Mapping the Lineage of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Family Trees
Related Articles: Mapping the Lineage of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Family Trees
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Lineage of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Family Trees. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Lineage of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Family Trees
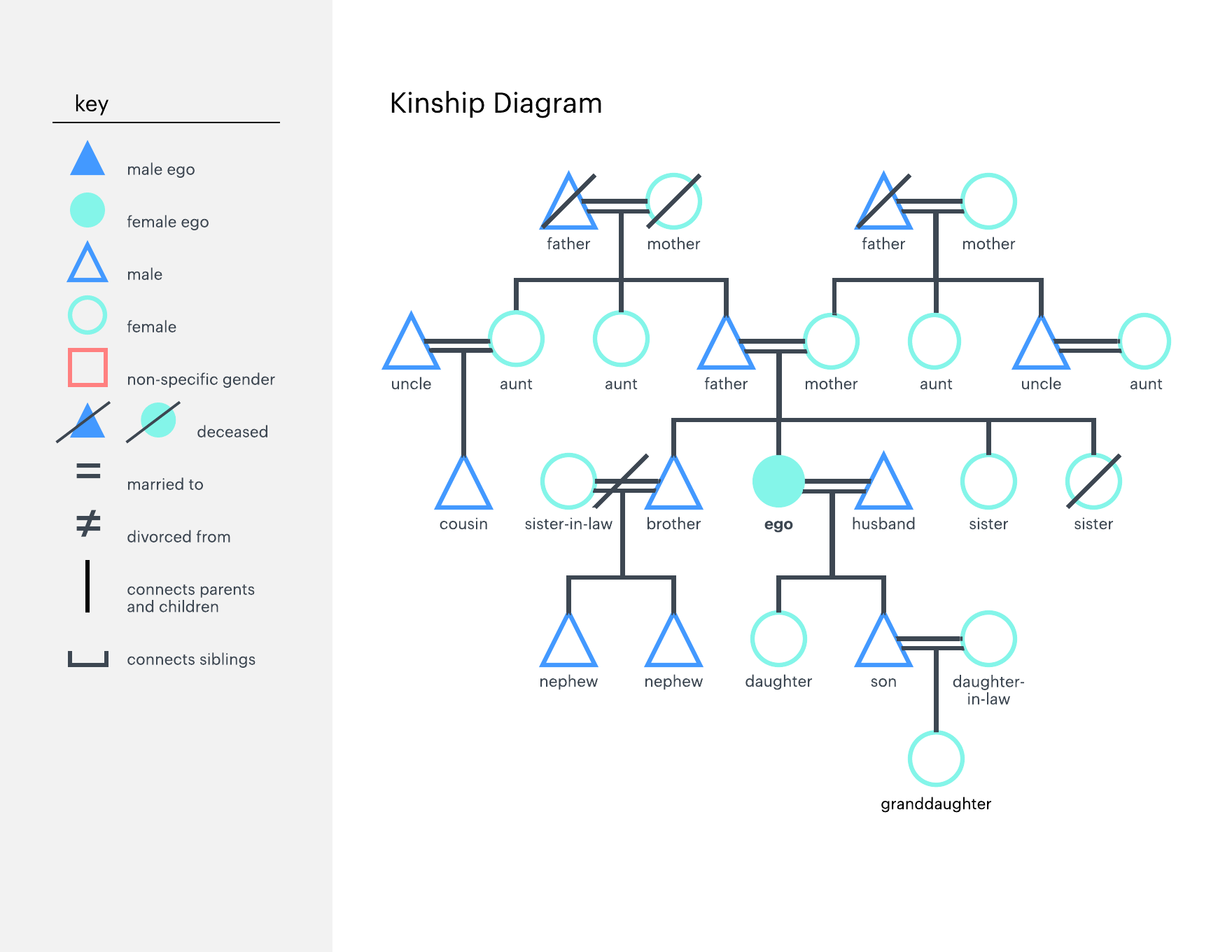
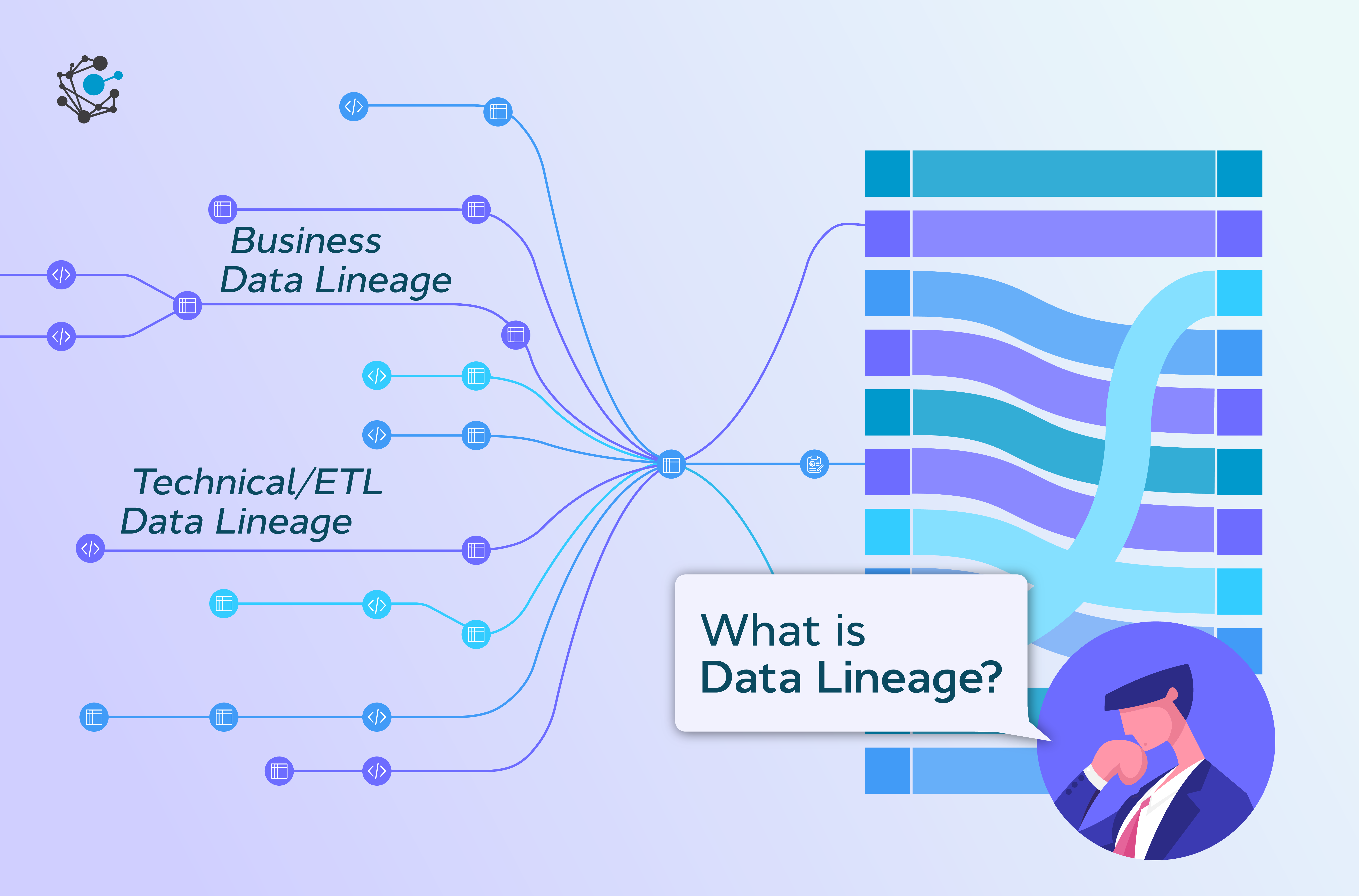
In the realm of data management and analysis, understanding the intricate relationships between data sources is paramount. This is where the concept of a "map family tree" emerges as a powerful tool for visualizing and comprehending the complex web of data dependencies. This article aims to demystify this concept, providing a comprehensive understanding of map family trees, their benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the Concept
A map family tree, also known as a data lineage map, is a visual representation of the origin, transformation, and usage of data within an organization. It resembles a traditional family tree, with data sources at the root and derived data, applications, and reports branching out as descendants. Each node in the tree represents a specific data entity, and the connecting lines illustrate the flow of data between them.
Building Blocks of a Map Family Tree
To construct a map family tree, several key components are crucial:
- Data Sources: These are the primary origins of data, including databases, files, APIs, and other external systems.
- Transformations: These represent the processes that manipulate data, such as data cleaning, enrichment, aggregation, and calculations.
- Derived Data: This encompasses the results of transformations, often stored in tables, files, or data warehouses.
- Applications: These are the software programs that consume and utilize the derived data for various purposes, such as reporting, analysis, and decision-making.
- Reports: These are the final outputs generated from the data, presenting information in a structured format for consumption by stakeholders.
Benefits of Using Map Family Trees
The adoption of map family trees offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Data Understanding: By visually representing the data flow, map family trees enable users to gain a comprehensive understanding of data origins, transformations, and usage.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Understanding the lineage of data allows organizations to identify potential data quality issues early on, leading to improved data accuracy and reliability.
- Simplified Data Governance: Map family trees provide a clear picture of data dependencies, facilitating the implementation of effective data governance policies and ensuring data compliance.
- Streamlined Data Integration: By visualizing the relationships between data sources, map family trees streamline data integration processes, minimizing errors and inconsistencies.
- Facilitated Data Discovery: Map family trees serve as a centralized repository of data information, enabling users to easily discover and access relevant data sources.
- Improved Data Security: By mapping data flows, organizations can identify vulnerabilities and implement appropriate security measures to protect sensitive data.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Map family trees promote collaboration between data teams, business users, and IT professionals, fostering a shared understanding of data and its usage.
Types of Map Family Trees
Map family trees can be classified into different types based on their scope and purpose:
- Source-to-Target Map: This type focuses on tracking the flow of data from a specific source to its final destination, highlighting the transformations applied along the way.
- Application-Centric Map: This type maps the data dependencies of a particular application, showcasing the data sources it consumes and the derived data it generates.
- Data Warehouse Map: This type provides a comprehensive overview of the data lineage within a data warehouse, including the source systems, transformations, and target tables.
- Business Process Map: This type integrates data lineage with business processes, illustrating how data flows through different stages of a business operation.
Creating and Maintaining Map Family Trees
The process of creating and maintaining map family trees involves several steps:
- Data Inventory: Begin by identifying all data sources, transformations, derived data, applications, and reports within the organization.
- Mapping Data Flow: Connect the identified data entities based on their relationships, representing the flow of data from source to destination.
- Documenting Transformations: Provide detailed descriptions of the transformations applied to data, including the logic used and the expected outputs.
- Regular Updates: Ensure that the map family tree is kept up-to-date as data sources, processes, and applications evolve over time.
Tools for Map Family Tree Creation
Several tools can assist in creating and maintaining map family trees:
- Data Lineage Software: Dedicated data lineage software provides automated mapping capabilities, simplifying the process of capturing data relationships.
- Data Modeling Tools: Data modeling tools, often used for database design, can also be leveraged to create map family trees by representing data dependencies visually.
- Data Visualization Tools: Data visualization tools offer graphical representations of data flow, enabling users to create custom map family trees based on their specific needs.
FAQs about Map Family Trees
Q: What are the challenges associated with implementing map family trees?
A: Implementing map family trees can be challenging, especially in organizations with complex data landscapes and limited data governance practices. Challenges include data inventorying, capturing accurate data relationships, maintaining consistent updates, and ensuring user adoption.
Q: How can organizations ensure the accuracy of map family trees?
A: To ensure accuracy, organizations should use reliable data sources for mapping, document transformations thoroughly, and implement validation processes to verify the correctness of data relationships.
Q: What are the best practices for creating and maintaining map family trees?
A: Best practices include prioritizing key data sources, focusing on high-impact data flows, using clear and consistent naming conventions, documenting transformations in detail, and regularly reviewing and updating the map family tree.
Q: How can map family trees be used for data quality improvement?
A: By understanding the lineage of data, organizations can identify potential sources of data quality issues and implement corrective measures to improve data accuracy and consistency.
Q: What are the future trends in map family tree technology?
A: Future trends include the integration of machine learning algorithms for automated data lineage mapping, the use of cloud-based solutions for scalability and accessibility, and the development of data lineage platforms that support multiple data sources and technologies.
Tips for Effective Map Family Tree Implementation
- Start Small: Begin by focusing on critical data sources and high-impact data flows to establish a foundation for the map family tree.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve data teams, business users, and IT professionals in the creation and maintenance of the map family tree to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Prioritize Data Quality: Implement data quality checks throughout the data flow to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the map family tree.
- Automate Where Possible: Leverage data lineage software and other tools to automate the mapping process, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and update the map family tree as data sources, processes, and applications evolve to maintain its relevance.
Conclusion
Map family trees are a valuable tool for organizations seeking to gain a comprehensive understanding of their data landscape. By visualizing data relationships and dependencies, these maps facilitate data governance, enhance data quality, streamline data integration, and improve data security. As data complexity continues to grow, map family trees will become increasingly essential for organizations to effectively manage and leverage their data assets. By embracing this powerful concept, organizations can unlock the full potential of their data and drive informed decision-making in today’s data-driven world.


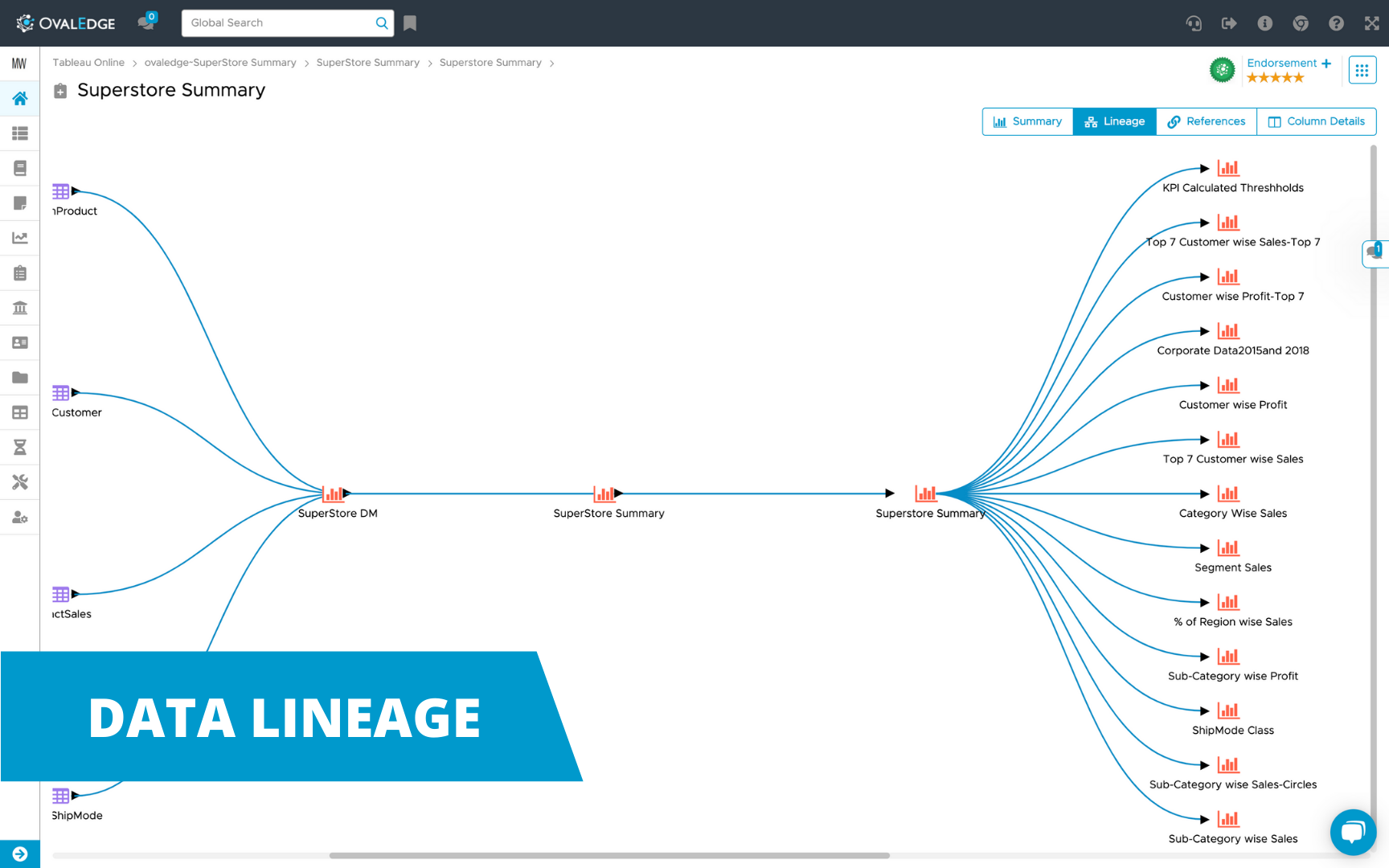


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Lineage of Data: A Comprehensive Guide to Map Family Trees. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!