Navigating the Web of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: Navigating the Web of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Web of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Web of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

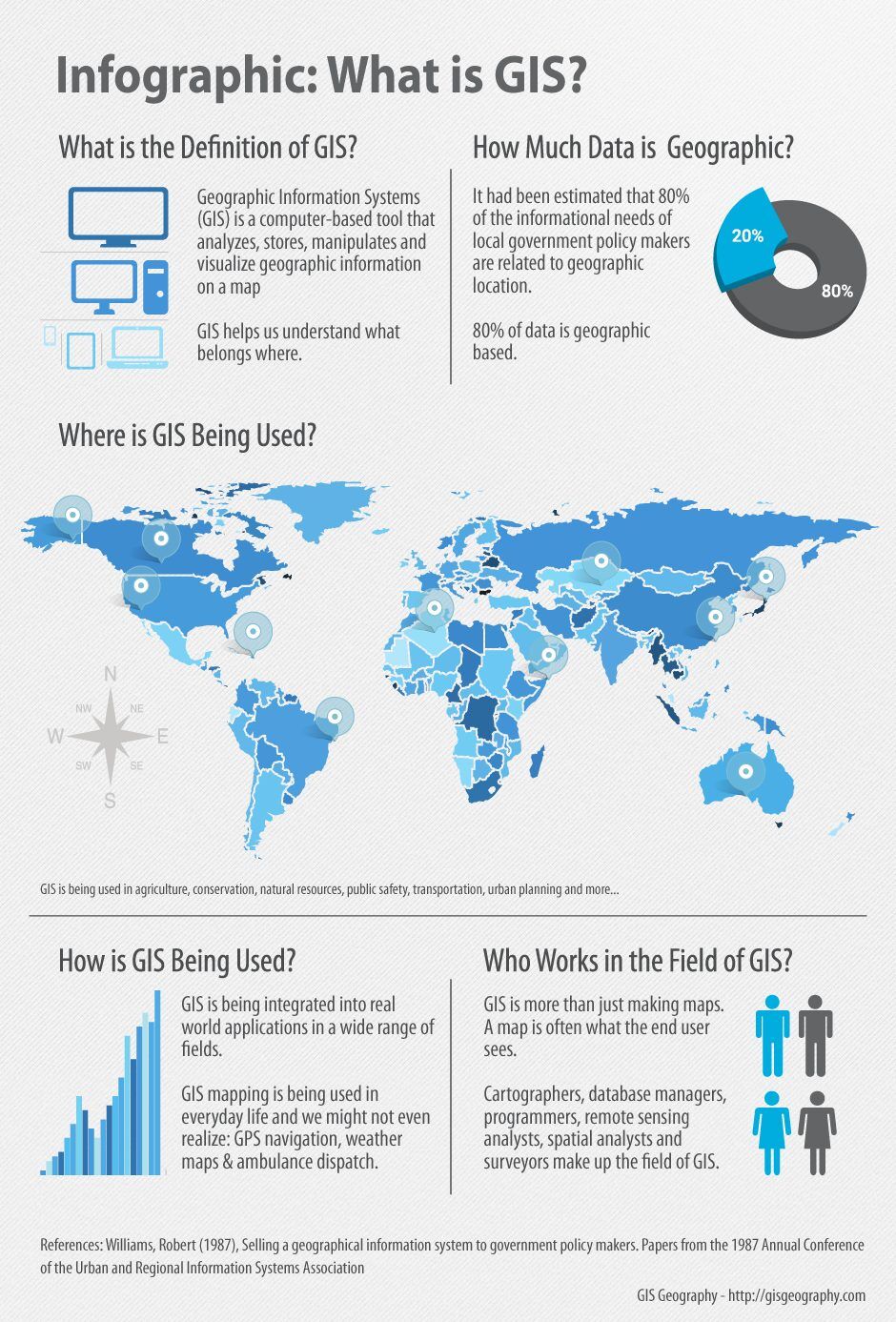
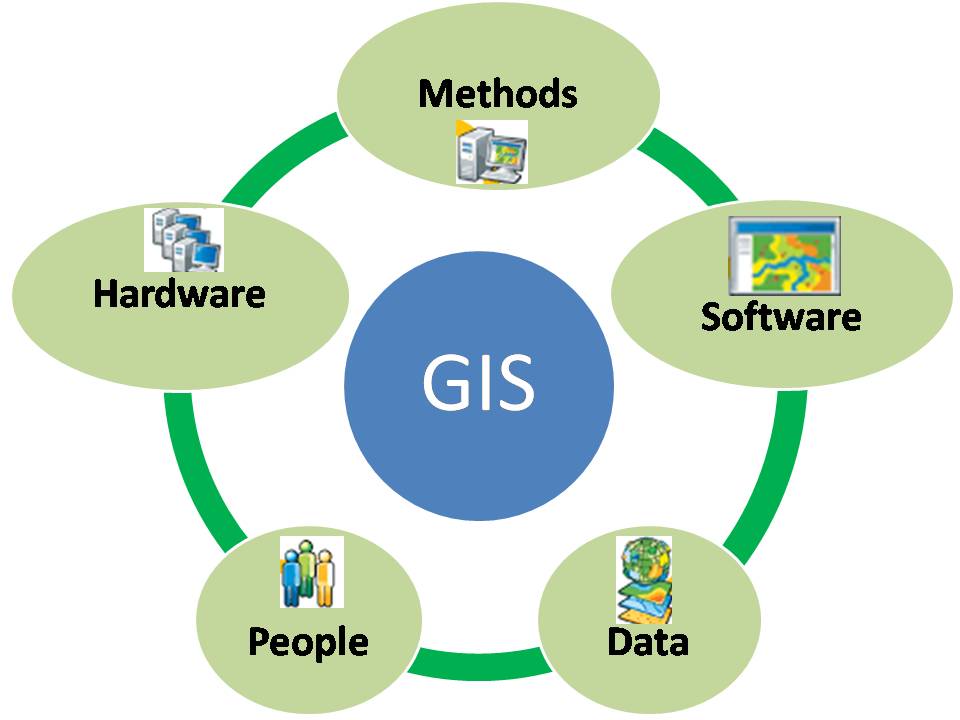
In an increasingly interconnected world, understanding our physical environment is paramount. Geographic information systems (GIS), often referred to as "map web," play a pivotal role in enabling this comprehension. This technology transcends simple map visualization, offering a powerful platform for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating geographic data.
The Foundation of GIS: Data and Analysis
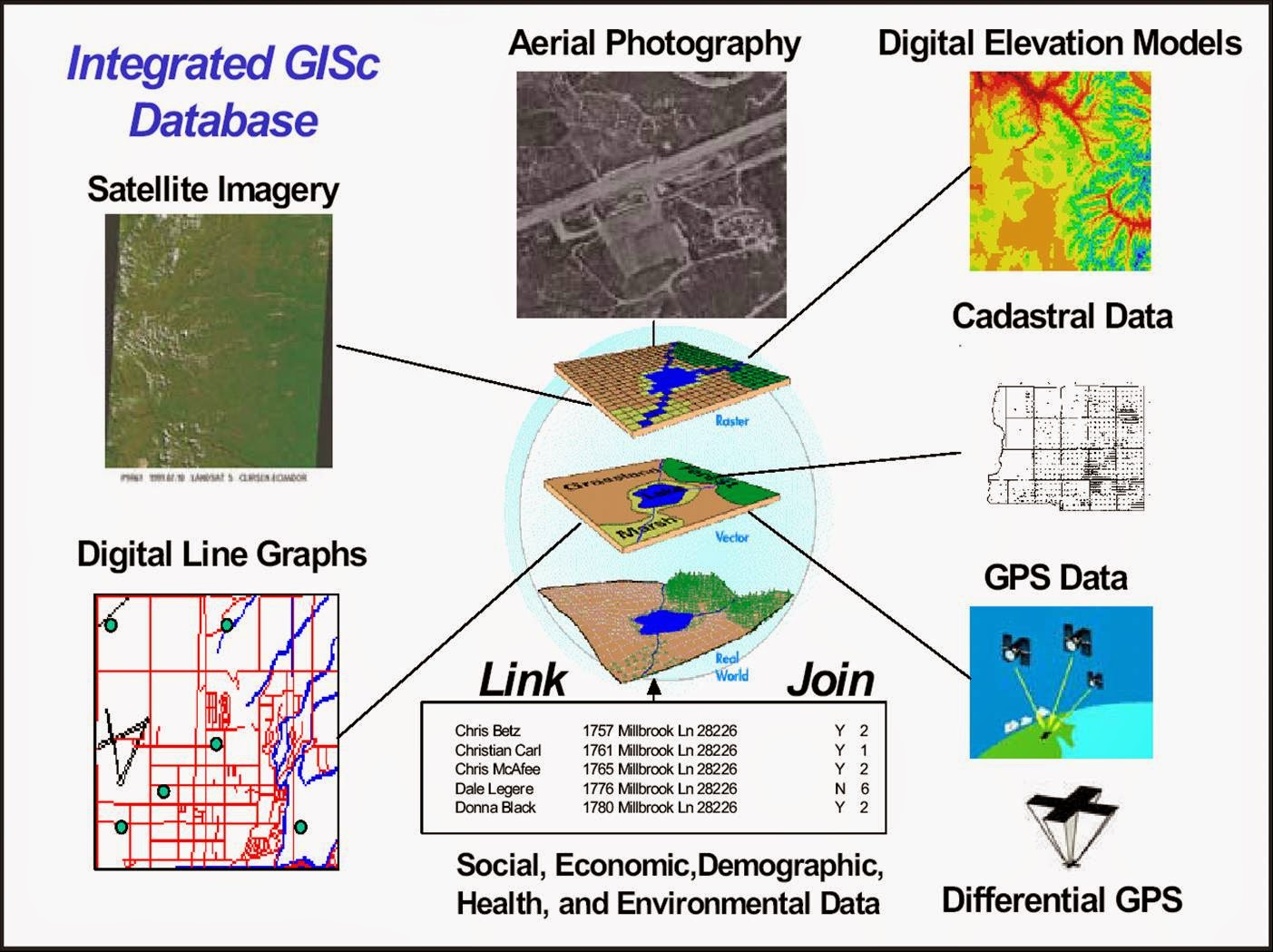
GIS relies on a fundamental principle: geospatial data. This data represents real-world features, locations, and events, imbued with geographic coordinates. These coordinates are the key to unlocking the power of GIS, allowing for spatial analysis and visualization.
Imagine a map depicting traffic congestion in a city. This map is not merely a visual representation; it’s a compilation of data points collected from various sources, including GPS devices, traffic sensors, and social media feeds. GIS software analyzes this data, identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies. This analysis can then be used to predict traffic flow, optimize routes, and improve traffic management strategies.
Beyond Visualization: The Power of Spatial Analysis
GIS goes beyond simply displaying maps. It empowers users to analyze geographic data, uncovering insights that would otherwise remain hidden. This analysis encompasses a wide range of techniques:
- Spatial Queries: Identifying features based on their location or proximity to other features. For instance, finding all hospitals within a 10-mile radius of a specific location.
- Buffering: Creating zones around features, allowing for analysis of areas influenced by specific points. This could involve determining the impact of a new factory on surrounding residential areas.
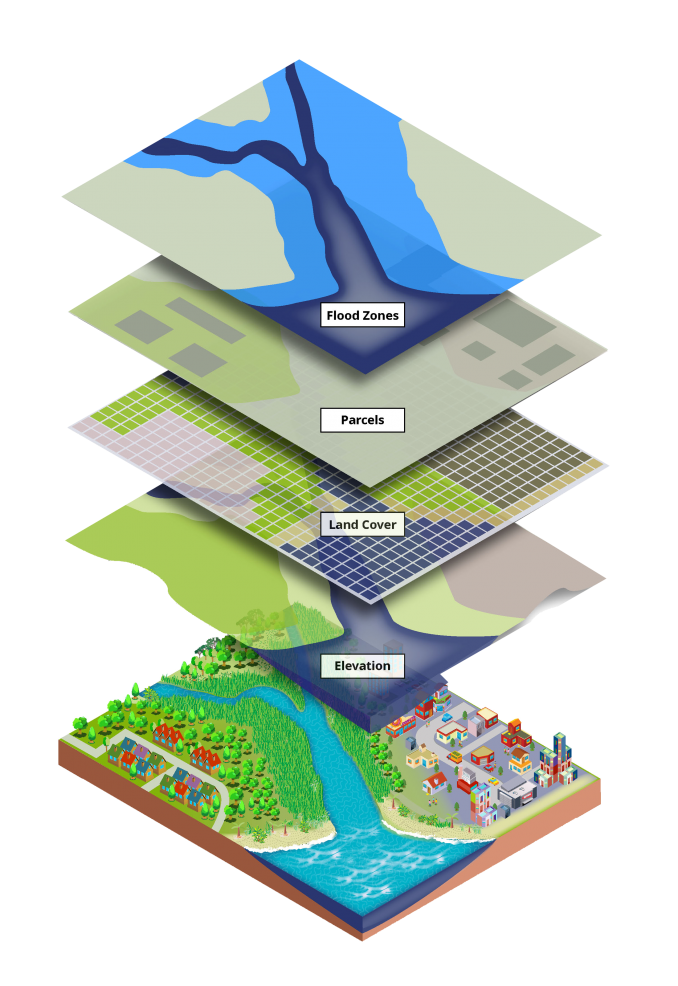
- Overlay Analysis: Combining multiple data layers to identify areas where specific conditions overlap. This technique can help understand the relationship between land use, soil type, and water resources.
- Network Analysis: Optimizing routes, flows, and connections within a network. Examples include finding the shortest path between two points, analyzing delivery routes, or optimizing emergency service response times.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
GIS has become an indispensable tool across various industries, revolutionizing the way we approach complex problems:
- Urban Planning: GIS aids in urban planning by analyzing population density, infrastructure, and land use patterns. This enables efficient resource allocation, transportation planning, and sustainable development.
- Environmental Management: GIS facilitates environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. Mapping deforestation, pollution levels, and wildlife habitats helps track environmental changes and implement effective conservation strategies.
- Agriculture: Precision agriculture leverages GIS to optimize crop yields, track soil conditions, and manage irrigation systems. This data-driven approach reduces resource waste and maximizes productivity.
- Disaster Management: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response. Mapping evacuation routes, identifying vulnerable areas, and tracking disaster impacts enables efficient coordination and resource allocation during emergencies.
- Healthcare: GIS assists in disease surveillance, identifying disease hotspots and predicting outbreaks. This helps allocate healthcare resources effectively and implement targeted public health interventions.
- Business and Marketing: GIS helps businesses understand customer demographics, target specific markets, and optimize supply chains. This data-driven approach enhances marketing campaigns and improves business operations.
Beyond the Map: The Future of GIS
GIS is constantly evolving, incorporating advancements in technology and data science. Key trends shaping the future of GIS include:
- Cloud-based GIS: Cloud computing enables accessibility and scalability, allowing users to access GIS services and data from anywhere, anytime.
- Big Data Integration: GIS is increasingly integrated with big data platforms, enabling analysis of massive datasets and uncovering complex relationships.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms enhance GIS capabilities, automating tasks, improving accuracy, and generating predictive models.
- 3D GIS and Virtual Reality (VR): 3D GIS allows for immersive visualization and analysis of complex environments, while VR enhances user interaction and understanding.
- Location-Based Services (LBS): GIS powers LBS applications, providing users with real-time location-specific information and services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about GIS
1. What is the difference between GIS and GPS?
GIS and GPS are often confused, but they serve distinct purposes. GPS (Global Positioning System) is a technology that determines a device’s location using satellites. GIS, on the other hand, utilizes this location data and other geographic information to analyze and visualize spatial patterns.
2. What are the benefits of using GIS?
GIS offers numerous benefits:
- Improved decision-making: GIS provides insights into spatial relationships, enabling data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced communication: GIS allows for clear and concise visualization of geographic data, facilitating communication and understanding.
- Efficient resource allocation: GIS helps optimize resource allocation by identifying areas with specific needs.
- Increased efficiency: GIS automates tasks, streamlining workflows and improving operational efficiency.
- Reduced costs: GIS helps identify cost-effective solutions by optimizing processes and resource utilization.
3. What are some examples of GIS applications in everyday life?
GIS is used in countless everyday applications, often without us realizing it:
- Navigation apps: Apps like Google Maps and Waze utilize GIS to provide directions, traffic updates, and location-based services.
- Weather apps: Weather apps rely on GIS to display weather forecasts and predict storm paths.
- Online shopping: E-commerce platforms use GIS to track shipments, optimize delivery routes, and identify local stores.
- Social media: Social media platforms use GIS to map user locations, track trends, and personalize content.
4. How can I learn more about GIS?
Numerous resources are available to learn about GIS:
- Online courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer comprehensive GIS courses.
- Universities and colleges: Many universities and colleges offer degree programs in GIS and related fields.
- Professional organizations: Organizations like the Geographic Information Systems Society (GISci) provide resources, training, and networking opportunities.
Tips for Effective GIS Use
- Define clear objectives: Clearly outline the goals of your GIS project before starting.
- Choose the right software: Select GIS software that meets your specific needs and skill level.
- Ensure data quality: Use reliable and accurate data sources for your analysis.
- Visualize effectively: Create clear and informative maps and visualizations.
- Communicate effectively: Present your GIS findings in a way that is easily understood by your audience.
Conclusion
GIS is a powerful tool for understanding and managing our complex world. From urban planning to environmental conservation, healthcare to business operations, GIS empowers us to make informed decisions, solve problems efficiently, and create a more sustainable future. As technology continues to advance, GIS will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our world, enabling us to navigate the web of geographic information with greater insight and precision.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Web of Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!