Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Brazil’s Federal Structure
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Brazil’s Federal Structure
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Brazil’s Federal Structure. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Brazil’s Federal Structure

Brazil, the fifth largest country in the world by land area, boasts a complex and diverse political landscape. Understanding this intricate web of federalism is crucial for grasping the nation’s history, culture, and current political dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of Brazil’s political map, exploring its historical origins, current structure, and the implications for governance and national identity.
The Genesis of Federalism: From Empire to Republic
Brazil’s journey towards federalism began with its transition from a Portuguese colony to an independent empire in 1822. Emperor Pedro I, seeking to consolidate his power and appease local elites, adopted a decentralized system of governance. This system, known as "provincialism," granted significant autonomy to the individual provinces, fostering a sense of regional identity and contributing to the development of unique cultural and economic characteristics.
However, this early form of federalism was ultimately unsustainable. The provinces, lacking a cohesive national framework, struggled to address issues of national importance. The subsequent abolition of slavery in 1888 further exacerbated tensions, leading to the overthrow of the monarchy and the establishment of the First Republic in 1889.
The First Republic (1889-1930) witnessed the formalization of federalism through the 1891 Constitution. This document divided the country into 20 states, each with its own constitution and elected government. The federal government, based in Rio de Janeiro, retained control over key areas such as defense, foreign policy, and national infrastructure.
The Evolution of Federalism: Shifting Power Dynamics
The federal system underwent significant transformations throughout the 20th century. The Vargas Era (1930-1945) saw a centralization of power under Getúlio Vargas, who sought to strengthen the national government and address economic and social challenges. The 1934 Constitution, while maintaining the federal framework, expanded the powers of the federal government and introduced social and economic reforms.
The military dictatorship (1964-1985) further consolidated federal power, curtailing state autonomy and suppressing political dissent. This period saw the implementation of a centralized economic model, with the federal government taking control of key industries and infrastructure projects.
The return to democracy in 1985 marked a shift towards greater decentralization. The 1988 Constitution, known as the "Citizen’s Constitution," reaffirmed the federal system, expanding the powers of the states and guaranteeing fundamental rights and freedoms. This period witnessed a resurgence of regional identity and a renewed focus on local development.
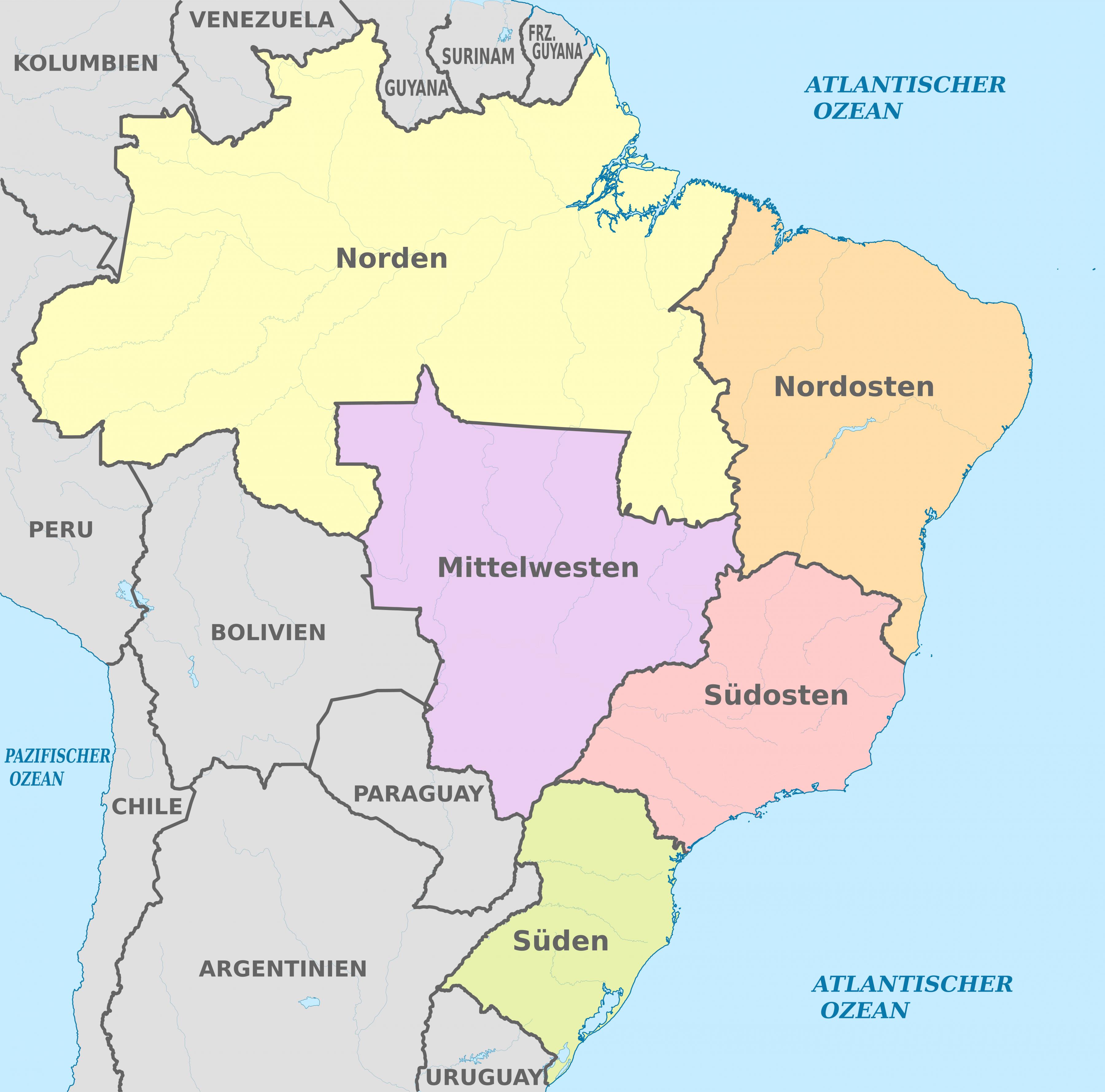
The Brazilian Political Map Today: A Complex Tapestry of Power
Brazil’s political map today reflects the country’s complex history and its ongoing struggle to balance federal and state power. The current structure, defined by the 1988 Constitution, comprises:
- Federal Government: Located in Brasília, the federal government holds authority over national affairs, including defense, foreign policy, taxation, and interstate commerce. It comprises the Executive Branch (President and Cabinet), the Legislative Branch (National Congress), and the Judicial Branch (Supreme Court).
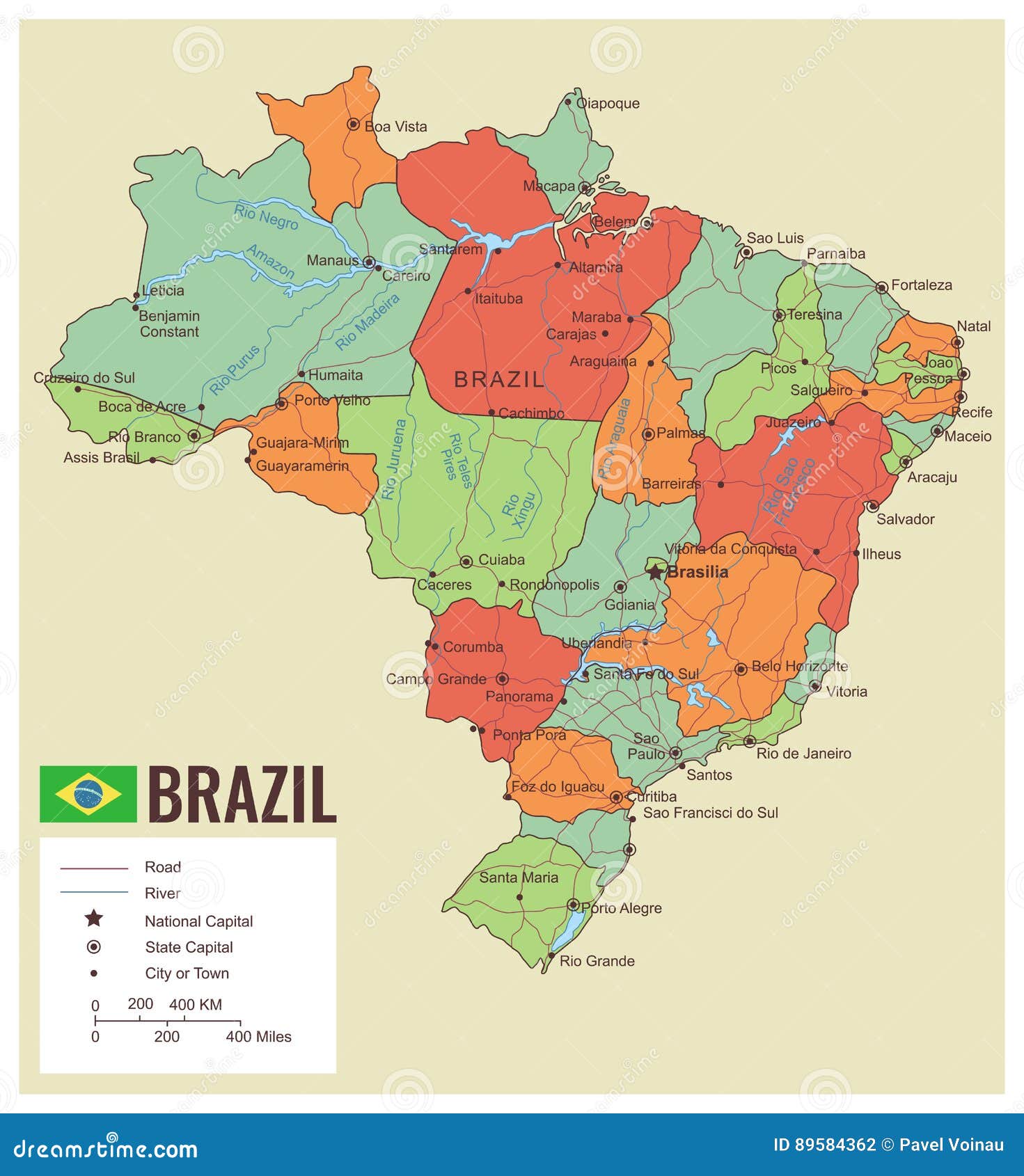
- States: Brazil is divided into 26 states, each with its own constitution, elected governor, and legislature. States have significant autonomy over local issues, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure.
- Federal District: Brasília, the capital city, is a federal district with a unique status, governed directly by the federal government.
- Municipalities: Within each state, there are numerous municipalities, each with its own elected mayor and council. Municipalities are responsible for local services, such as garbage collection, public transportation, and social welfare programs.
This complex system of governance reflects the country’s diverse population, its vast territorial expanse, and the need to balance national unity with regional autonomy.
The Importance of Understanding Brazil’s Federal Structure
The Brazilian political map holds significant importance for various reasons:
- Understanding Political Dynamics: The federal structure influences the distribution of power and resources, shaping political alliances and influencing policy decisions. Understanding this structure is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of national and regional politics.
- Regional Development: The decentralized nature of the system empowers states to address local needs and priorities. This fosters regional development and allows for tailored solutions to address unique challenges.
- Cultural Identity: The federal system has played a role in preserving and nurturing regional cultures and traditions. By granting states autonomy, it allows for the expression of diverse identities within a unified nation.
- Governance and Policy: The federal structure impacts the implementation of national policies. Understanding the division of powers and responsibilities is crucial for effective policy design and implementation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major political parties in Brazil?
Brazil has a multi-party system, with numerous parties competing for power at all levels of government. Some of the major parties include the Workers’ Party (PT), the Brazilian Social Democracy Party (PSDB), the Brazilian Democratic Movement (MDB), and the Liberal Party (PL).
2. How does the electoral system work in Brazil?
Brazil utilizes a proportional representation system for legislative elections, with seats allocated based on the percentage of votes received by each party. For presidential elections, the candidate who receives the most votes wins, provided they secure more than 50% of the valid votes. If no candidate reaches this threshold, a runoff election is held between the two top candidates.
3. What are the key challenges facing Brazilian federalism today?
Brazil faces challenges in balancing federal and state power, managing regional disparities, and ensuring equitable distribution of resources. Other challenges include corruption, political instability, and the need for greater transparency and accountability.
4. How does the federal structure impact economic development in Brazil?
The federal structure influences economic development through the allocation of resources, tax policies, and infrastructure investments. While decentralization empowers states to address local needs, it can also lead to disparities in development levels across regions.
5. What are the implications of the federal system for social policy in Brazil?
The federal system influences social policy by determining the division of responsibilities for areas like education, healthcare, and social welfare. While states have significant autonomy in these areas, the federal government sets national standards and provides funding for essential programs.
Tips for Navigating the Brazilian Political Map
- Stay Informed: Follow news and political analysis from reputable sources to stay updated on current events and key political figures.
- Learn about Regional Differences: Explore the diverse cultures, histories, and economic realities of different regions within Brazil. This will provide a deeper understanding of regional politics and their influence on national politics.
- Engage in Political Discourse: Participate in constructive discussions about political issues and engage with diverse perspectives. This will help you develop a more informed understanding of the complexities of Brazilian politics.
- Support Democratic Institutions: Advocate for transparency, accountability, and the rule of law in Brazilian politics. This is essential for maintaining a stable and functioning democracy.
Conclusion
Brazil’s political map is a dynamic and evolving landscape, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse population, and ongoing challenges. Understanding the intricacies of its federal structure is crucial for navigating the complexities of Brazilian politics, appreciating the country’s cultural tapestry, and recognizing the importance of regional development. As Brazil continues to evolve, its political map will undoubtedly continue to shape the nation’s destiny.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape: A Guide to Brazil’s Federal Structure. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!