Mapping Food Insecurity: The USDA Food Desert Map and its Impact
Related Articles: Mapping Food Insecurity: The USDA Food Desert Map and its Impact
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping Food Insecurity: The USDA Food Desert Map and its Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Food Insecurity: The USDA Food Desert Map and its Impact
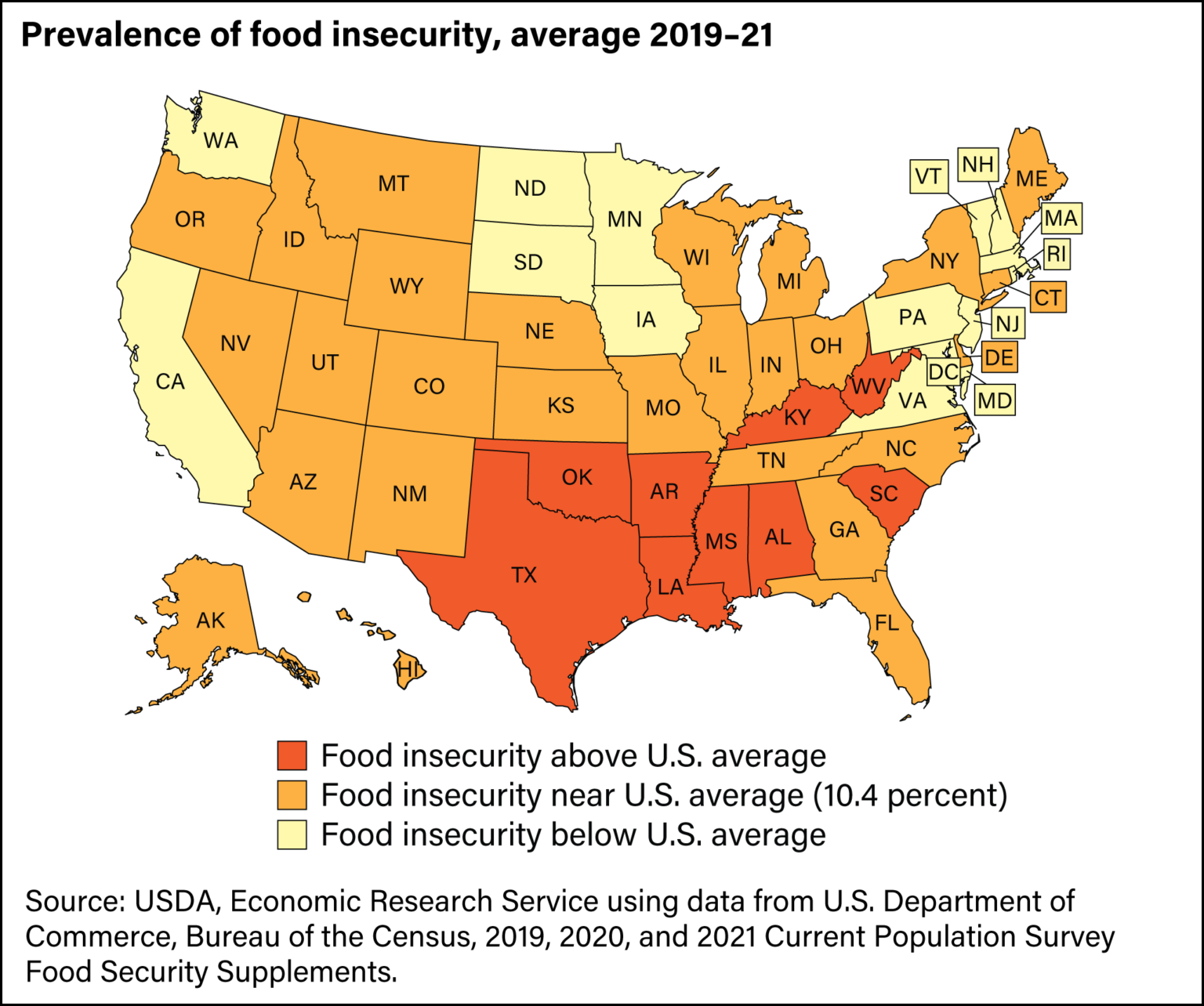
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Food Desert Map is a powerful tool that visualizes a critical issue facing millions of Americans: food insecurity. This map, updated periodically, pinpoints areas where access to affordable and nutritious food is limited. By highlighting these geographic disparities, the USDA Food Desert Map serves as a crucial resource for policymakers, community organizations, and researchers striving to address food insecurity and promote equitable access to healthy food options.
Understanding the Concept of Food Deserts
The term "food desert" refers to a geographic area, typically characterized by low-income neighborhoods, where residents lack access to affordable and nutritious food options. This lack of access can stem from several factors:
- Limited Availability: Grocery stores and supermarkets offering fresh produce, lean proteins, and whole grains may be scarce in these areas.
- Distance: Residents may have to travel long distances to reach a supermarket, often lacking reliable transportation.
- Cost: Food prices in these areas are often higher than in more affluent neighborhoods, making it difficult for low-income families to afford healthy food.
- Limited Options: Convenience stores and fast-food restaurants often dominate the food landscape in food deserts, offering limited healthy choices and contributing to dietary disparities.
The USDA Food Desert Map: A Vital Tool for Understanding Food Insecurity
The USDA Food Desert Map provides a comprehensive visual representation of food deserts across the United States. It relies on several key data points:
- Distance to a Supermarket: The map measures the distance between residents and the nearest supermarket, using a threshold of one mile for urban areas and ten miles for rural areas.
- Population Density: It considers the concentration of residents within a specific geographic area, focusing on areas with high populations and limited access to supermarkets.
- Poverty Rates: The map incorporates data on poverty levels within a given area, recognizing the correlation between low income and food insecurity.
- Vehicle Ownership: It assesses the availability of vehicles within a community, understanding that limited transportation options can exacerbate food access challenges.
By combining these data points, the USDA Food Desert Map identifies areas where residents face significant barriers to accessing healthy food options. This visual representation allows policymakers, community organizations, and researchers to:
- Identify Areas in Need: The map provides a clear picture of where food deserts are located, enabling targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Track Progress: Over time, the USDA Food Desert Map can be used to monitor the effectiveness of programs aimed at addressing food insecurity and improving food access.
- Raise Awareness: The map serves as a powerful tool to raise public awareness about the issue of food deserts and its impact on communities.
- Promote Collaboration: The map facilitates collaboration between stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private businesses, to address the problem collectively.
The Impact of Food Deserts on Communities
Food deserts have far-reaching consequences for individuals and communities:
- Health Disparities: Limited access to healthy food options contributes to diet-related health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
- Economic Disparities: Food insecurity can lead to financial strain, diverting resources from other essential needs like housing and education.
- Social Disparities: Food deserts can perpetuate cycles of poverty and disadvantage, hindering economic mobility and social integration.
- Environmental Disparities: Food deserts often lack access to fresh produce, contributing to a reliance on processed foods with high environmental footprints.
Addressing Food Deserts: Strategies and Solutions
The USDA Food Desert Map serves as a starting point for addressing food insecurity and promoting equitable access to healthy food options. Several strategies can be implemented to combat food deserts:
- Incentivize Grocery Store Development: Providing financial incentives to supermarkets to open stores in underserved areas can increase access to fresh produce and healthy food options.
- Support Community Gardens: Fostering community gardens and urban agriculture initiatives can provide residents with access to fresh, locally grown produce and enhance community cohesion.
- Expand Mobile Food Markets: Implementing mobile food markets that transport fresh produce and other healthy food options to underserved areas can improve access and convenience.
- Promote Food Policy Initiatives: Implementing food policy initiatives, such as SNAP benefits and tax credits for healthy food purchases, can increase affordability and access to nutritious food.
- Invest in Transportation Infrastructure: Improving public transportation options can connect residents in food deserts to supermarkets and other food resources.
- Educate and Empower Residents: Providing nutrition education and cooking classes can empower residents to make healthier food choices and reduce reliance on processed foods.
Frequently Asked Questions about the USDA Food Desert Map
1. How is the USDA Food Desert Map created?
The USDA Food Desert Map is created using data from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau, the USDA Economic Research Service, and the National Agricultural Statistics Service. This data includes population density, poverty rates, vehicle ownership, and the location of supermarkets and grocery stores.
2. How often is the USDA Food Desert Map updated?
The USDA Food Desert Map is updated periodically, typically every few years, to reflect changes in population density, poverty rates, and food retail availability.
3. What are the limitations of the USDA Food Desert Map?
The USDA Food Desert Map provides a valuable snapshot of food access challenges, but it has limitations. It does not account for factors such as the quality of food available in stores, the availability of alternative food sources like farmers markets, and the cultural preferences of residents.
4. How can I use the USDA Food Desert Map to make a difference?
The USDA Food Desert Map can be used to advocate for policies that promote food access, support community-based initiatives that address food insecurity, and educate others about the issue of food deserts.
5. What are some examples of successful initiatives that have addressed food deserts?
Several initiatives have successfully addressed food deserts, including the development of community gardens, the expansion of mobile food markets, and the implementation of SNAP benefits.
Tips for Using the USDA Food Desert Map
- Explore your local area: Identify food deserts in your community and understand the specific challenges faced by residents.
- Connect with local organizations: Collaborate with community organizations working to address food insecurity and access to healthy food options.
- Advocate for policy change: Support policies that promote food access, such as incentives for grocery store development and expansion of SNAP benefits.
- Educate others: Raise awareness about the issue of food deserts and its impact on communities.
- Support local food systems: Encourage the development of local food systems, such as farmers markets and community gardens, to increase access to fresh produce.
Conclusion
The USDA Food Desert Map is a powerful tool for understanding and addressing food insecurity in the United States. By highlighting areas where residents lack access to affordable and nutritious food options, the map provides a foundation for developing targeted interventions, promoting policy change, and fostering community-based solutions. Through collaborative efforts and a commitment to equitable access to healthy food, we can work towards a future where food deserts are a thing of the past.

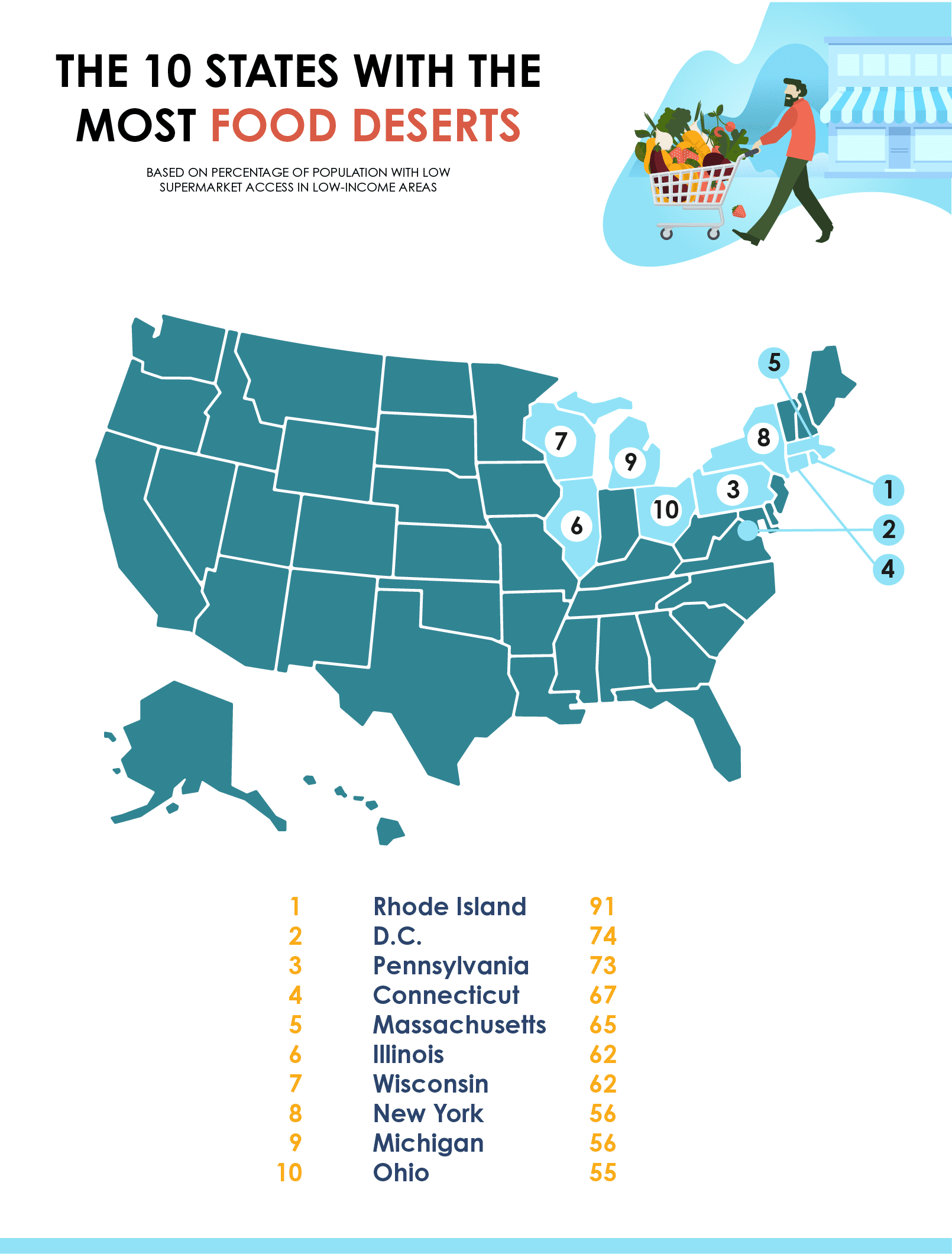

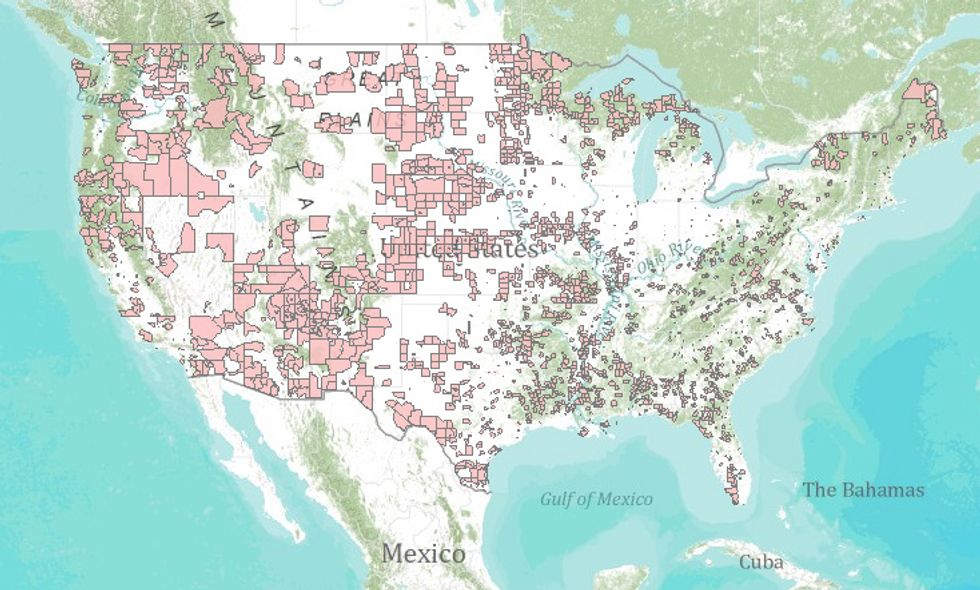

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Food Insecurity: The USDA Food Desert Map and its Impact. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!