The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe
Related Articles: The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe

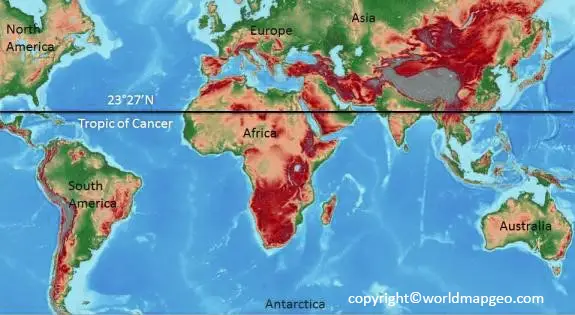
The Tropic of Cancer, an imaginary line circling the Earth at approximately 23.5 degrees north latitude, is a significant geographical feature that plays a vital role in shaping the planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human civilizations. This line, often depicted on world maps as a dotted or dashed line, serves as a marker for a crucial transition zone in Earth’s geography and climate.
Understanding the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer derives its name from the fact that when the sun reaches its northernmost declination, on the summer solstice around June 21st, it appears directly overhead at noon for locations situated on this line. The sun’s rays strike the Earth at a near-vertical angle, resulting in the highest solar insolation and the longest daylight hours within the region.
This geographical marker is a consequence of the Earth’s axial tilt, which is approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt causes the sun’s rays to fall at different angles on different parts of the Earth throughout the year, leading to the varying seasons.
The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe
The Tropic of Cancer traverses through a diverse range of landmasses and oceans, impacting the climates and ecosystems of these regions. Its influence is evident in:
-
Climate: The region lying between the Tropic of Cancer and the Equator experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. This region is often referred to as the "tropics," and it is home to some of the most biodiverse ecosystems on Earth.
-
Agriculture: The tropical climate along the Tropic of Cancer supports a wide range of agricultural activities. The abundant rainfall and warm temperatures allow for the cultivation of a variety of crops, including rice, sugarcane, coffee, and tropical fruits.
-
Biodiversity: The Tropic of Cancer is home to a remarkable array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region. The tropical rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs found within this zone are renowned for their biodiversity, playing a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance of the planet.
-
Human Civilization: The Tropic of Cancer has played a significant role in the development of human civilizations. The fertile lands and abundant resources found in the tropics have attracted people for centuries, leading to the emergence of diverse cultures and societies.
Exploring the Impact of the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer has a profound impact on various aspects of life on Earth, influencing:
-
Weather Patterns: The Tropic of Cancer is a key factor in shaping global weather patterns. The intense solar radiation received at this latitude drives the formation of large-scale atmospheric circulation patterns, including the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) and the trade winds. These patterns influence rainfall distribution, temperature variations, and the occurrence of extreme weather events.
-
Ocean Currents: The Tropic of Cancer influences the flow of ocean currents, which play a crucial role in regulating global temperatures and distributing nutrients. The warm currents flowing along the Tropic of Cancer contribute to the warm, humid climate of the region, while the cold currents flowing along the eastern coasts of continents bring cooler temperatures and nutrient-rich waters to these areas.
-
Ecosystems: The Tropic of Cancer is a key boundary for various ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, savannas, and deserts. The unique climatic conditions along this line support a wide range of plant and animal species, contributing to the remarkable biodiversity of the region.
-
Human Societies: The Tropic of Cancer has played a significant role in the development of human societies. The fertile lands and abundant resources found in the tropics have attracted people for centuries, leading to the emergence of diverse cultures and societies. The region has been a center of trade, innovation, and cultural exchange for thousands of years.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What countries does the Tropic of Cancer pass through?
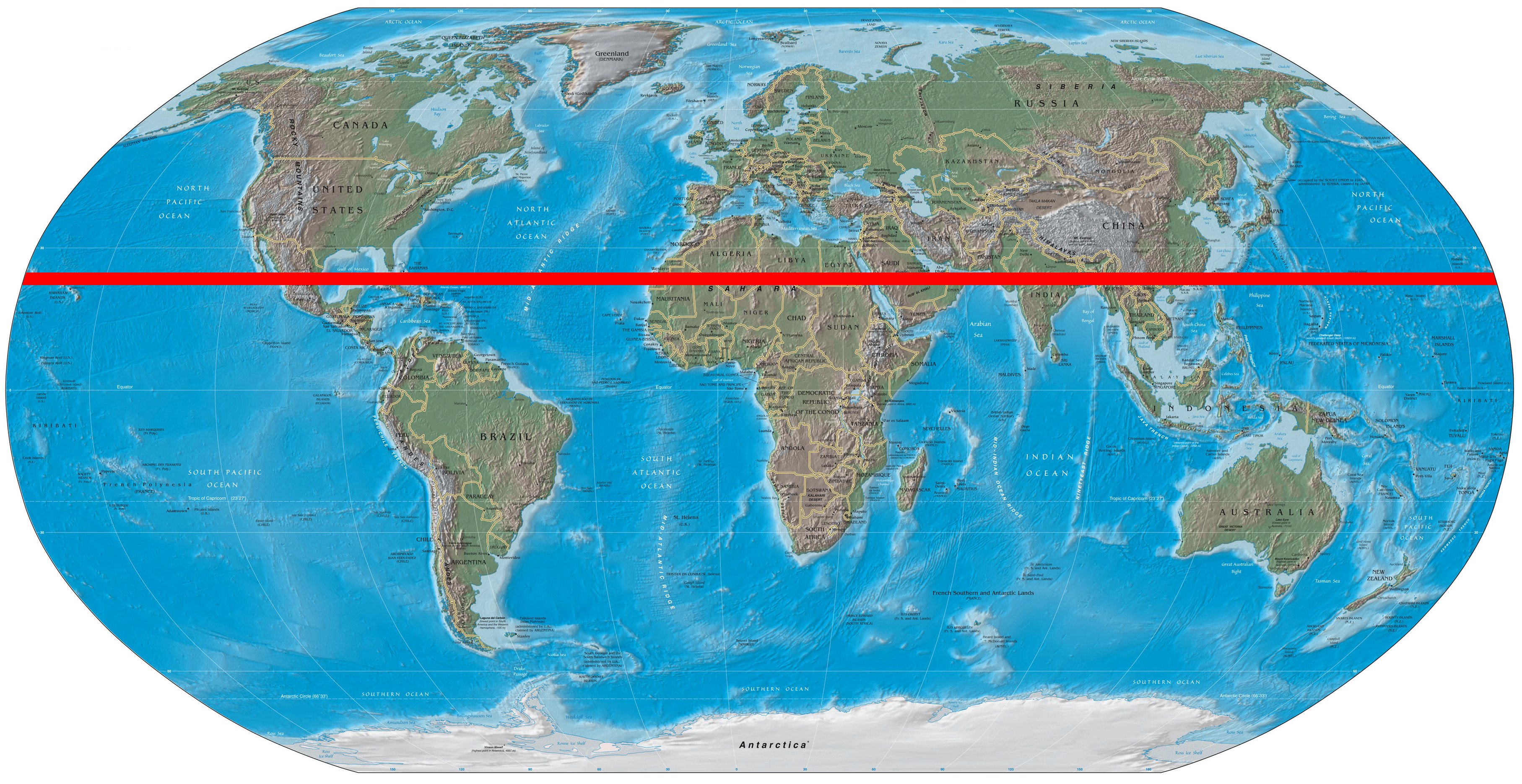
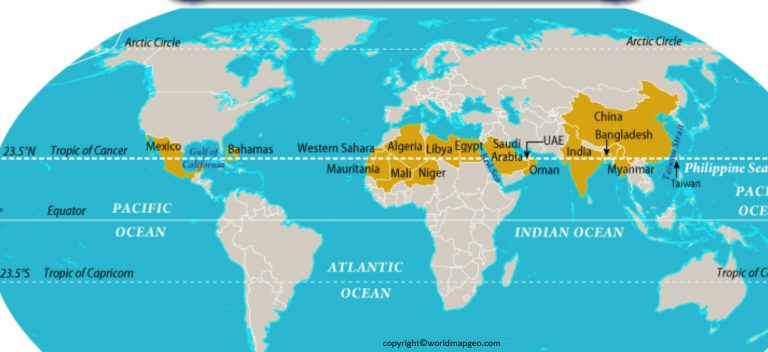
A: The Tropic of Cancer passes through 16 countries: Mexico, Bahamas, Egypt, Libya, Algeria, Niger, Mali, Mauritania, Western Sahara, Morocco, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, China, Taiwan, and the United States (Hawaii).
Q: What are the main characteristics of the climate along the Tropic of Cancer?
A: The climate along the Tropic of Cancer is characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity. The region experiences a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons.
Q: What are some of the major ecosystems found along the Tropic of Cancer?
A: The Tropic of Cancer is home to a variety of ecosystems, including tropical rainforests, savannas, deserts, and coral reefs. These ecosystems are characterized by their high biodiversity and unique adaptations to the tropical climate.
Q: What are some of the challenges faced by people living along the Tropic of Cancer?
A: People living along the Tropic of Cancer face a number of challenges, including deforestation, climate change, poverty, and conflict. These challenges are exacerbated by the region’s high population density, limited resources, and vulnerability to extreme weather events.
Tips for Understanding the Tropic of Cancer
- Use a world map: A world map is an essential tool for understanding the location and significance of the Tropic of Cancer. Locate the line on the map and trace its path across the globe.
- Explore the region: If you have the opportunity, visit countries located along the Tropic of Cancer. Experience the diverse cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems of this region firsthand.
- Learn about the climate: Research the climate patterns and weather conditions along the Tropic of Cancer. Understand how the region’s unique climate influences its ecosystems and human societies.
- Study the ecosystems: Learn about the different ecosystems found along the Tropic of Cancer, such as tropical rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs. Explore the diversity of plant and animal life in these ecosystems.
- Engage in environmental conservation: The Tropic of Cancer is a region of immense ecological value. Support efforts to conserve the region’s biodiversity and protect its ecosystems from degradation.
Conclusion
The Tropic of Cancer is more than just an imaginary line on a map. It is a vital geographical feature that shapes the planet’s climate, ecosystems, and human civilizations. Understanding the significance of the Tropic of Cancer is crucial for appreciating the interconnectedness of the Earth’s systems and for addressing the challenges facing the region. By learning about this important geographical marker, we can gain a deeper understanding of our planet and its diverse inhabitants.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Tropic of Cancer: A Lifeline Across the Globe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!