Mapping the Land of Canaan: A Journey Through Ancient History
Related Articles: Mapping the Land of Canaan: A Journey Through Ancient History
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Land of Canaan: A Journey Through Ancient History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Land of Canaan: A Journey Through Ancient History
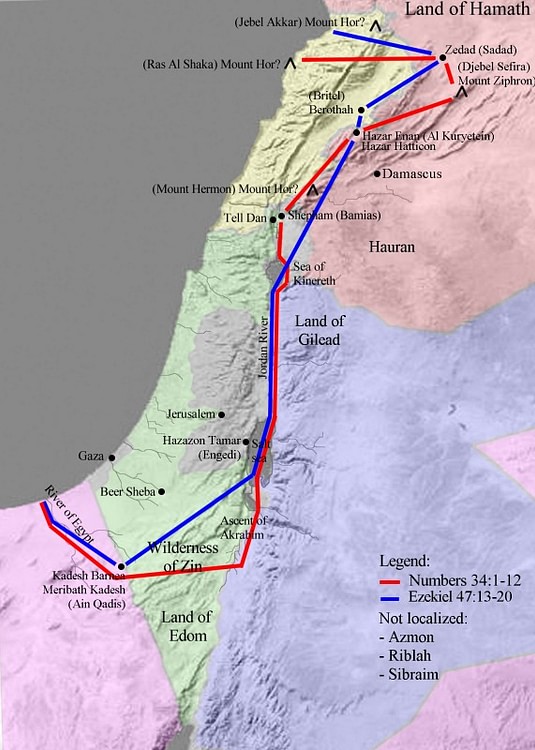
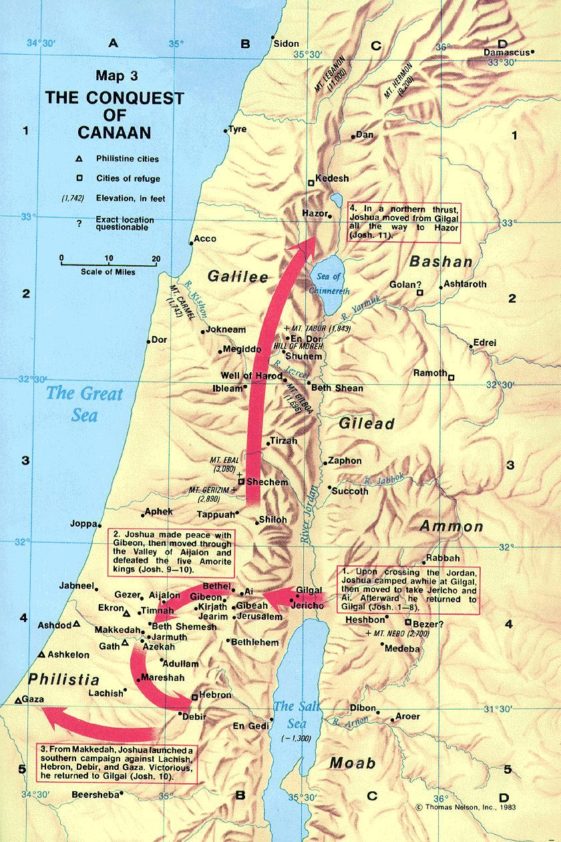
The land of Canaan, a geographical and cultural entity that played a pivotal role in ancient history, continues to intrigue historians, archaeologists, and biblical scholars alike. Its significance lies in its role as the setting for the biblical narratives of Abraham, Isaac, and Jacob, as well as for the emergence of the Israelite nation. Understanding the geographical landscape of Canaan is crucial for comprehending the social, political, and religious developments that shaped this region.
The Geographical Context:
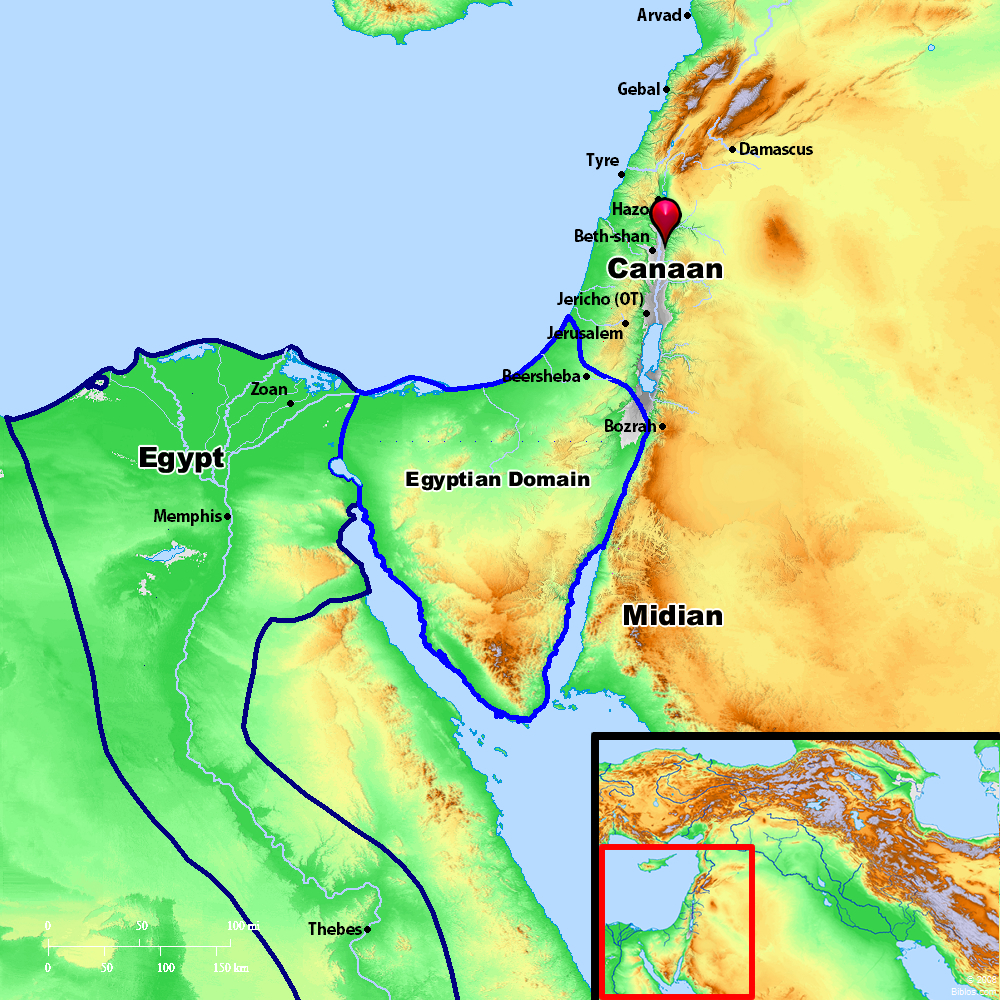
Canaan, situated in the southeastern Mediterranean region, encompassed a diverse landscape ranging from the fertile coastal plains to the rugged hills of the interior and the arid Negev desert in the south. Its geographical boundaries were fluid, with the precise extent of the land varying over time. Generally, it encompassed the modern-day territories of Israel, Palestine, Lebanon, and parts of Jordan and Syria.
Key Geographical Features:
- The Coastal Plain: This fertile strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea provided ideal conditions for agriculture and was a major trade route connecting Canaan to the wider Mediterranean world.
- The Central Highlands: These hilly regions, interspersed with valleys and plains, offered strategic locations for settlements and provided grazing land for livestock.
- The Jordan Valley: This rift valley, running north-south, was a fertile region with abundant water resources, making it suitable for agriculture and supporting a diverse population.
- The Negev Desert: Located in the south, this arid region was sparsely populated but offered valuable resources like copper and salt.
Political and Cultural Landscape:
Canaan was not a unified entity but rather a patchwork of city-states, each with its own political structures, cultural practices, and religious beliefs. These city-states interacted with each other through trade, warfare, and diplomacy, forming a complex web of relationships.
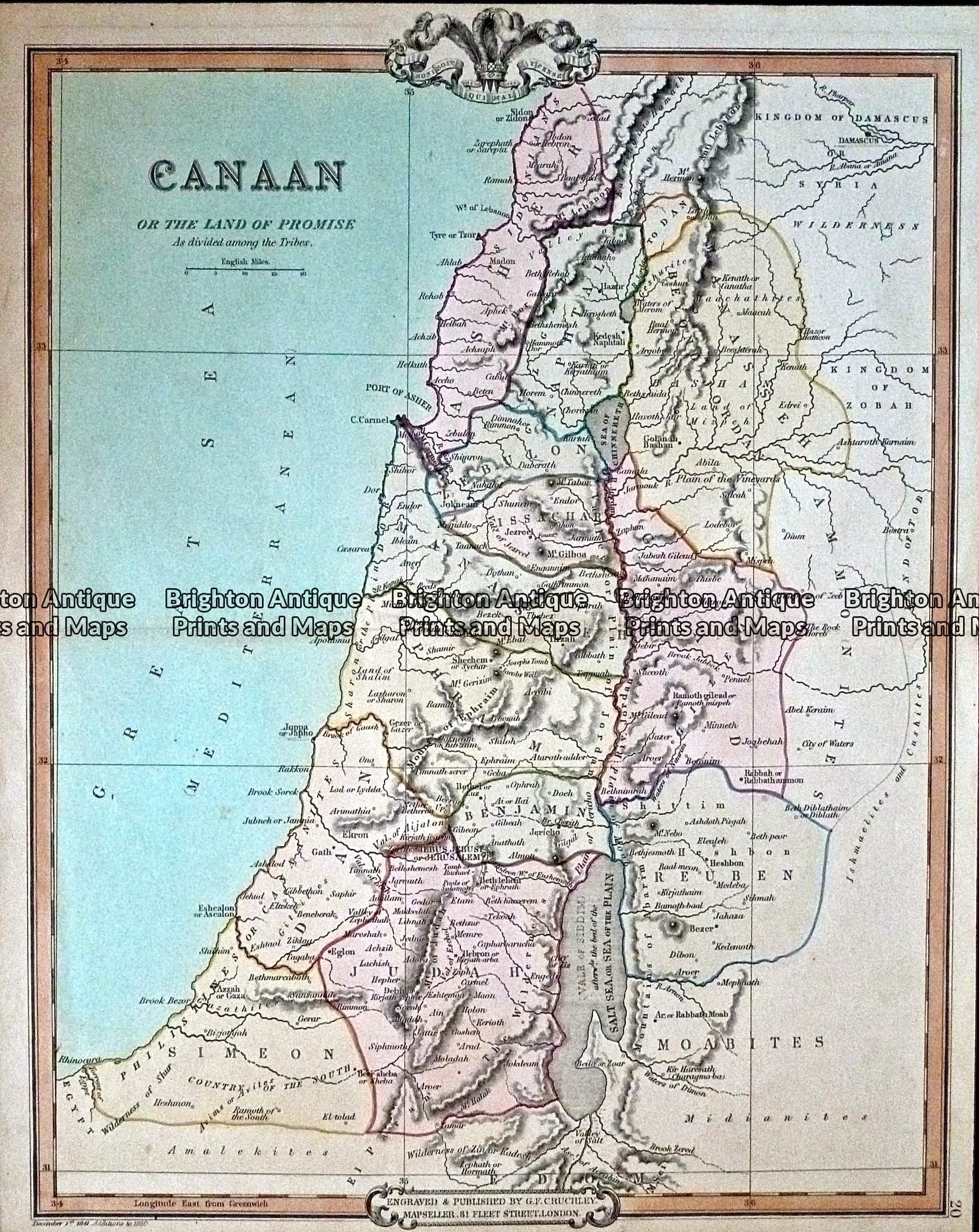
Major City-States:
- Jerusalem: A strategically located city in the central highlands, Jerusalem was a major religious center, with temples dedicated to various deities, including El, the Canaanite high god.
- Jericho: Located in the Jordan Valley, Jericho was one of the oldest cities in the world, known for its agricultural wealth and its impressive fortifications.
- Megiddo: Situated in the Jezreel Valley, Megiddo was a prominent military stronghold, renowned for its strategically significant location.
- Byblos: A coastal city in present-day Lebanon, Byblos was a major center for trade, particularly in timber and papyrus.
Religious Practices:
Canaanite religion was polytheistic, with a pantheon of deities associated with various aspects of nature and human life. The most important deities included El, Baal, Asherah, and Anat. Canaanite temples, often located on hilltops, served as centers for religious rituals, including sacrifices and festivals.
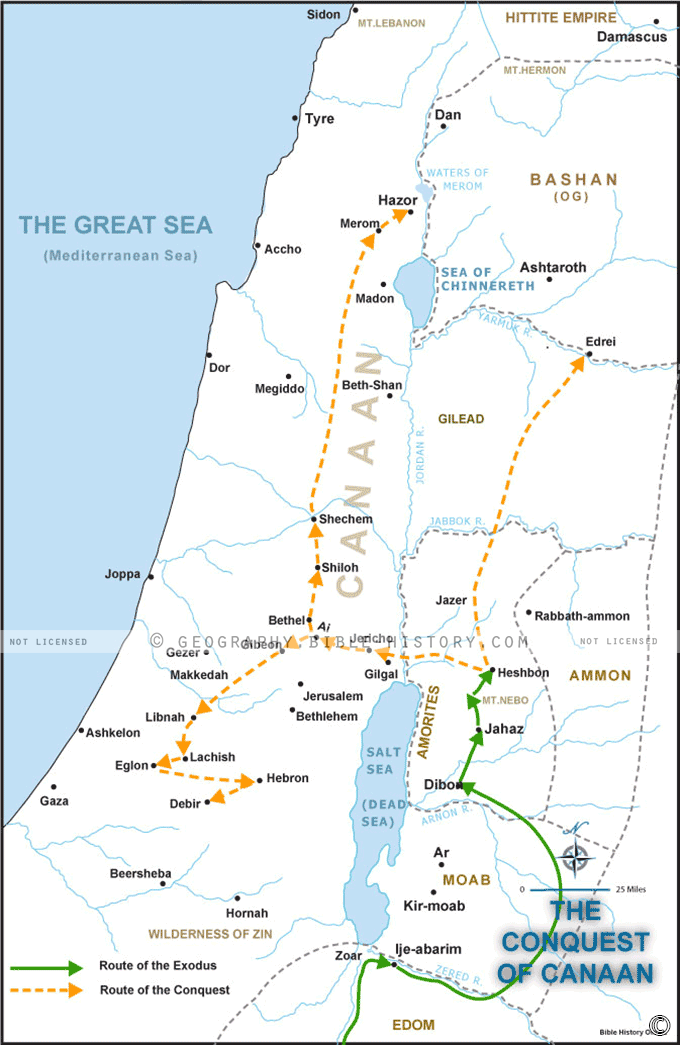
The Arrival of the Israelites:
The arrival of the Israelites in Canaan, as described in the Hebrew Bible, marked a significant turning point in the region’s history. The Israelites, initially nomadic pastoralists, settled in Canaan and gradually established their own political and religious institutions. Their arrival led to conflicts with the existing Canaanite city-states, ultimately culminating in the establishment of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah.
The Significance of Canaan:
The land of Canaan holds immense historical, religious, and cultural significance. It was the cradle of ancient civilizations, witnessed the rise and fall of empires, and served as the setting for some of the most influential religious texts in history. Understanding the map of ancient Canaan provides a crucial lens through which to interpret the complex tapestry of human history and the enduring influence of its cultural legacy.
FAQs about the Map of Ancient Canaan:
Q: What is the significance of the geographical features of Canaan?
A: Canaan’s diverse geography, including fertile plains, rugged hills, and a strategically important valley, played a crucial role in shaping its history. The fertile land supported a diverse population and facilitated trade, while the strategic locations of settlements and the availability of resources influenced political and military developments.
Q: What were the major city-states of Canaan and their importance?
A: Canaan was characterized by a network of city-states, each with its own political and cultural identity. Major cities like Jerusalem, Jericho, Megiddo, and Byblos played vital roles in trade, religion, and military power, shaping the political landscape of the region.
Q: What were the main religious beliefs and practices of the Canaanites?
A: Canaanite religion was polytheistic, with a pantheon of deities associated with various aspects of nature and human life. Their temples, often located on hilltops, served as centers for religious rituals, including sacrifices and festivals.
Q: How did the arrival of the Israelites impact Canaan?
A: The arrival of the Israelites in Canaan marked a significant turning point in the region’s history. Their arrival led to conflicts with the existing Canaanite city-states, ultimately culminating in the establishment of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah.
Q: What are some of the benefits of studying the map of ancient Canaan?
A: Studying the map of ancient Canaan provides valuable insights into the complex political, social, and religious dynamics of this region. It allows us to understand the geographic factors that shaped the lives of its inhabitants, the interactions between different cultures, and the origins of major religious traditions.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Ancient Canaan:
- Focus on key geographical features: Pay attention to the coastal plain, the central highlands, the Jordan Valley, and the Negev Desert, as these features significantly influenced the development of Canaanite society.
- Identify major city-states: Locate cities like Jerusalem, Jericho, Megiddo, and Byblos on the map and understand their strategic importance.
- Explore the religious landscape: Recognize the locations of major Canaanite temples and understand the significance of their religious practices.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the timeline of events, including the arrival of the Israelites and the establishment of the Israelite kingdoms, to grasp the broader historical context.
Conclusion:
The map of ancient Canaan is a powerful tool for understanding the rich and complex history of this region. It reveals the interconnectedness of geography, politics, religion, and culture, providing a window into the lives of the people who inhabited this land and the enduring influence of their legacy on the world today. By exploring the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the profound impact of Canaan on the course of human history and the enduring relevance of its cultural and religious traditions.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Land of Canaan: A Journey Through Ancient History. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!