The Minnesota Senate Districts Map: A Blueprint for Representation
Related Articles: The Minnesota Senate Districts Map: A Blueprint for Representation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Minnesota Senate Districts Map: A Blueprint for Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Minnesota Senate Districts Map: A Blueprint for Representation
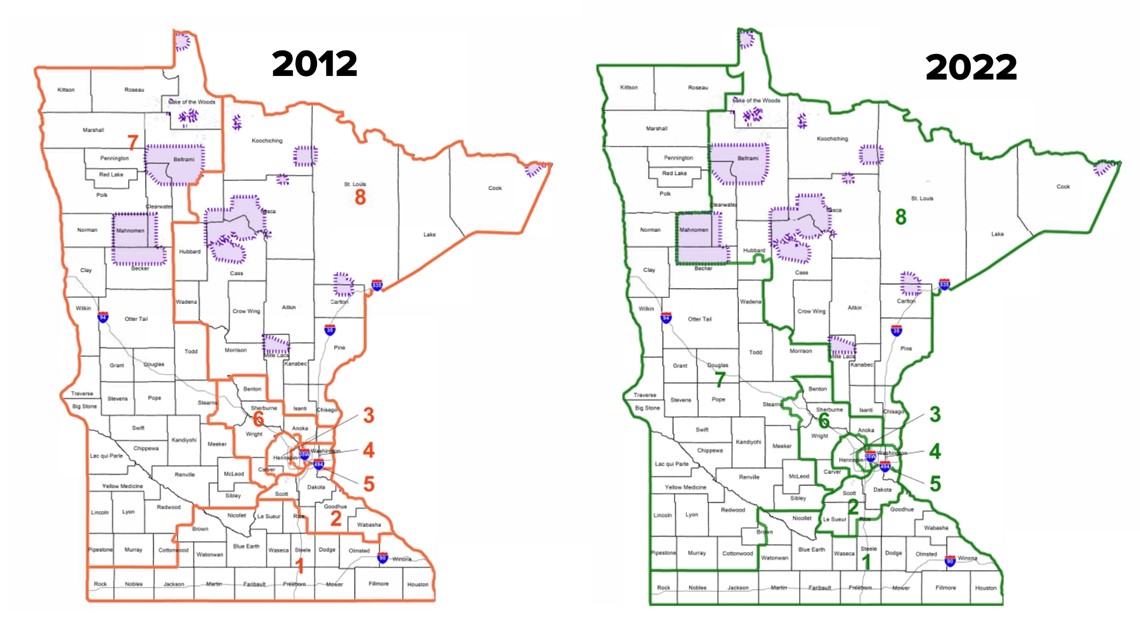
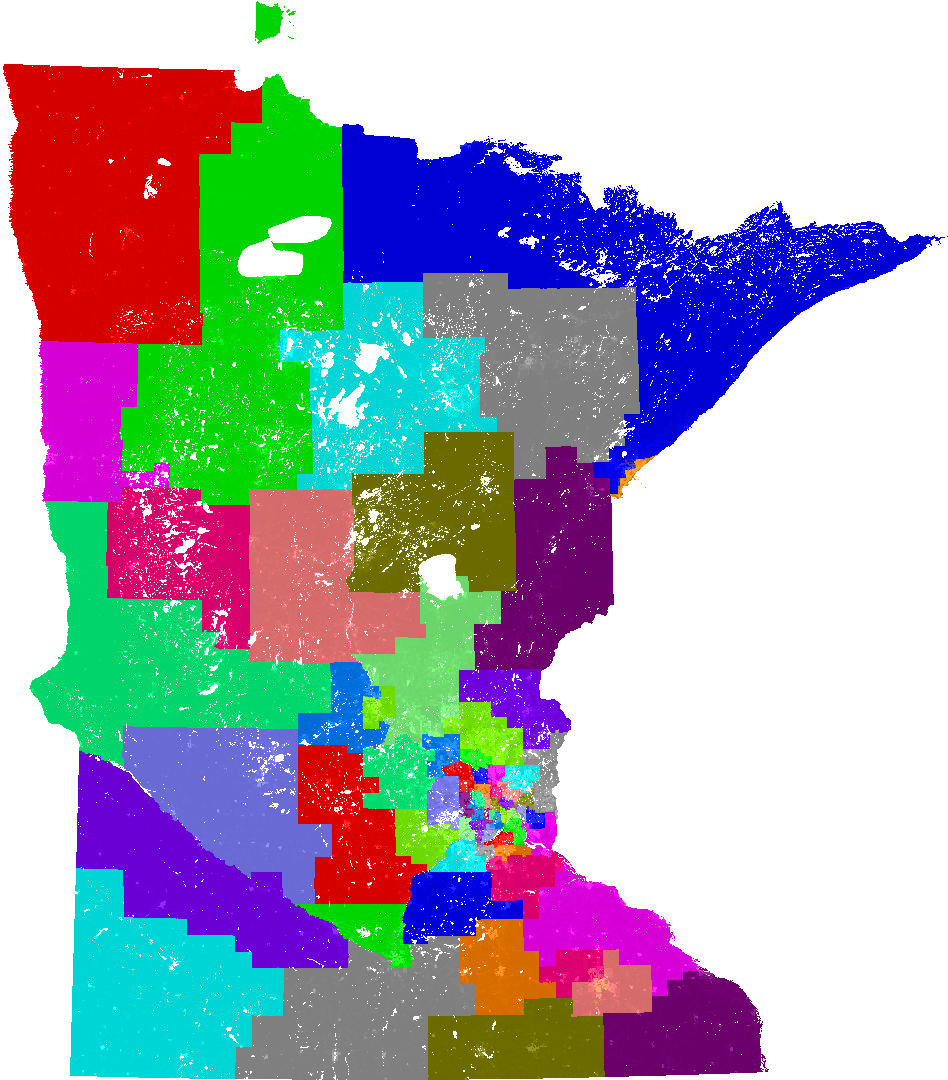
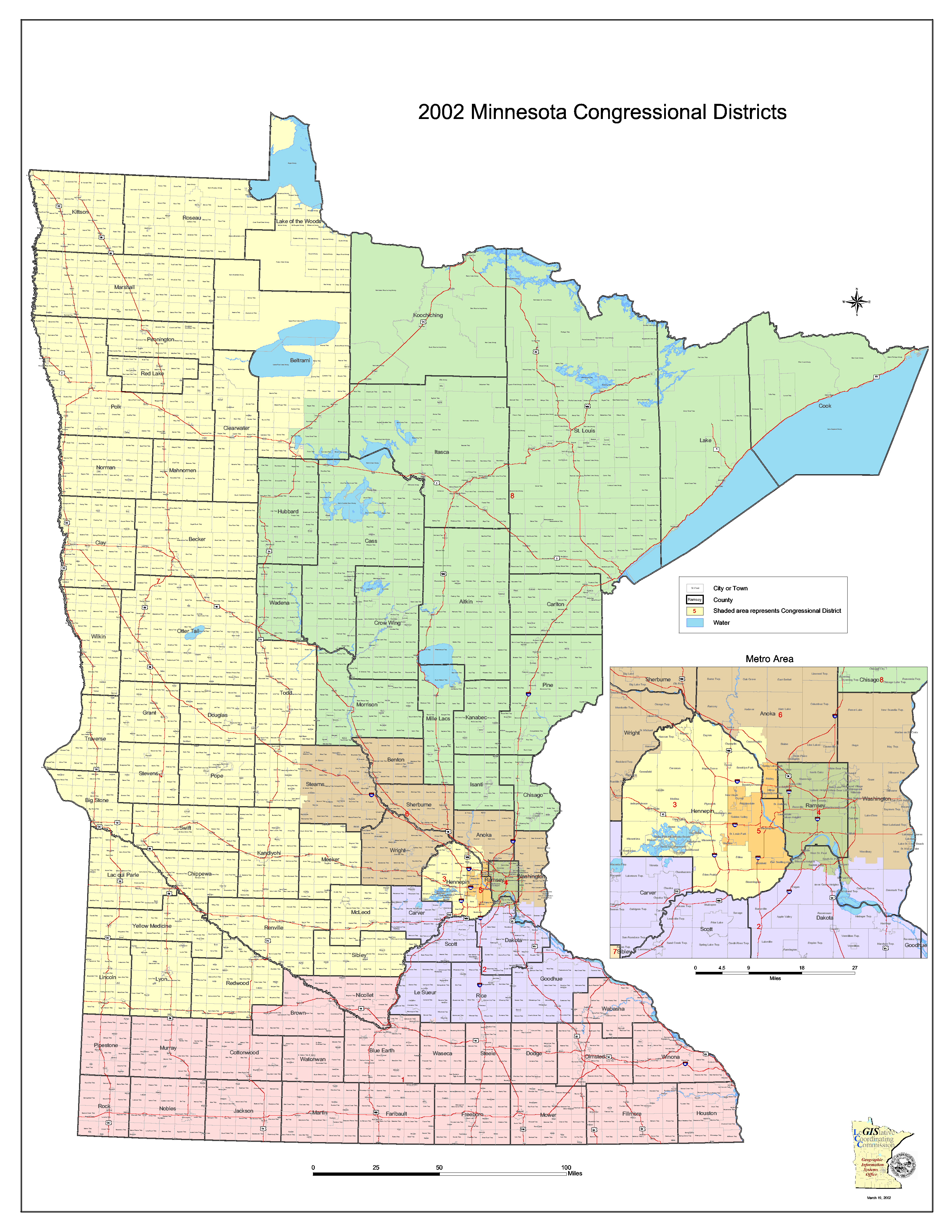
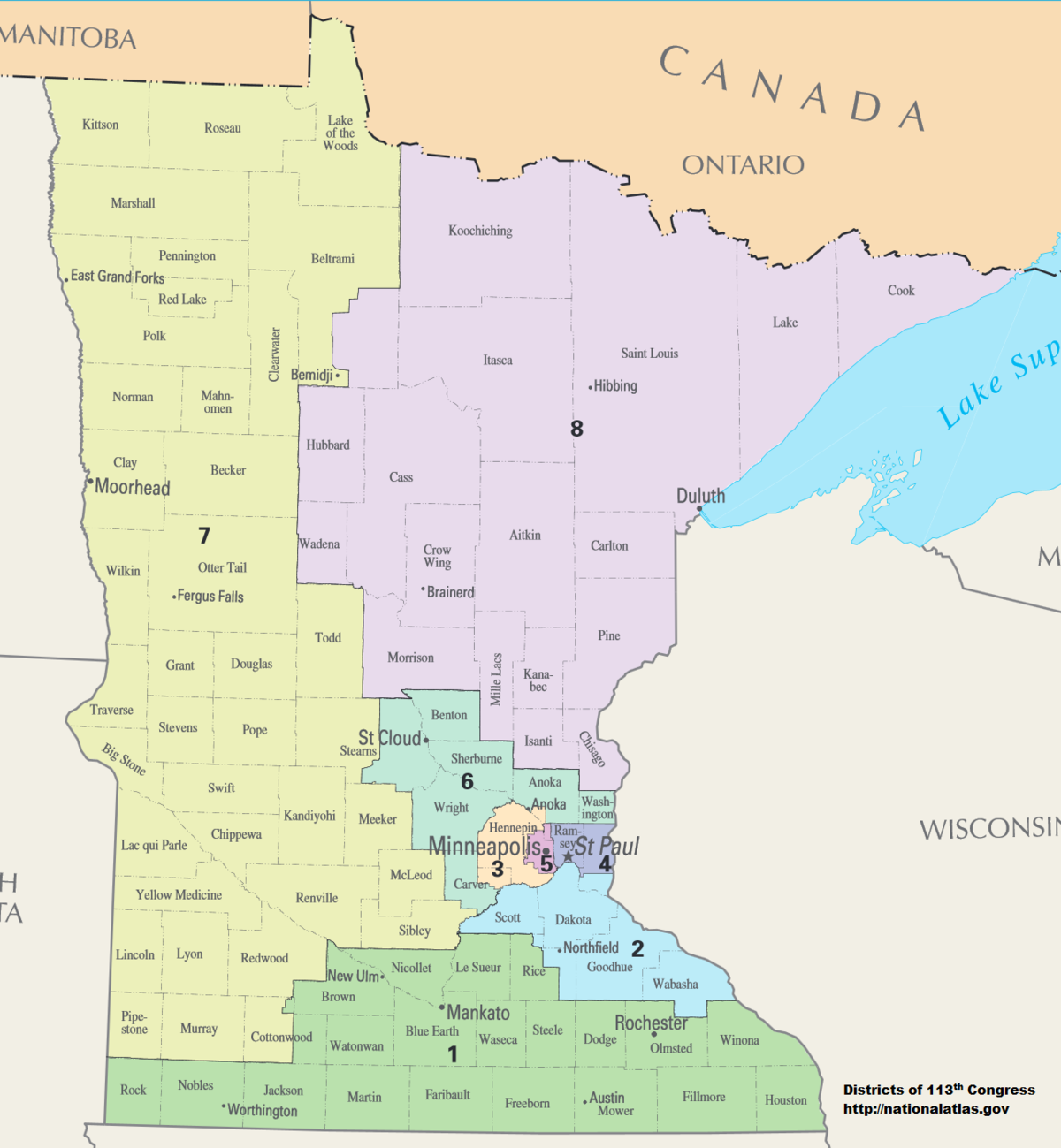
The Minnesota Senate Districts Map is a vital document that underpins the state’s political landscape. It outlines the geographic boundaries of each of the 67 districts that elect senators to the Minnesota Senate, a chamber of the state legislature. This map, subject to periodic redrawing, directly impacts the composition of the Senate and, consequently, the legislative process and policy outcomes. Understanding the map’s significance and the processes behind its creation is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of Minnesota’s political system.
The Significance of District Boundaries
The drawing of district boundaries, known as redistricting, is a complex and politically charged process. Its significance stems from its direct influence on:
- Representation: The boundaries of a district determine which voters will elect a specific senator. This, in turn, influences the demographics and interests represented by that senator.
- Political Power: The balance of power in the Senate can be significantly impacted by how districts are drawn. Strategic manipulation of boundaries can lead to advantages for certain political parties or groups.
- Policy Outcomes: The composition of the Senate, shaped by the district map, directly affects the legislative agenda and the policies that are prioritized and enacted.
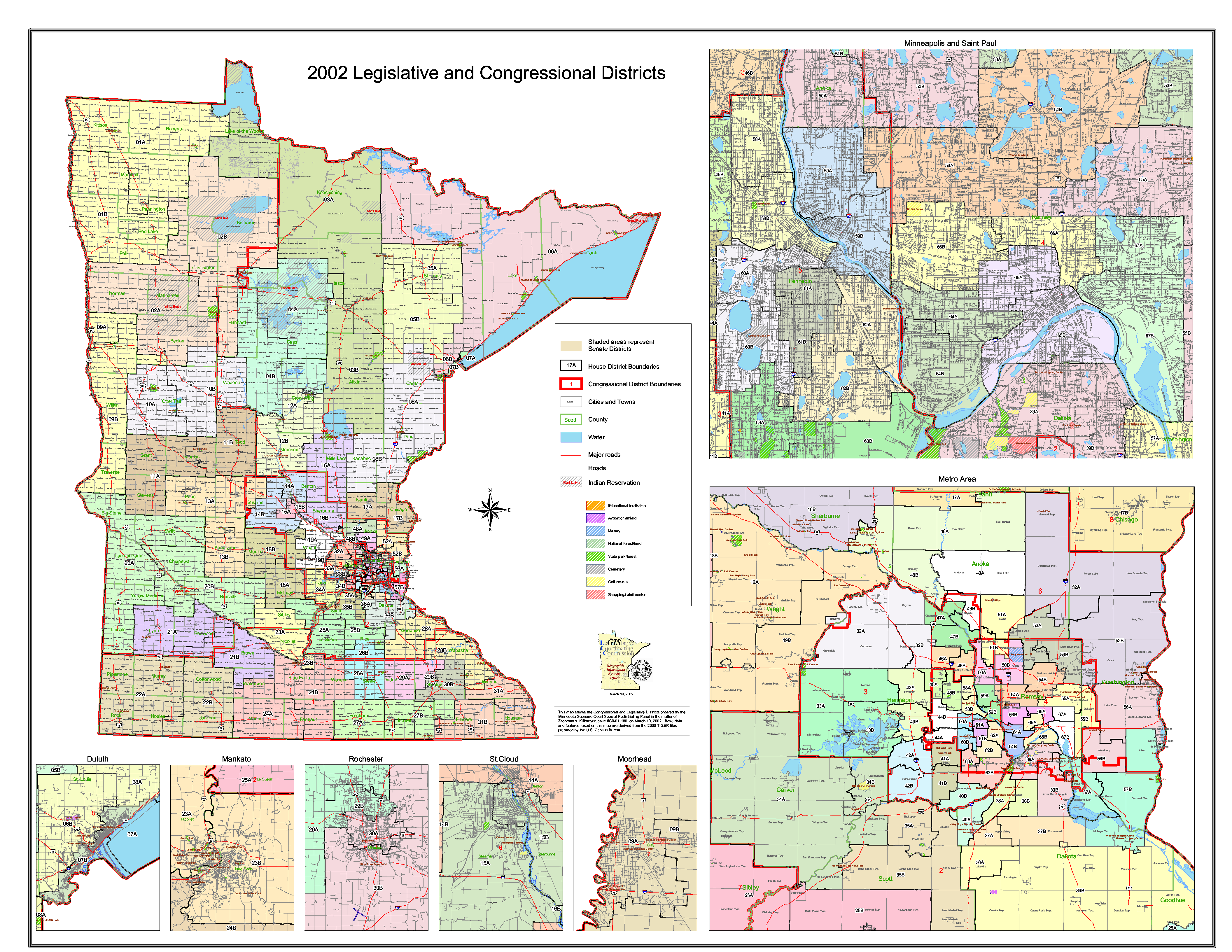
The Redistricting Process in Minnesota
Minnesota’s redistricting process is governed by the Minnesota Constitution and state laws. The process unfolds in the following steps:
- Data Collection: The Minnesota Legislative Redistricting Commission gathers data on population, demographics, and geographic features. This data is crucial for ensuring that districts are roughly equal in population, as required by the "one person, one vote" principle.
- District Design: The Commission, composed of members from both major political parties, develops proposed maps for the Senate and House districts. These maps are subject to public hearings and input from interested parties.
- Legislative Approval: The proposed maps are then presented to the Minnesota Legislature for consideration. The Legislature can amend the proposed maps, but ultimately must approve a final version.
- Judicial Review: If there are disputes about the legality or fairness of the approved maps, they can be challenged in court. The Minnesota Supreme Court has the final say in resolving any disputes.
The Importance of Fair Redistricting
The integrity of the redistricting process is paramount for ensuring fair and representative government. Key principles that guide fair redistricting include:
- Population Equality: Districts should have roughly equal populations to ensure that each voter’s voice carries equal weight.
- Compactness: Districts should be geographically cohesive and avoid sprawling or oddly shaped boundaries.
- Respect for Communities of Interest: Districts should avoid dividing communities with shared interests or cultural ties.
- Minimizing Partisan Gerrymandering: The drawing of districts should not be manipulated to favor one political party over another.
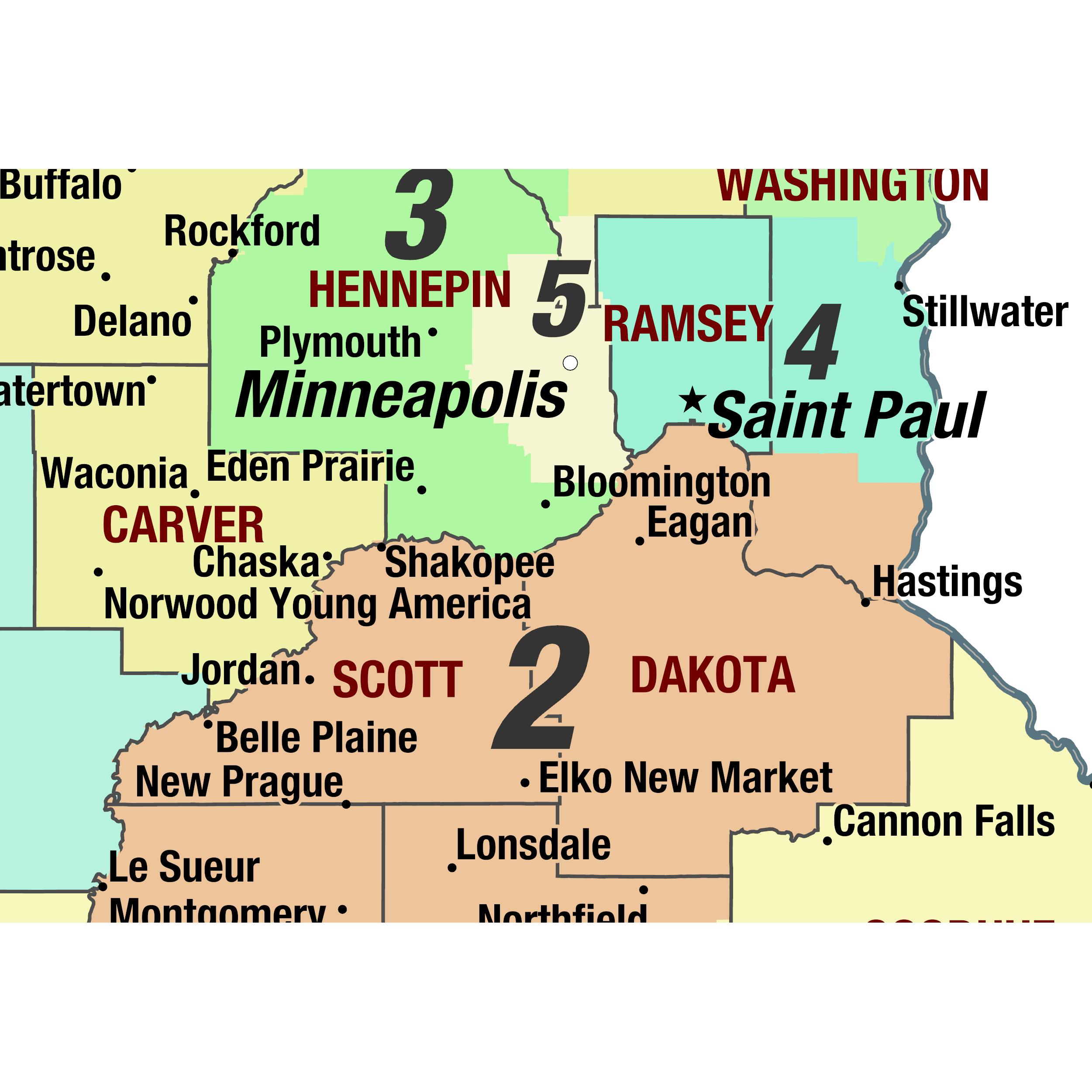
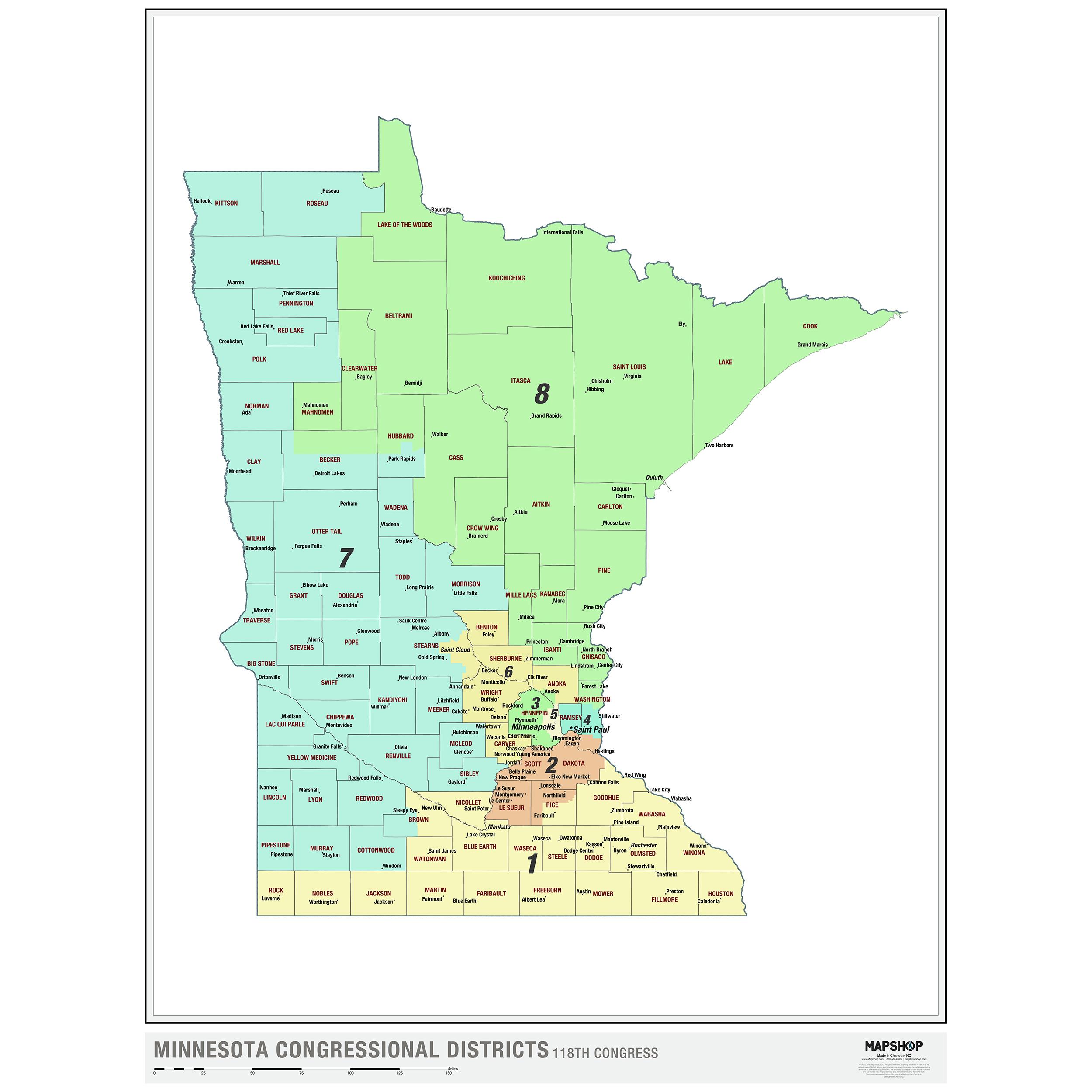
The Current Minnesota Senate Districts Map
The current Senate Districts Map, adopted in 2012, reflects the outcome of the most recent redistricting cycle. It is a complex map with a mix of urban, suburban, and rural districts, reflecting the diverse geography and demographics of Minnesota.
Understanding the Map: Key Considerations
When examining the Minnesota Senate Districts Map, it is essential to consider:
- District Numbers: Each district is assigned a unique number for identification purposes.
- District Boundaries: The lines on the map delineate the geographic boundaries of each district.
- Population Distribution: The map can be analyzed to understand how population density varies across different districts.
- Political Leanings: Historical voting data can be used to assess the typical political leanings of different districts.
- Demographic Factors: The map can be overlaid with demographic data to understand the racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic composition of each district.
FAQs about the Minnesota Senate Districts Map
Q: How often is the map redrawn?
A: The Minnesota Senate Districts Map is redrawn every ten years, following the decennial census.
Q: Who is responsible for drawing the map?
A: The Minnesota Legislative Redistricting Commission is responsible for drawing the map, with input from the legislature and the public.
Q: How can I find the map?
A: The Minnesota Legislative Redistricting Commission website provides access to the official map and related data.
Q: What are the consequences of unfair redistricting?
A: Unfair redistricting can lead to underrepresentation of certain groups, distortion of political power, and erosion of public trust in government.
Tips for Understanding the Minnesota Senate Districts Map
- Explore the map online: Utilize interactive maps and tools provided by the Minnesota Legislative Redistricting Commission to gain a deeper understanding of district boundaries and demographics.
- Compare maps over time: Analyze how district boundaries have changed over different redistricting cycles to understand historical trends and their potential impact.
- Engage in public discussions: Participate in public hearings and discussions about redistricting to voice your concerns and contribute to the process.
Conclusion: The Map as a Foundation for Democracy
The Minnesota Senate Districts Map is more than just a geographic representation; it serves as a foundation for the state’s democratic processes. Understanding its creation, its impact on representation, and the principles that guide its redrawing is crucial for ensuring a fair and representative political system. By engaging in informed discussion and actively participating in the redistricting process, citizens can contribute to shaping a map that reflects the diverse interests and voices of all Minnesotans.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Minnesota Senate Districts Map: A Blueprint for Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!