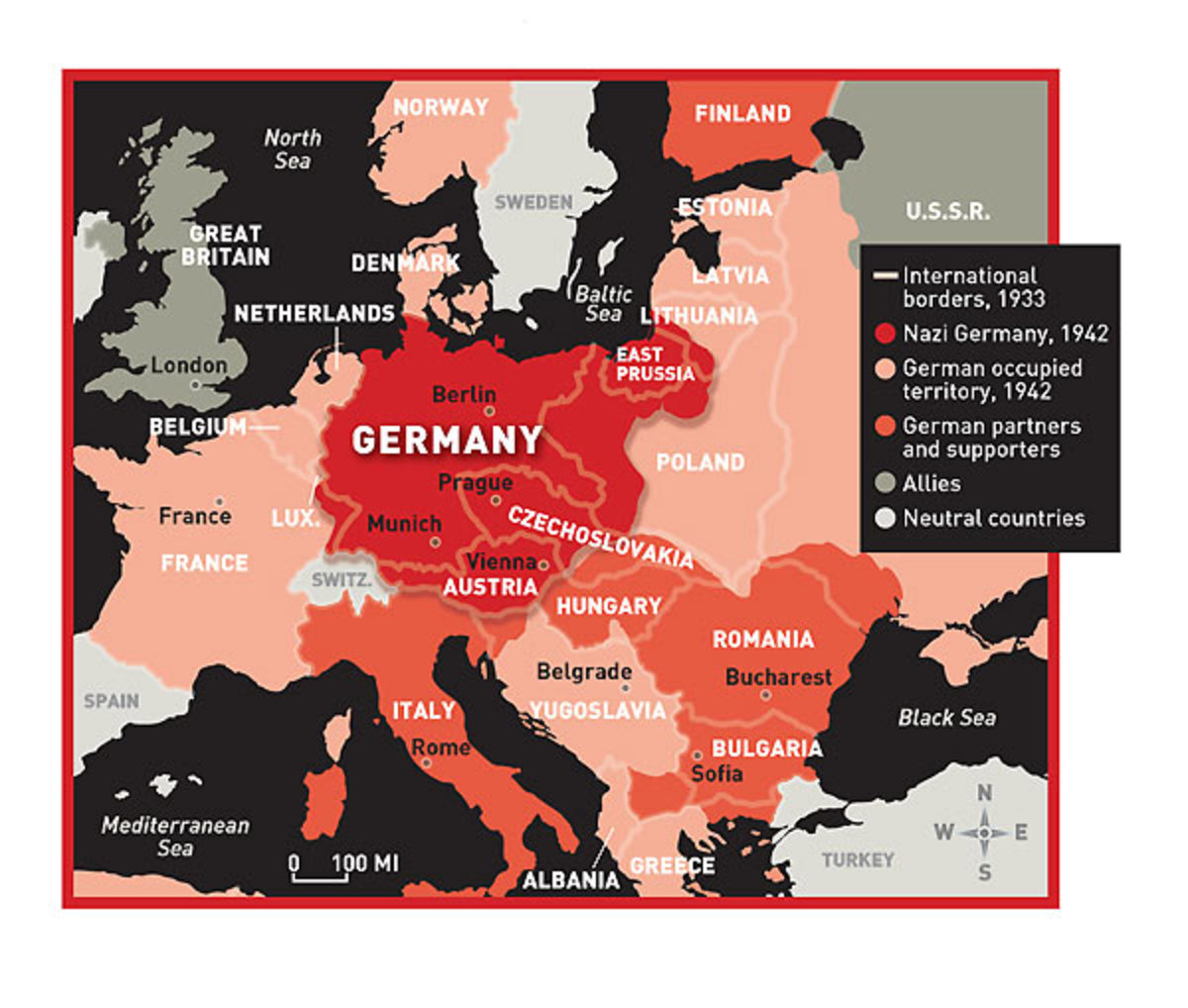
The map of Germany in 1939 encapsulates the ambitions and aggression of the Nazi regime. It reveals a nation driven by a fervent ideology of racial superiority and territorial expansion, willing to resort to violence and intimidation to achieve its goals. This map is a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism and the devastating consequences of war.
Beyond the Borders:
The 1939 map also reveals the complex geopolitical landscape of Europe at the time. It highlights the power vacuum created by the appeasement policy of the Western powers, which emboldened Hitler and his expansionist ambitions. It also underscores the vulnerability of smaller nations facing the aggressive designs of a powerful neighbor.
FAQs Regarding the Map of Germany in 1939:
1. What were the main reasons for Germany’s expansion in 1939?
- The Nazi ideology of racial superiority and the belief in Germany’s right to dominate Europe.
- The desire to reverse the territorial losses imposed by the Treaty of Versailles.
- The belief that Germany’s economic and military strength required a larger Lebensraum (living space).
2. How did the annexation of Austria and the Sudetenland contribute to the outbreak of World War II?
- These actions demonstrated Hitler’s willingness to use force to achieve his goals, undermining any remaining faith in peaceful diplomacy.
- The annexation of Czechoslovakia emboldened Hitler and fueled his ambitions for further expansion, ultimately leading to the invasion of Poland.
3. What were the consequences of Germany’s expansion in 1939?
- The outbreak of World War II, which resulted in millions of deaths and widespread destruction.
- The creation of a totalitarian regime in Germany that suppressed individual freedoms and human rights.
- The establishment of a racial hierarchy that led to the persecution and genocide of Jews and other minority groups.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Germany in 1939:
- Contextualize the map: Understand the historical events and political factors that led to the changes depicted.
- Examine the borders: Analyze the specific territories annexed and the geopolitical implications of these changes.
- Consider the impact: Reflect on the consequences of Germany’s expansion for both the German people and the wider world.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany in 1939 is a powerful visual representation of the Nazi regime’s aggressive expansionism and the tragic consequences it unleashed. It serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism, the importance of international cooperation, and the enduring need to uphold human rights and democracy. By studying this map, we can gain a deeper understanding of the events that shaped the 20th century and the lessons learned from the horrors of war.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!