Measuring Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Measuring Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Measuring Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Measuring Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide

The ability to determine the area of a region on a map is a fundamental skill with applications across various fields. From land surveying and urban planning to environmental research and resource management, accurately measuring areas on maps provides valuable insights for decision-making and analysis. This comprehensive guide explores the methods, tools, and applications of area measurement on maps, providing a detailed understanding of this essential practice.
Understanding Map Scales and Projections
Before embarking on area measurement, it is crucial to understand the concept of map scale and projections. Map scale represents the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This ratio, often expressed as a fraction or a verbal statement (e.g., 1:100,000), determines the level of detail and accuracy in area calculations.
Map projections, on the other hand, are mathematical transformations that represent the curved surface of the Earth onto a flat map. Different projections distort distances and shapes in different ways, influencing the accuracy of area measurements. Therefore, understanding the specific projection used for a map is vital for accurate results.
Methods for Measuring Area on Maps
Several methods are employed for measuring areas on maps, each with its own advantages and limitations:
1. Grid Method: This classic method involves overlaying a grid of squares over the area to be measured. The squares are then counted, and their individual areas are summed to obtain the total area. The size of the grid squares should be chosen based on the scale of the map and the desired level of accuracy.
2. Planimeter: A planimeter is a mechanical device that traces the perimeter of an area on the map. It calculates the area by measuring the distance traveled by its tracing arm. While effective, planimeters are becoming less common due to the availability of digital tools.
3. Digital Mapping Software: Modern Geographic Information System (GIS) software offers sophisticated tools for area measurement. These programs allow users to import maps, define boundaries, and calculate areas with high precision. GIS software often incorporates various map projections and supports different unit systems, ensuring flexibility and accuracy.
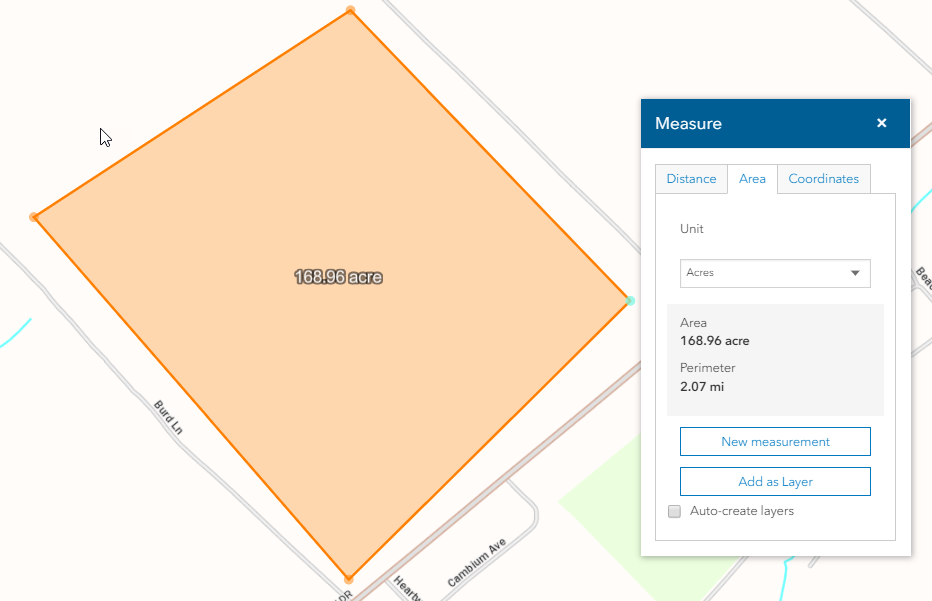
4. Online Mapping Tools: Several online mapping platforms, such as Google Maps and Bing Maps, provide built-in tools for area measurement. Users can simply draw shapes on the map, and the tool automatically calculates the area. These tools are convenient and accessible but may have limitations in terms of accuracy and projection options.
Factors Influencing Area Measurement Accuracy
Several factors can influence the accuracy of area measurements on maps:
- Map Scale: Larger-scale maps (smaller ratios) provide more detail and generally lead to more accurate area measurements.
- Map Projection: As mentioned earlier, different map projections distort distances and shapes differently, affecting area calculations.
- Measurement Method: The choice of measurement method, whether manual or digital, can impact accuracy.
- Data Quality: The accuracy of the underlying map data influences the reliability of area measurements.
- Shape Complexity: Irregular or complex shapes can be more challenging to measure accurately, especially with manual methods.
Applications of Area Measurement on Maps
Area measurement on maps finds wide applications in diverse fields:
- Land Surveying: Land surveyors use area measurements to determine property boundaries, calculate land value, and plan infrastructure development.
- Urban Planning: Planners rely on area measurements to analyze urban growth patterns, assess land use, and design efficient infrastructure.
- Environmental Research: Researchers utilize area measurements to study habitat fragmentation, analyze deforestation rates, and monitor changes in land cover.
- Resource Management: Area measurements are crucial for managing natural resources, such as forests, fisheries, and water resources.
- Disaster Response: Area measurements help assess the impact of natural disasters, such as floods and earthquakes, and guide relief efforts.
- Agriculture: Farmers use area measurements to plan crop rotations, optimize fertilizer application, and track yields.
- Military Operations: Area measurements are essential for planning military maneuvers, targeting operations, and assessing strategic locations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Area Measurement on Maps
Q: What is the difference between area and perimeter on a map?
A: Area refers to the amount of space enclosed within a boundary, while perimeter is the total length of the boundary itself.
Q: What units are typically used for measuring area on maps?
A: Common units for area measurement include square meters (m²), square kilometers (km²), square miles (mi²), and acres. The choice of units depends on the scale of the map and the specific application.
Q: How can I improve the accuracy of area measurements on maps?
A: To enhance accuracy, use maps with larger scales, employ digital measurement tools, and ensure the map’s projection is appropriate for the area being measured.
Q: What are the limitations of online mapping tools for area measurement?
A: Online tools may offer limited accuracy, lack control over map projections, and have restrictions on the size of areas that can be measured.
Tips for Measuring Area on Maps
- Select the appropriate map scale: Choose a map with a scale that provides sufficient detail for the area being measured.
- Understand the map projection: Be aware of the projection used for the map and its potential distortions.
- Use the right tools: Choose the most appropriate method for the task, whether manual or digital.
- Verify measurements: Double-check measurements and use multiple methods for comparison.
- Consider data quality: Be mindful of the accuracy and reliability of the underlying map data.
Conclusion
Accurate area measurement on maps is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. By understanding the principles of map scales, projections, and measurement methods, users can effectively determine areas on maps, providing valuable insights for planning, analysis, and decision-making across diverse fields. As technology continues to advance, digital mapping tools will continue to play an increasingly important role in area measurement, offering enhanced precision, flexibility, and ease of use.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Measuring Area on Maps: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!