Navigating the World: Understanding the ITU Zone Map
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding the ITU Zone Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding the ITU Zone Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the World: Understanding the ITU Zone Map
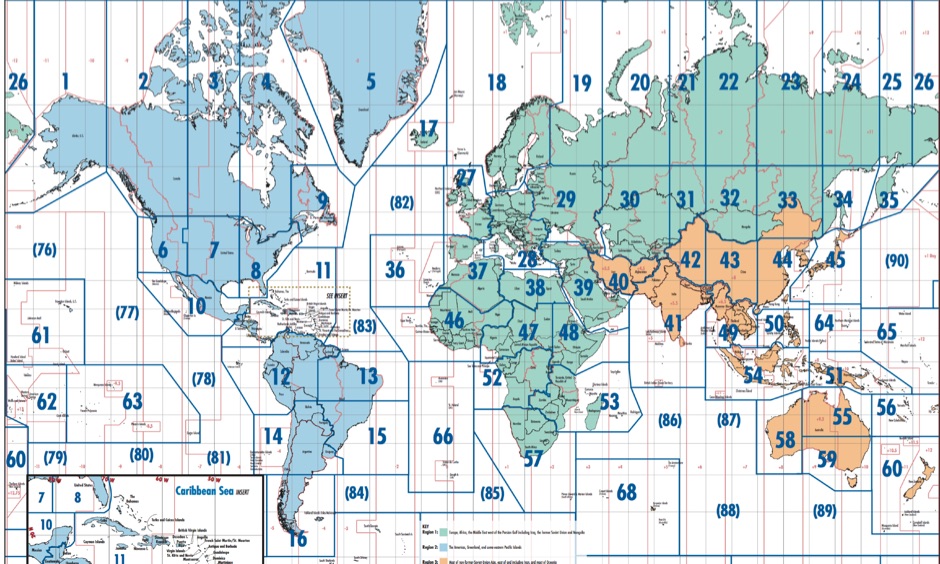
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Zone Map is a fundamental tool for understanding global telecommunications infrastructure and its implications. It divides the world into three distinct zones, each with unique characteristics that influence telecommunications regulations, frequency allocation, and the deployment of various technologies. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the ITU Zone Map, delving into its historical context, underlying principles, and practical applications.
A Brief History of the ITU Zone Map
The ITU, established in 1865, plays a crucial role in coordinating and regulating international telecommunications. Its efforts to standardize and allocate radio frequencies date back to the early 20th century, leading to the creation of the ITU Zone Map in 1912. The map initially divided the world into two zones, later expanded to three in 1947. This division aimed to address the increasing demand for radio spectrum and ensure efficient utilization across different regions.
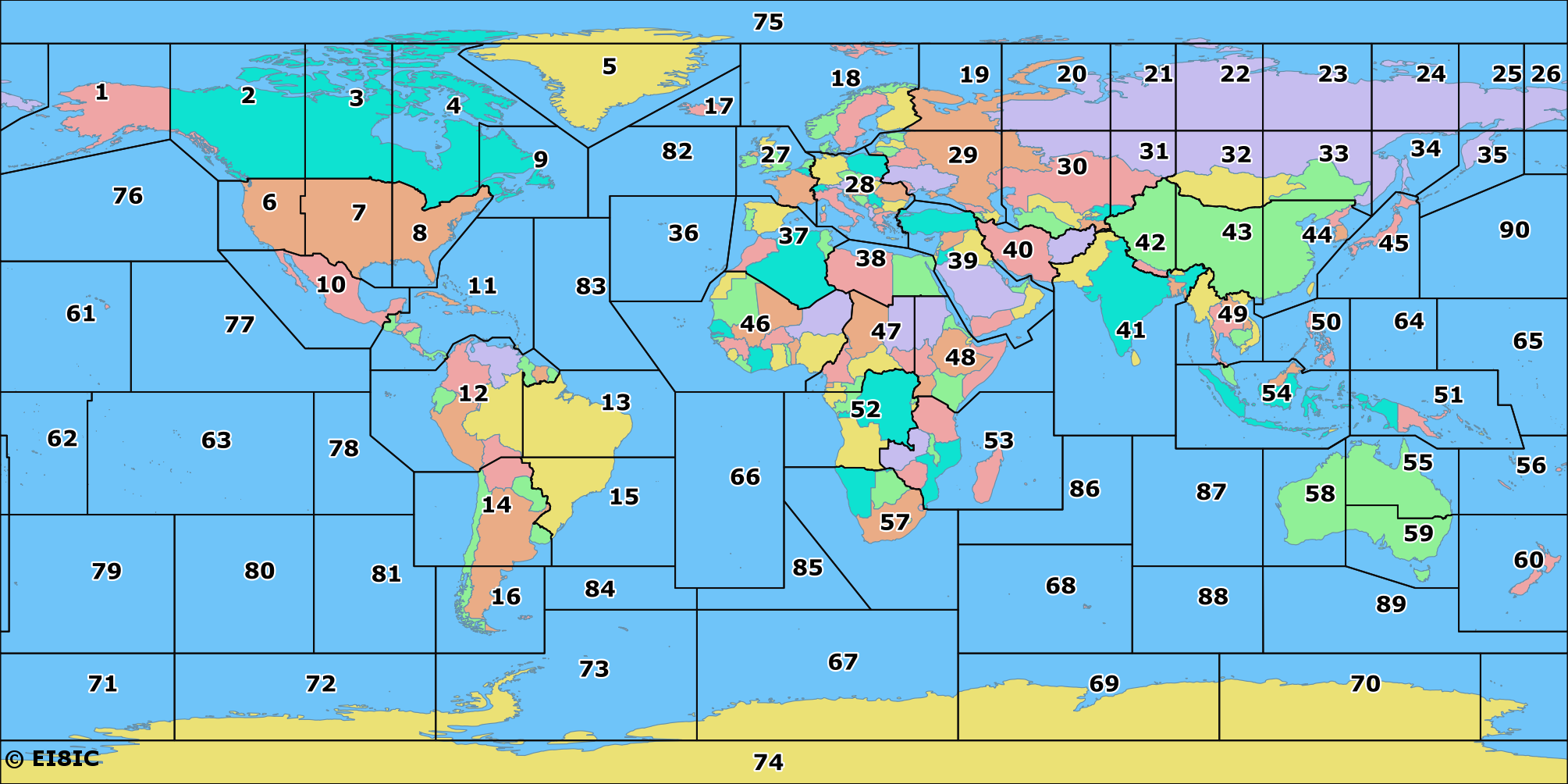
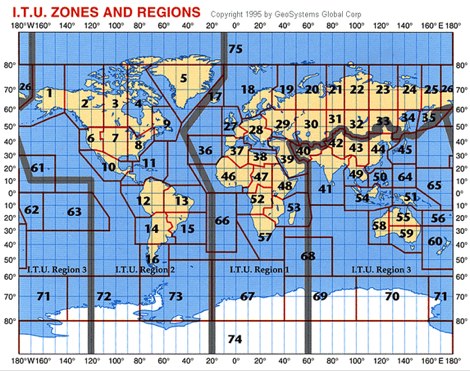
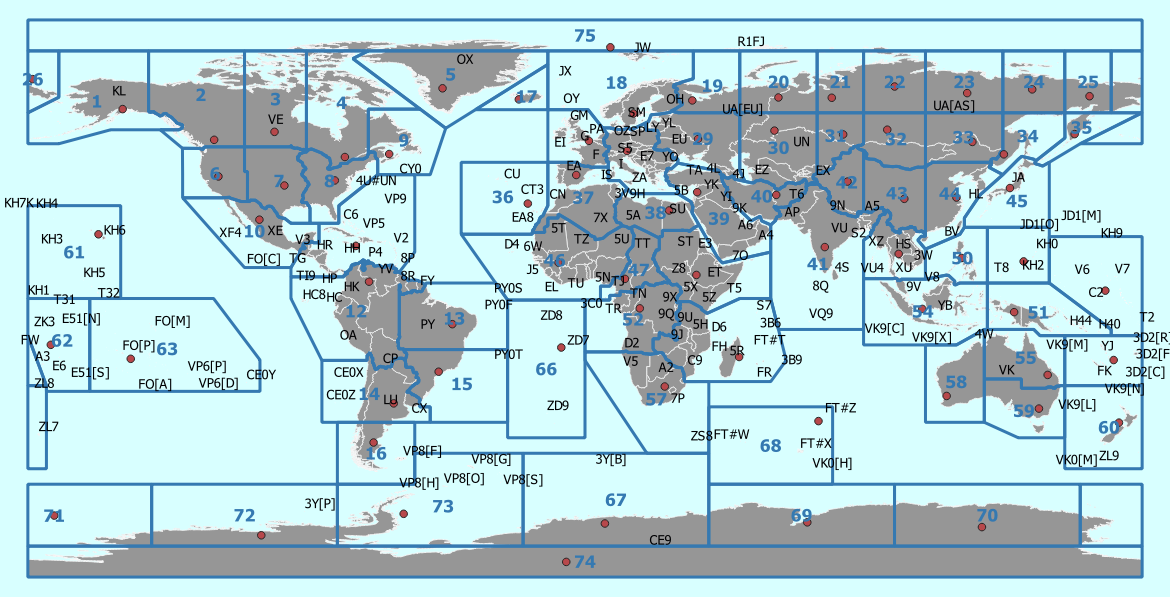
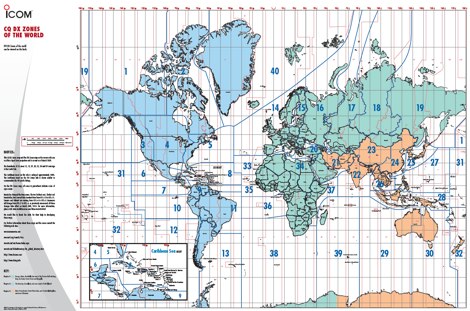
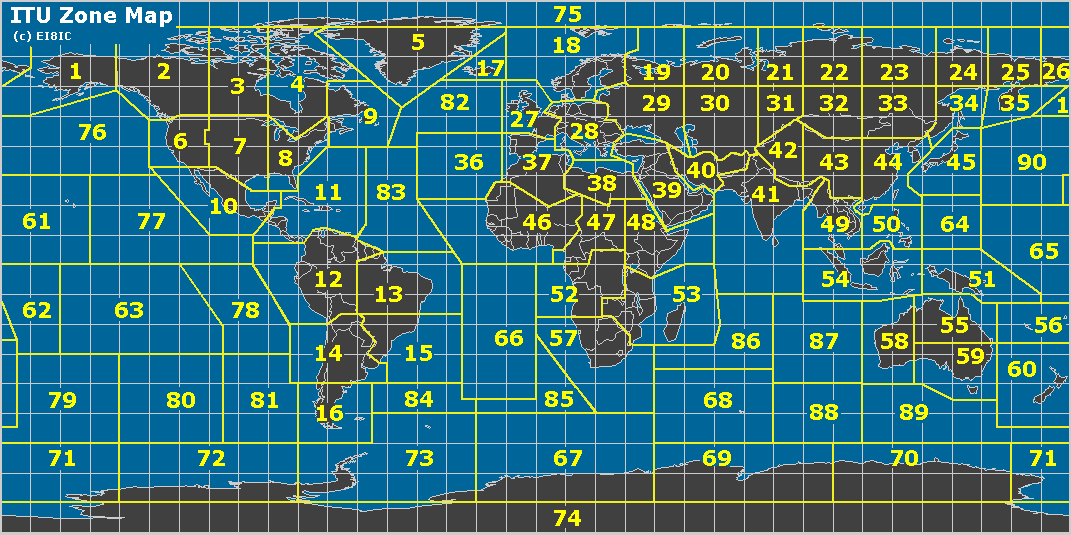
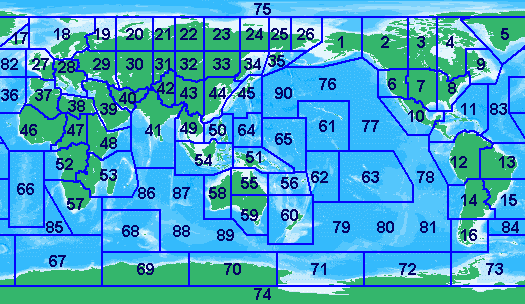
The Three Zones: A Geographical and Regulatory Framework
The ITU Zone Map divides the world into:
- Region 1: Encompassing Europe, Africa, parts of the Middle East, and Northern Asia.
- Region 2: Covering North and South America, as well as parts of the Caribbean and Greenland.
- Region 3: Comprising Asia, Australia, and Oceania.
Each region has its own set of regulations and frequency allocation plans, reflecting the specific needs and technological advancements of its member states. This division ensures that radio frequency spectrum is utilized efficiently and avoids interference between different countries and regions.
Frequency Allocation and its Importance
The ITU Zone Map plays a critical role in frequency allocation, a complex process that involves dividing the radio spectrum into specific bands for different purposes. These bands are allocated to various services, including broadcasting, mobile communications, satellite communications, and scientific research.
Benefits of the ITU Zone Map
The ITU Zone Map provides several benefits, including:
- Harmonization and Standardization: It establishes a common framework for frequency allocation, promoting interoperability and minimizing interference between different countries and regions.
- Efficient Spectrum Utilization: By dividing the spectrum into distinct bands, the map ensures that frequencies are allocated to the most suitable services, maximizing their utilization.
- International Cooperation: The map fosters collaboration among ITU members, facilitating the development of shared technical standards and regulatory frameworks.
- Technological Advancement: The ITU Zone Map enables the deployment of new technologies by providing a clear understanding of available frequencies and regulatory requirements.
Practical Applications of the ITU Zone Map
The ITU Zone Map has numerous practical applications in various sectors:
- Telecommunications Industry: Telecommunications companies use the map to determine available frequencies for their services, ensuring compliance with local regulations and maximizing their network coverage.
- Broadcasting: Broadcasters rely on the map to obtain licenses and operate within allocated frequency bands, ensuring clear reception and avoiding interference.
- Satellite Communications: Satellite operators use the map to plan their satellite constellations and ensure that their operations comply with international regulations.
- Scientific Research: Researchers utilize the map to obtain licenses for specific frequency bands, facilitating scientific experiments and data collection.
Understanding the ITU Zone Map: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why is the ITU Zone Map divided into three regions?
A: The division into three regions reflects the diverse needs and technological advancements of different parts of the world. This approach ensures that frequency allocation plans are tailored to the specific requirements of each region, optimizing spectrum utilization and promoting international cooperation.
Q2: How does the ITU Zone Map impact frequency allocation?
A: The map serves as a guide for allocating frequency bands to different services. It defines specific frequency ranges that are available for use in each region, ensuring that services operate within designated bands and minimize interference.
Q3: Can countries within the same ITU region use the same frequencies?
A: While countries within the same region share a common frequency allocation plan, they may have specific regulations regarding the use of specific frequencies. It is essential for telecommunications companies and other stakeholders to consult with national authorities to understand local regulations.
Q4: How can I access the ITU Zone Map and its related information?
A: The ITU website provides access to the Zone Map, frequency allocation tables, and other relevant documents. It also offers a range of resources, including publications, technical reports, and online tools, to support users in understanding and applying the map.
Q5: What are the implications of the ITU Zone Map for the future of telecommunications?
A: As technology evolves, the demand for radio spectrum continues to grow. The ITU Zone Map will play a crucial role in managing this demand, facilitating the deployment of new technologies and ensuring efficient spectrum utilization. The ITU is continuously reviewing and updating the map to address emerging technologies and ensure its relevance in the future.
Tips for Navigating the ITU Zone Map
- Understand the Scope: Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations and frequency allocation plans for your region.
- Consult National Authorities: Contact your country’s national telecommunications authority for guidance on local regulations and licensing procedures.
- Utilize Online Resources: Access the ITU website for detailed information, including frequency allocation tables and technical documents.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of updates and changes to the ITU Zone Map and related regulations to ensure compliance.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Global Telecommunications
The ITU Zone Map serves as a cornerstone of global telecommunications, providing a framework for frequency allocation, promoting international cooperation, and facilitating technological advancement. Understanding the map’s principles and applications is crucial for organizations and individuals involved in various telecommunications sectors. By adhering to the map’s guidelines and embracing its principles, the global community can ensure the efficient and sustainable development of telecommunications infrastructure, driving innovation and connecting people across the world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding the ITU Zone Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!