Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Northern Europe
Related Articles: Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Northern Europe
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Northern Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Northern Europe
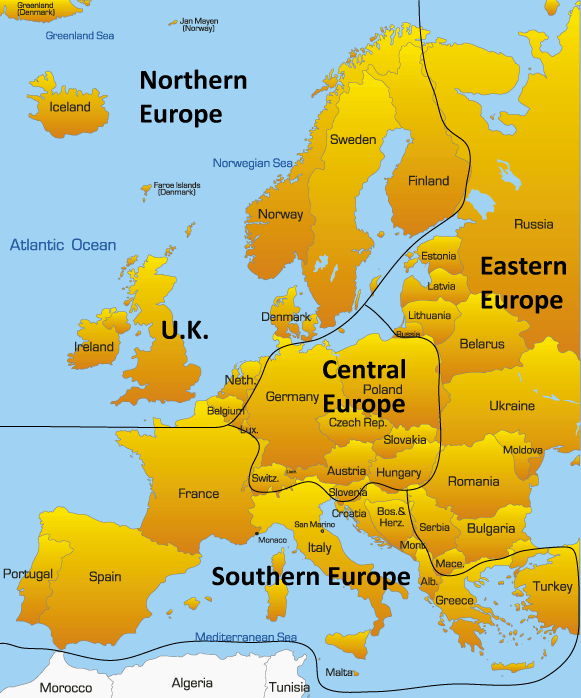
Northern Europe, a region encompassing the Scandinavian Peninsula, the Baltic States, and parts of the British Isles, is a land of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures. Understanding the geography of this region through its map provides valuable insights into its unique characteristics and the interconnectedness of its nations.
Defining the Boundaries:
Defining the exact boundaries of Northern Europe can be somewhat subjective, as different geographical and cultural perspectives exist. However, a commonly accepted definition includes:
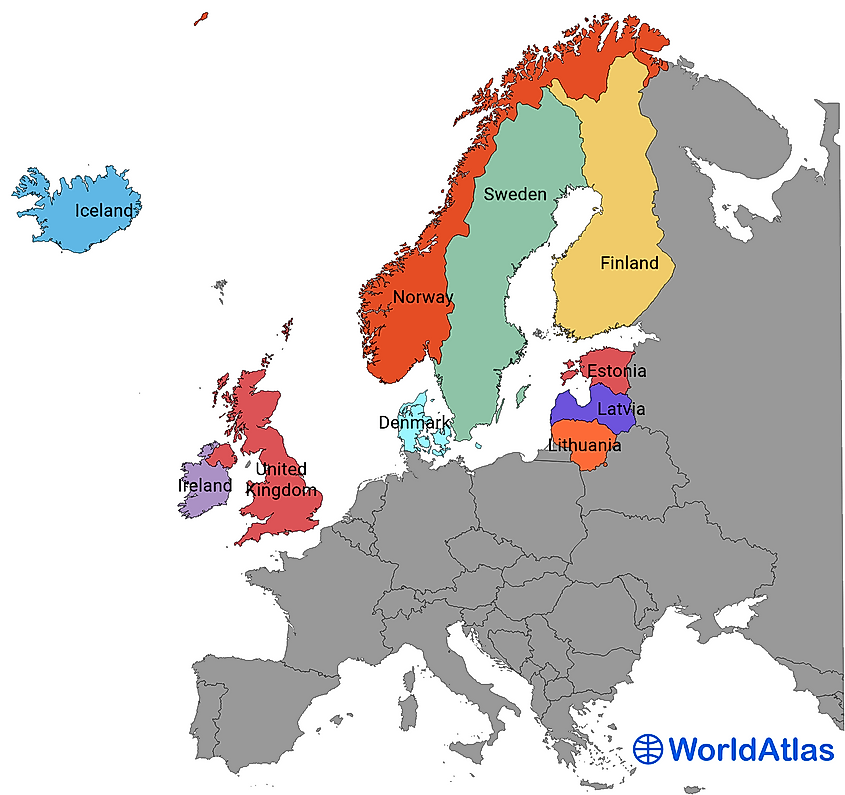
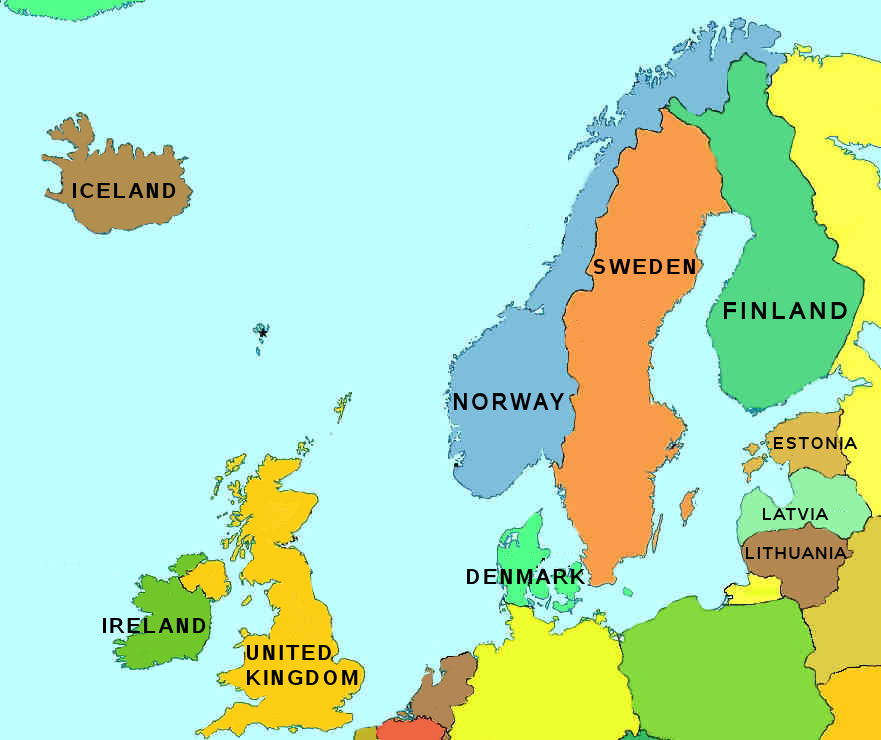
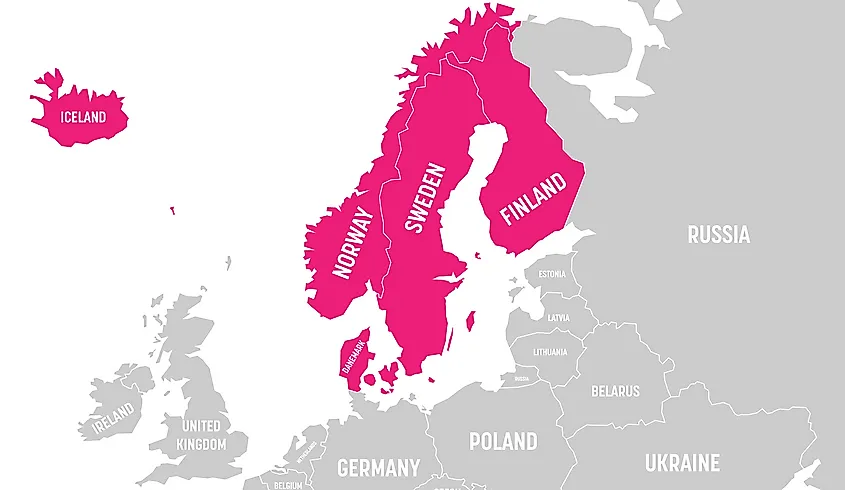
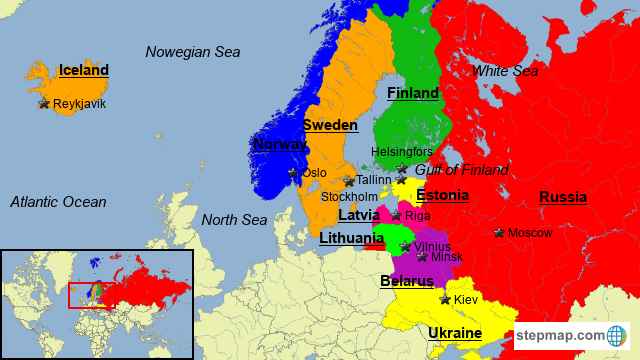
- Scandinavia: Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Iceland.
- The Baltic States: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- Finland: Often considered part of both Scandinavia and the Baltic region due to its shared history and cultural ties.
- The British Isles: While geographically closer to Western Europe, some argue for the inclusion of Northern Ireland and Scotland due to their historical and cultural connections to Scandinavia.
Navigating the Map: Key Geographical Features:
The map of Northern Europe reveals several key geographical features that have shaped the region’s history and culture:
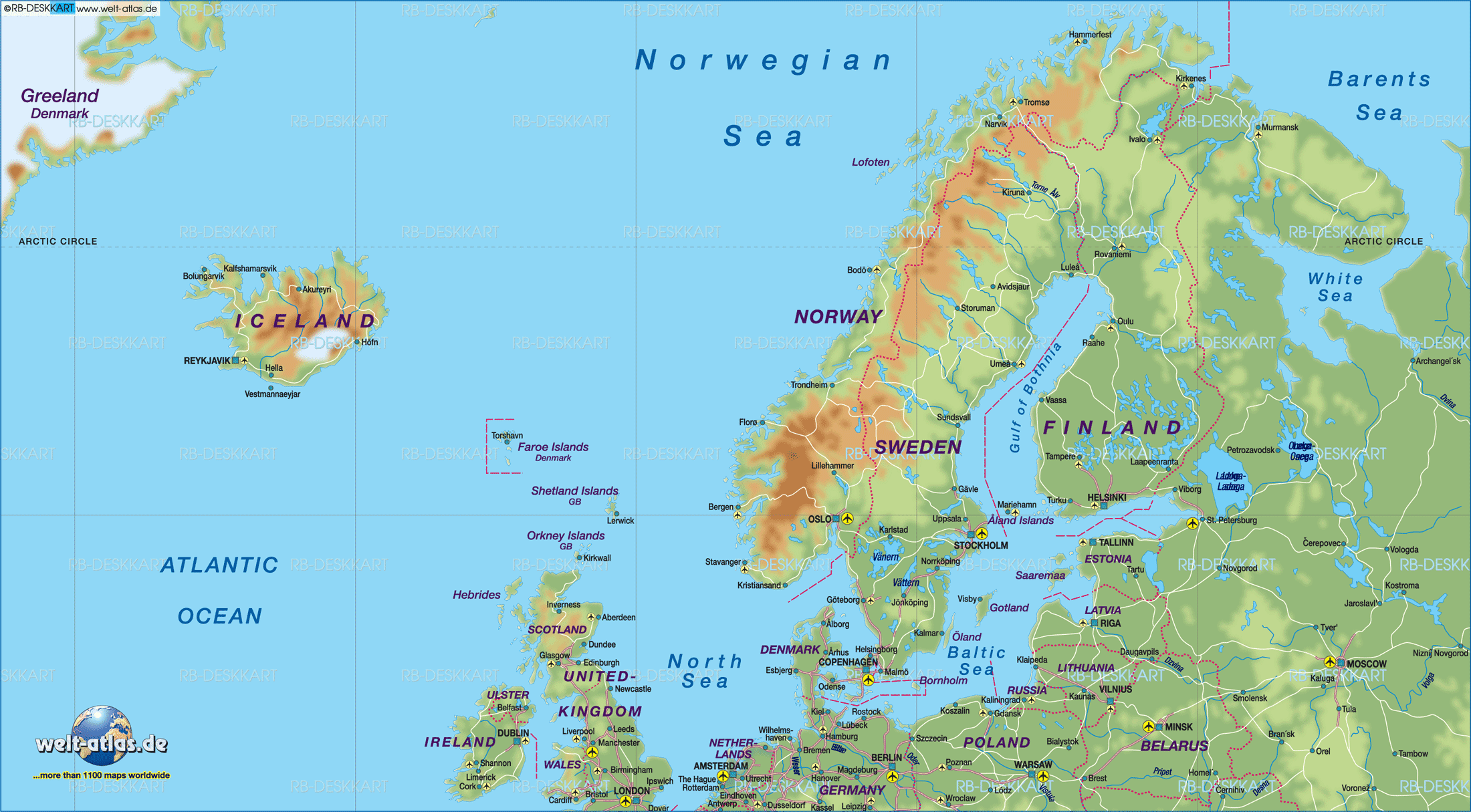
- The Scandinavian Peninsula: This vast landmass, shared by Norway and Sweden, is characterized by its mountainous terrain, extensive forests, and numerous fjords. The peninsula’s rugged landscape has historically influenced transportation and settlement patterns, fostering a strong sense of regional identity.
- The Baltic Sea: A vital waterway connecting the region to the rest of Europe, the Baltic Sea has played a significant role in trade, migration, and cultural exchange. Its numerous islands, including the Åland Islands (Finland) and Bornholm (Denmark), hold historical and cultural significance.
- The North Atlantic Ocean: The vast expanse of the North Atlantic provides access to fishing grounds and maritime trade routes, contributing to the region’s economic development and cultural exchange.
- The Arctic Circle: The northernmost regions of Northern Europe, including parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland, lie within the Arctic Circle, experiencing long periods of daylight in summer and darkness in winter. This unique climate has shaped the region’s ecology and influenced its traditional lifestyles.
A Tapestry of Nations:
Each country within Northern Europe possesses its own distinct identity, shaped by its history, culture, and geography. Examining these nations individually through the lens of the map provides a deeper understanding of the region’s diversity:
- Denmark: Known for its flat landscape, maritime heritage, and vibrant cities like Copenhagen, Denmark has played a pivotal role in shaping the region’s history and culture. Its strategic location in the Baltic Sea has made it a significant trade hub and cultural bridge between Scandinavia and mainland Europe.
- Norway: Characterized by its stunning fjords, rugged mountains, and rich oil reserves, Norway has developed a unique identity rooted in its natural beauty and strong social welfare system. Its long coastline and proximity to the North Atlantic have fostered a strong maritime tradition and fishing industry.
- Sweden: With its vast forests, lakes, and vibrant cities like Stockholm, Sweden is known for its high quality of life, innovative industries, and strong social welfare system. Its central location in the Scandinavian Peninsula has made it a hub for trade and cultural exchange within the region.
- Iceland: A volcanic island nation located in the North Atlantic, Iceland boasts stunning natural landscapes, including glaciers, volcanoes, and geothermal hot springs. Its unique geographical location has fostered a distinctive culture, with a strong emphasis on sustainability and environmental preservation.
- Estonia: This Baltic nation is known for its rich history, vibrant culture, and innovative technology sector. Its location on the eastern edge of the Baltic Sea has made it a bridge between Scandinavia and Eastern Europe.
- Latvia: With its beautiful coastline, charming towns, and diverse cultural heritage, Latvia has a strong history of independence and resilience. Its location on the Baltic Sea has fostered a vibrant maritime industry and cultural exchange with neighboring countries.
- Lithuania: The largest of the Baltic states, Lithuania is known for its rich history, cultural traditions, and natural beauty. Its strategic location on the eastern edge of the Baltic Sea has made it a key player in regional trade and cultural exchange.
- Finland: Situated on the border between Scandinavia and the Baltic region, Finland boasts a unique identity shaped by its beautiful lakes, forests, and strong social welfare system. Its history as a bridge between East and West has fostered a unique cultural blend.
The Importance of Understanding the Map:
Understanding the map of Northern Europe provides a crucial framework for comprehending the region’s historical, cultural, and economic dynamics. It helps us:
- Appreciate the interconnectedness of nations: The map reveals the geographical proximity and historical interactions between the countries of Northern Europe, highlighting their shared cultural heritage and economic interdependence.
- Understand the impact of geography on development: The region’s diverse landscapes, from the rugged mountains of Norway to the flat plains of Denmark, have shaped its settlement patterns, economic activities, and cultural traditions.
- Recognize the importance of maritime trade: The Baltic Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean have played a crucial role in shaping the region’s history and economy, facilitating trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
- Appreciate the region’s unique identity: The map provides a visual representation of the distinct cultures and identities that have emerged within Northern Europe, highlighting the region’s diverse and vibrant tapestry.
FAQs about the Map of Northern Europe:
Q: What is the largest country in Northern Europe?
A: Sweden, with a land area of 449,964 square kilometers, is the largest country in Northern Europe.
Q: What is the smallest country in Northern Europe?
A: Iceland, with a land area of 103,000 square kilometers, is the smallest country in Northern Europe.
Q: What is the most densely populated country in Northern Europe?
A: The Netherlands, with a population density of 508 people per square kilometer, is the most densely populated country in Northern Europe. However, it is not considered part of Northern Europe by most definitions.
Q: What are the major languages spoken in Northern Europe?
A: The major languages spoken in Northern Europe include:
- Scandinavian languages: Swedish, Norwegian, Danish, Icelandic, and Faroese.
- Baltic languages: Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian.
- English: Spoken in the British Isles, including Northern Ireland and Scotland.
- Finnish: A Finno-Ugric language spoken in Finland.
Q: What are the major industries in Northern Europe?
A: The major industries in Northern Europe include:
- Fishing: A traditional industry in coastal areas, particularly in Norway, Iceland, and Denmark.
- Forestry: A significant industry in Sweden, Finland, and Norway, providing timber and paper products.
- Mining: Important in Norway, Sweden, and Finland, extracting minerals like iron ore, copper, and zinc.
- Manufacturing: A key sector in Sweden, Denmark, and Finland, producing automobiles, machinery, and electronics.
- Tourism: A growing industry in many countries, driven by the region’s stunning natural beauty and cultural attractions.
Tips for Using the Map of Northern Europe:
- Focus on the key geographical features: The map highlights the region’s diverse landscapes, from the fjords of Norway to the forests of Sweden, providing insights into its history and culture.
- Explore the individual countries: Each country within Northern Europe possesses its own unique identity, shaped by its history, culture, and geography.
- Consider the region’s historical connections: The map reveals the interconnectedness of the region’s nations, highlighting their shared cultural heritage and economic interdependence.
- Analyze the region’s economic activities: The map provides insights into the region’s major industries, including fishing, forestry, mining, manufacturing, and tourism.
- Use the map as a starting point for further exploration: The map serves as a valuable tool for understanding the region’s geography, history, and culture, sparking further research and travel plans.
Conclusion:
The map of Northern Europe is a valuable resource for understanding the region’s diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures. It provides a visual representation of the interconnectedness of its nations, highlighting their shared cultural heritage and economic interdependence. By understanding the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the region’s unique identity and the importance of its geographical features in shaping its development. The map serves as a powerful tool for exploring the region’s past, present, and future, inspiring further research, travel, and engagement with this fascinating corner of the world.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the North: A Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Northern Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!