Understanding Michigan’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Related Articles: Understanding Michigan’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Michigan’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Michigan’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
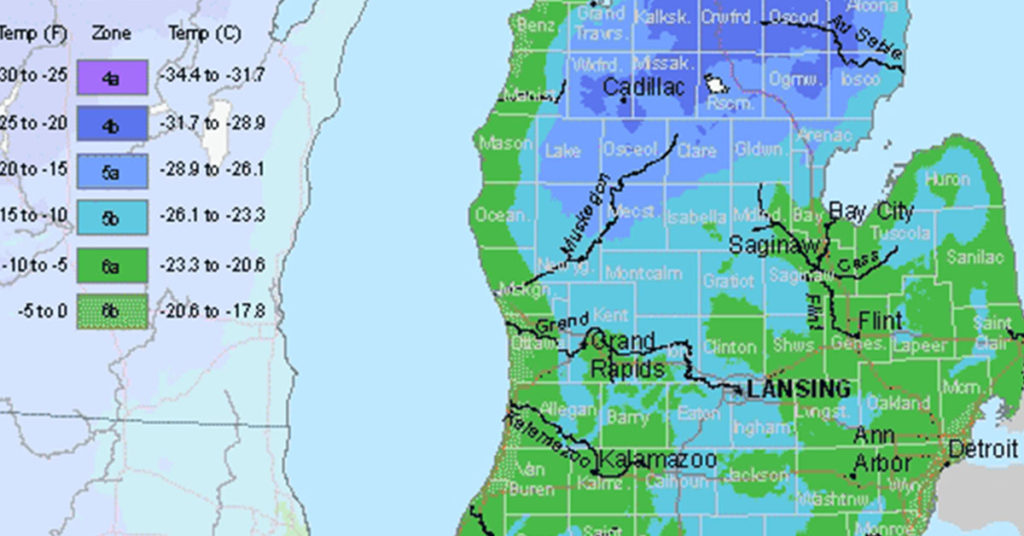
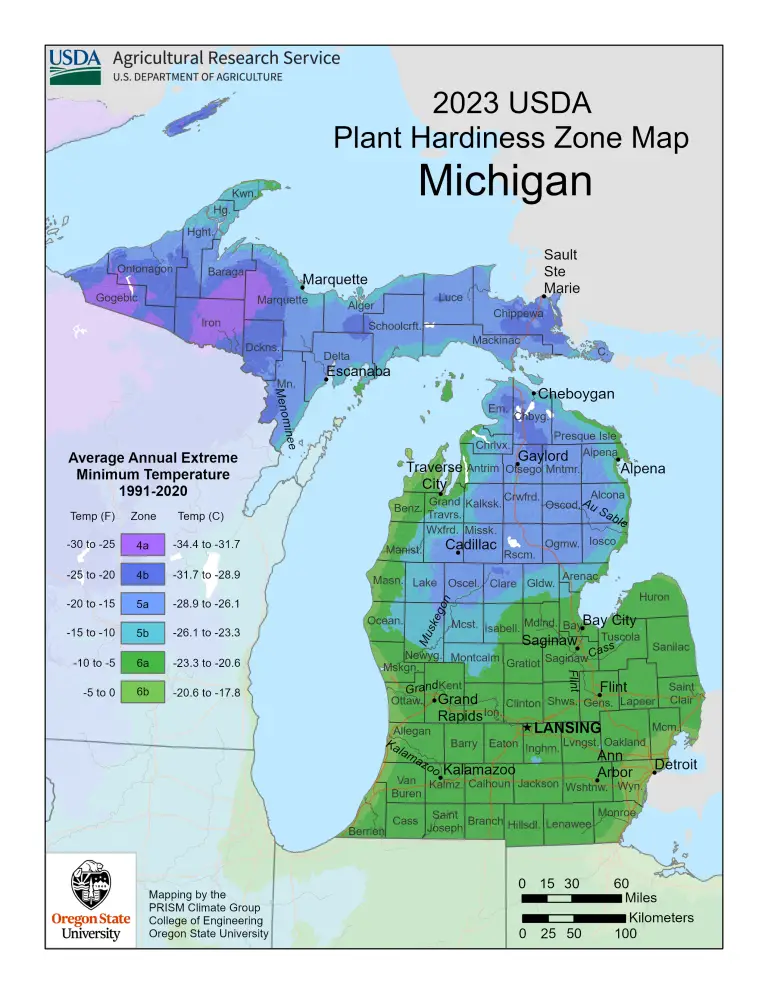
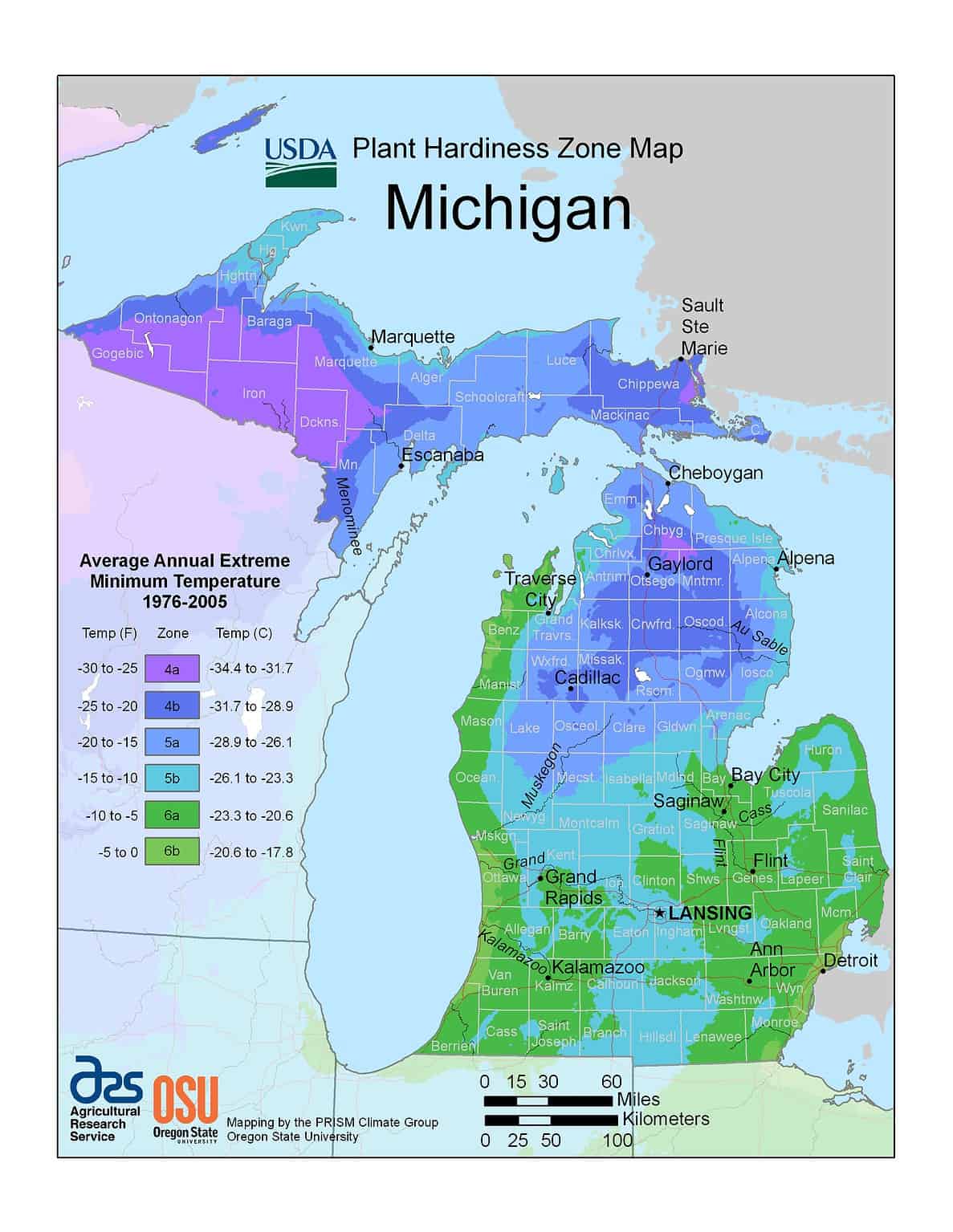
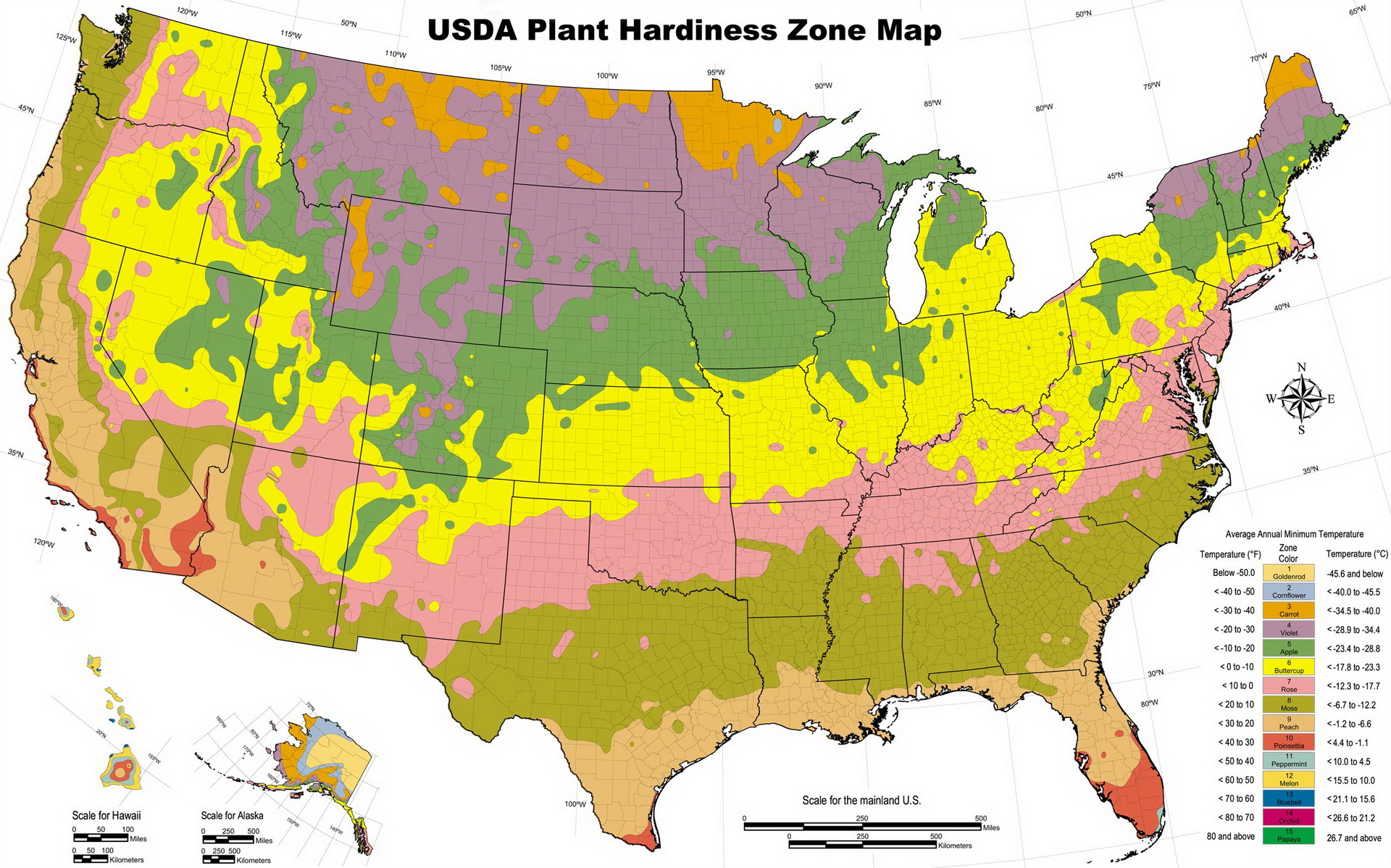
Michigan, with its diverse climate and varying microclimates, presents a unique challenge for gardeners. To navigate this landscape, the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for Michigan provides essential information for successful gardening. This map, a valuable tool for both seasoned and novice gardeners, categorizes different regions of the state based on their average minimum winter temperatures. This information enables gardeners to select plants that are likely to thrive in their specific area.
Deciphering the Zones:
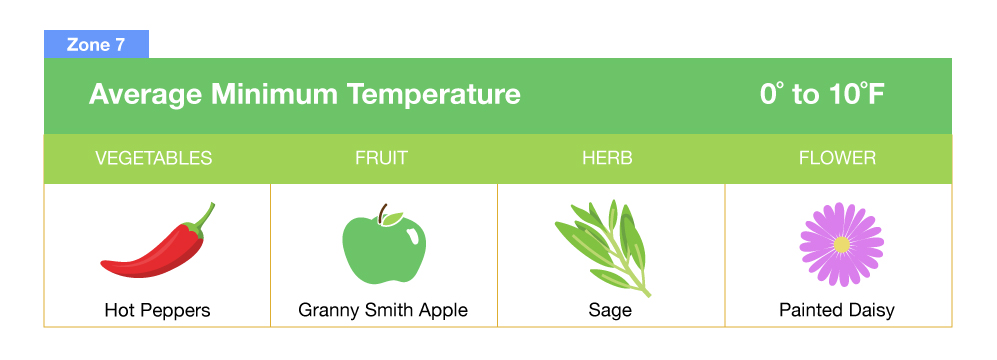
Michigan is divided into six distinct hardiness zones, ranging from Zone 4a in the Upper Peninsula to Zone 6b in the southernmost regions. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in average minimum winter temperature. For instance, Zone 4a experiences average minimum winter temperatures between -30 and -25 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 6b experiences temperatures between 0 and 5 degrees Fahrenheit.
The Significance of Zones:
Understanding the hardiness zone for your location is crucial for choosing plants that will survive and flourish. Plants within a specific zone are adapted to withstand the minimum winter temperatures of that region. Planting species outside their designated zone risks frost damage, winterkill, or failure to thrive.
Utilizing the Map:
The Michigan planting zone map is readily available online and in print. To determine your zone, simply locate your city or town on the map. The corresponding zone number will indicate the average minimum winter temperature range for your area.
Beyond the Basics:
While the hardiness zone map provides a general guideline, it’s essential to consider additional factors that can influence plant success:
- Microclimates: Within a single zone, variations in topography, elevation, proximity to water bodies, and urban heat island effects can create microclimates with slightly different temperature ranges.
- Site-Specific Conditions: Factors like soil type, drainage, sunlight exposure, and wind patterns can also impact plant growth and survival.
- Variety Selection: Within a species, different cultivars may have varying levels of cold tolerance. Researching specific cultivars for your zone is crucial for optimal plant performance.
Benefits of Using the Planting Zone Map:
- Increased Success Rates: Choosing plants suited to your zone significantly increases the chances of successful gardening.
- Reduced Costs: Avoiding unnecessary plant losses translates to financial savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: By selecting appropriate plants, gardeners contribute to a healthier environment by minimizing the need for replacements.
- Enhanced Garden Aesthetics: Thriving plants contribute to a more visually appealing and enjoyable garden.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What if my location falls on the boundary between two zones?
A: If your location falls on the boundary between two zones, consider the average minimum winter temperatures of both zones and select plants that are suitable for the colder zone.
Q: Can I plant a plant that is rated for a warmer zone than mine?
A: While it might be possible to grow a plant outside its designated zone, there is a higher risk of damage or failure. Consider choosing a variety that is known for its cold tolerance.
Q: Can I extend my gardening season by using a greenhouse or other protective structures?
A: Yes, using greenhouses, row covers, or other protective structures can extend the gardening season and allow you to grow plants that may not be suitable for your zone’s open-air climate.
Q: What are some other resources for choosing plants for my zone?
A: Local nurseries, garden centers, and extension services offer valuable resources for choosing plants suited to your region.
Tips for Successful Gardening in Michigan:
- Start Small: Begin with a few plants that are known to be successful in your zone. Gradually expand your garden as you gain experience.
- Choose the Right Location: Select a site with adequate sunlight, drainage, and soil conditions for your chosen plants.
- Prepare the Soil: Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve fertility and drainage.
- Water Wisely: Water deeply and infrequently to encourage deep root development and promote healthy growth.
- Protect from Pests and Diseases: Use integrated pest management techniques to prevent and control pests and diseases.
- Consider a Fall Garden: Extend your gardening season by planting fall-hardy crops like kale, spinach, and Brussels sprouts.
Conclusion:
The Michigan planting zone map is an invaluable tool for gardeners in Michigan. By understanding the hardiness zones and considering other factors that influence plant growth, gardeners can make informed decisions about plant selection and increase their chances of success. With careful planning and attention to detail, even novice gardeners can cultivate beautiful and productive gardens in Michigan’s diverse climate.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Michigan’s Planting Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!