Navigating the Path to Sustainability: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Development Roadmaps
Related Articles: Navigating the Path to Sustainability: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Development Roadmaps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Path to Sustainability: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Development Roadmaps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Path to Sustainability: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Development Roadmaps

The concept of sustainable development has become increasingly crucial as the world grapples with environmental degradation, social inequalities, and economic instability. To address these interconnected challenges, organizations and governments alike are adopting Sustainable Development Roadmaps (SDRs) as a strategic framework to guide their journey towards a more sustainable future.
What is a Sustainable Development Roadmap?
An SDR is a comprehensive, long-term plan that outlines an organization’s or a nation’s vision for sustainable development. It serves as a guide, setting specific goals, targets, and action plans across economic, social, and environmental dimensions. The roadmap typically includes:
- Vision and Mission: Defining the desired future state and the overarching purpose of the sustainability journey.
- Key Objectives: Establishing measurable targets and indicators for progress across sustainability pillars.
- Action Plans: Detailing specific initiatives, strategies, and timelines for achieving objectives.
- Resource Allocation: Identifying and allocating resources, including financial, human, and technological, to support action plans.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Establishing systems for tracking progress, measuring impact, and adapting strategies as needed.
The Importance of Sustainable Development Roadmaps:
SDRs play a pivotal role in achieving sustainable development by offering several key benefits:
- Clarity and Direction: They provide a clear roadmap, aligning efforts towards a common goal and ensuring all stakeholders are working towards the same vision.
- Accountability and Transparency: The defined goals and targets enhance accountability, allowing stakeholders to track progress and measure the effectiveness of initiatives.
- Prioritization and Resource Allocation: By outlining specific actions and resource requirements, SDRs enable efficient allocation of resources and focus on the most impactful initiatives.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The development and implementation of SDRs require collaboration and input from various stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding and commitment to sustainability.
- Resilience and Adaptability: SDRs allow for continuous monitoring and evaluation, enabling organizations to adapt their strategies to changing circumstances and emerging challenges.
Key Elements of a Sustainable Development Roadmap:
A robust SDR encompasses a comprehensive set of elements that address the interconnected nature of sustainability:
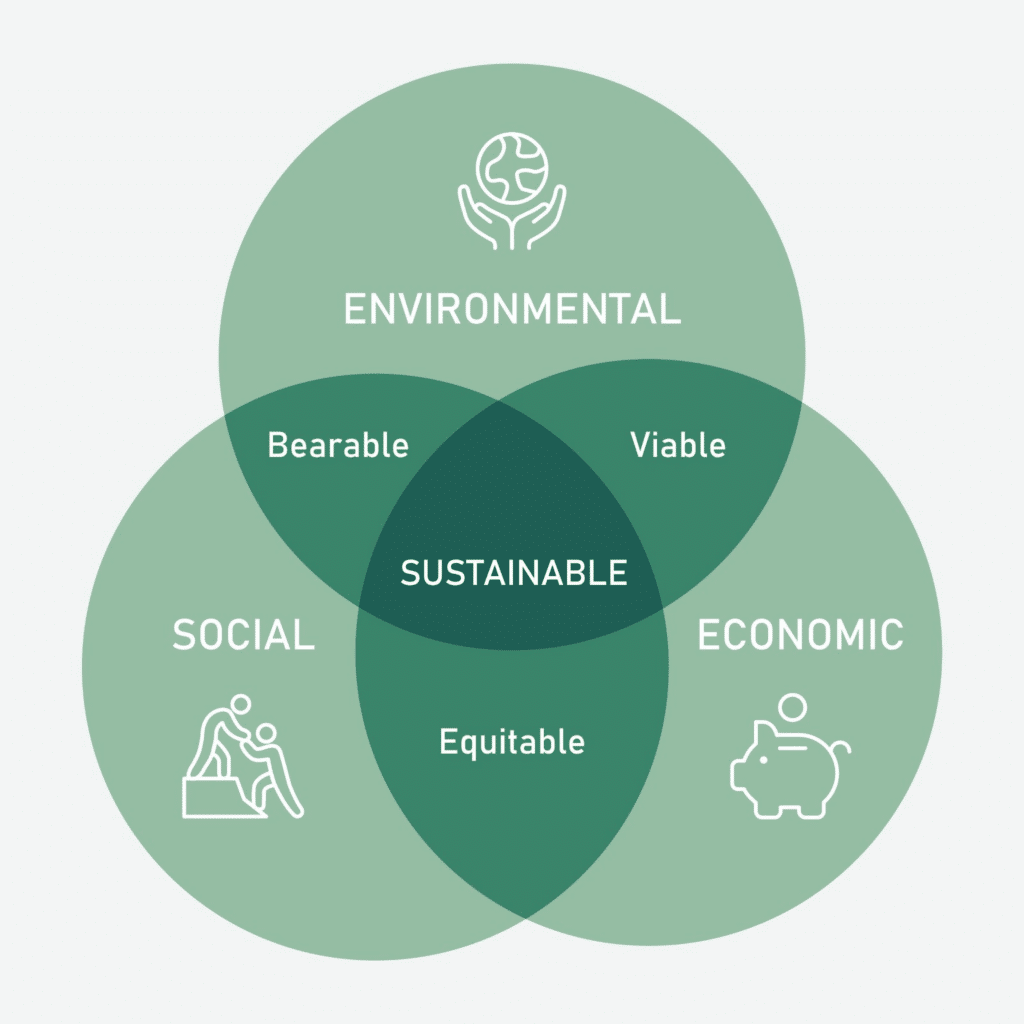
- Economic Sustainability: Focusing on economic growth that is inclusive, equitable, and environmentally responsible.
- Social Sustainability: Promoting social equity, human rights, and well-being for all.
- Environmental Sustainability: Protecting and preserving natural resources, mitigating climate change, and promoting biodiversity.
- Governance: Ensuring transparency, accountability, and effective decision-making processes.
- Innovation: Encouraging technological advancements and innovative solutions to address sustainability challenges.
Developing a Sustainable Development Roadmap:
The process of developing an SDR involves several key steps:
- Defining the Scope and Context: Identifying the specific goals, boundaries, and stakeholders involved in the roadmap.
- Conducting a Baseline Assessment: Analyzing the current state of sustainability performance across various dimensions.
- Setting Goals and Targets: Establishing clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
- Developing Action Plans: Outlining specific initiatives, strategies, and timelines for achieving objectives.
- Identifying Resources and Funding: Allocating financial, human, and technological resources to support action plans.
- Establishing Monitoring and Evaluation Systems: Developing mechanisms for tracking progress, measuring impact, and adapting strategies.
- Communicating and Engaging Stakeholders: Sharing the roadmap with stakeholders, fostering transparency, and encouraging participation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Sustainable Development Roadmaps:
1. What is the difference between a Sustainable Development Roadmap and a Sustainability Report?
A sustainability report provides a retrospective account of an organization’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, while an SDR outlines a forward-looking plan for achieving sustainability goals.
2. How long should a Sustainable Development Roadmap be?
The duration of an SDR can vary depending on the organization’s goals and the complexity of the initiatives. It can range from a few years to several decades.
3. Who should be involved in developing a Sustainable Development Roadmap?
Developing a comprehensive SDR requires input from diverse stakeholders, including:
- Management: Setting the strategic direction and allocating resources.
- Employees: Contributing expertise and ideas for action plans.
- Customers: Providing insights into their expectations and preferences.
- Suppliers: Collaborating on sustainable supply chain practices.
- Communities: Engaging in dialogue and addressing local concerns.
4. How can an organization ensure its Sustainable Development Roadmap is effective?
- Clear Objectives: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Actionable Plans: Outline concrete steps, timelines, and responsible parties for each initiative.
- Regular Monitoring: Track progress, measure impact, and adjust strategies as needed.
- Open Communication: Share the roadmap with stakeholders, foster transparency, and encourage feedback.
5. What are some examples of successful Sustainable Development Roadmaps?
Numerous organizations and governments have implemented successful SDRs, including:
- IKEA: Their "People & Planet Positive" roadmap focuses on climate action, circularity, and social responsibility.
- The City of Copenhagen: Their "Copenhagen 2025" roadmap aims to become a carbon-neutral city by 2025.
- The United Nations: The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a global framework for achieving sustainable development by 2030.
Tips for Developing a Sustainable Development Roadmap:
- Start with a Clear Vision: Define the desired future state and the overarching purpose of the sustainability journey.
- Involve Stakeholders: Foster collaboration and input from diverse stakeholders to ensure inclusivity and ownership.
- Focus on Measurable Goals: Establish SMART objectives to track progress and measure impact.
- Prioritize Actions: Identify the most impactful initiatives and allocate resources accordingly.
- Embrace Continuous Improvement: Regularly monitor progress, adapt strategies, and learn from experience.
Conclusion:
Sustainable Development Roadmaps are essential tools for navigating the path towards a more sustainable future. By setting clear goals, outlining action plans, and fostering stakeholder engagement, SDRs provide a framework for organizations and governments to achieve their sustainability ambitions. Implementing robust SDRs is not only a strategic necessity but also a moral imperative, ensuring a prosperous and equitable future for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Path to Sustainability: A Comprehensive Guide to Sustainable Development Roadmaps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!