The Limpopo River: A Lifeline Through Southern Africa
Related Articles: The Limpopo River: A Lifeline Through Southern Africa
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Limpopo River: A Lifeline Through Southern Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Limpopo River: A Lifeline Through Southern Africa
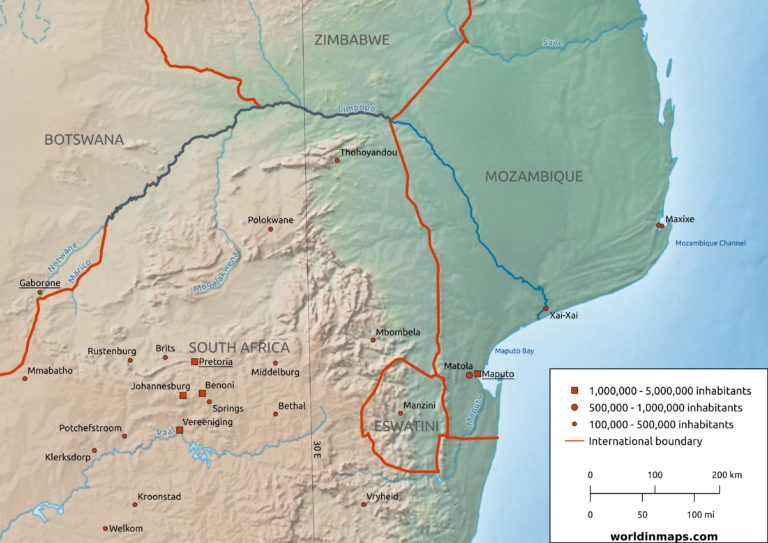
The Limpopo River, a vital artery of southern Africa, winds its way for over 1,750 kilometers, tracing a serpentine path through South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique. This majestic river, often referred to as the "Crocodile River" in its upper reaches, is a testament to the region’s diverse geography and rich history. Understanding the Limpopo’s course, its tributaries, and its ecological significance provides valuable insights into the intricate web of life and human activity that it sustains.
A Journey Through Diverse Landscapes:
The Limpopo River originates in the Drakensberg Mountains of South Africa, specifically in the Mpumalanga province. Its source is a small spring known as the "Limpopo Spring," nestled amidst the towering peaks. From this humble beginning, the river embarks on a journey that takes it through a variety of landscapes, each with its own unique characteristics.
The Upper Limpopo:
The upper reaches of the Limpopo are characterized by steep gradients and rocky terrain. The river flows through the mountainous regions of South Africa and Zimbabwe, carving its way through narrow gorges and cascading over waterfalls. This section of the river is known for its dramatic beauty and challenging rapids, attracting adventure seekers and kayakers alike.
The Middle Limpopo:
As the Limpopo flows into Botswana, it enters a more gentle, meandering course. The riverbed widens, and the surrounding landscape transitions from mountainous to a more open savanna. This section of the river is characterized by extensive floodplains, which are vital for grazing animals and support a rich ecosystem.
The Lower Limpopo:
The lower reaches of the Limpopo flow through Mozambique, where the river becomes increasingly wide and slow-moving. The river flows through a vast delta, a network of channels and lagoons, before finally emptying into the Indian Ocean. This section of the river is known for its rich biodiversity, including diverse fish species and a variety of birdlife.
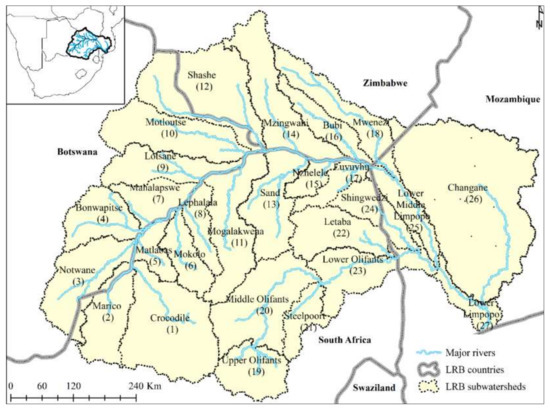
Tributaries and the River System:
The Limpopo River is fed by numerous tributaries, each adding its own unique characteristics to the overall river system. Some of the most notable tributaries include:
- The Marico River: This tributary joins the Limpopo in South Africa, contributing a significant volume of water to the main river.
- The Shashe River: Originating in Botswana, the Shashe River flows into the Limpopo, forming a significant tributary in the middle reaches.
- The Nuanetsi River: This tributary originates in Zimbabwe and joins the Limpopo in Mozambique, adding a significant volume of water to the lower reaches.
The Limpopo River and its tributaries form a complex network of waterways that play a vital role in the region’s ecosystem. They provide water for human use, support a diverse range of wildlife, and help to regulate the local climate.
Ecological Significance:
The Limpopo River is a vital lifeline for the diverse ecosystems it traverses. The river’s floodplains support a rich tapestry of life, including grazing animals such as zebras, wildebeest, and elephants. The river also provides habitat for a variety of fish species, including catfish, barbel, and tilapia. The Limpopo’s riparian zones, the areas along the riverbanks, are home to a diverse array of plants and animals, including acacia trees, reeds, and crocodiles.
Human Impact and Conservation:
The Limpopo River has been a source of life and sustenance for centuries, but human activities have also had a significant impact on its health. Overgrazing, deforestation, and agricultural practices have led to soil erosion and sedimentation, which can impact the river’s flow and water quality. Pollution from industrial and urban areas also poses a threat to the river’s health.
Recognizing the importance of the Limpopo River, various conservation efforts have been implemented to protect and restore its health. These efforts include:
- Establishment of national parks and protected areas: These areas help to preserve the river’s natural ecosystems and provide refuge for wildlife.
- Water management strategies: These strategies aim to ensure sustainable use of the river’s water resources, balancing human needs with the needs of the environment.
- Pollution control measures: These measures aim to reduce the amount of pollutants entering the river, protecting its water quality and the health of its ecosystems.
Economic Importance:
The Limpopo River plays a vital role in the economies of the countries it traverses. The river provides water for irrigation, supporting agriculture in the region. The river also serves as a transportation route, facilitating trade and movement of goods. Tourism, particularly fishing and wildlife viewing, is another important economic activity associated with the Limpopo River.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Limpopo River faces a number of challenges, including:
- Water scarcity: The region experiences periods of drought, which can lead to water shortages and conflict over water resources.
- Pollution: Industrial and urban pollution pose a threat to the river’s health and the well-being of the communities that depend on it.
- Climate change: Climate change is expected to exacerbate water scarcity and increase the frequency and intensity of floods, posing significant challenges to the river’s ecosystem and human populations.
Despite these challenges, the Limpopo River also presents opportunities for sustainable development. By implementing sound water management practices, promoting sustainable agriculture, and investing in renewable energy sources, the countries that share the Limpopo River can work together to ensure a healthy and prosperous future for the river and its people.
FAQs about the Limpopo River:
Q: Where does the Limpopo River start and end?
A: The Limpopo River originates in the Drakensberg Mountains of South Africa and flows into the Indian Ocean in Mozambique.
Q: What countries does the Limpopo River flow through?
A: The Limpopo River flows through South Africa, Botswana, Zimbabwe, and Mozambique.
Q: What are some of the major tributaries of the Limpopo River?
A: Some of the most notable tributaries include the Marico River, the Shashe River, and the Nuanetsi River.
Q: What is the ecological significance of the Limpopo River?
A: The Limpopo River supports a diverse range of wildlife, including grazing animals, fish species, and birds. It also plays a vital role in regulating the local climate.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Limpopo River?
A: The Limpopo River faces challenges such as water scarcity, pollution, and the impacts of climate change.
Q: What are some of the opportunities for sustainable development associated with the Limpopo River?
A: The Limpopo River presents opportunities for sustainable development through sound water management practices, sustainable agriculture, and renewable energy sources.
Tips for Exploring the Limpopo River:
- Visit Kruger National Park: This world-renowned park offers opportunities to experience the diverse wildlife and ecosystems of the Limpopo River.
- Take a river cruise: Several companies offer river cruises along the Limpopo, providing a unique perspective on the river’s beauty and wildlife.
- Go kayaking or canoeing: The Limpopo River offers opportunities for kayaking and canoeing, allowing you to explore the river’s rapids and scenic landscapes.
- Learn about local communities: The Limpopo River is home to numerous communities that have a deep connection to the river. Learning about their culture and traditions can enhance your understanding of the river’s importance.
Conclusion:
The Limpopo River is a vital artery of southern Africa, connecting diverse landscapes and supporting a rich tapestry of life. Its journey through mountains, savannas, and deltas is a testament to the region’s beauty and resilience. Understanding the Limpopo’s course, its tributaries, and its ecological significance is crucial for ensuring its continued health and the well-being of the communities that depend on it. By embracing sustainable practices and working together to protect this vital resource, we can ensure that the Limpopo River continues to flow for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Limpopo River: A Lifeline Through Southern Africa. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!