Understanding the Flood Insurance Map: A Guide to Navigating Risk and Protection
Related Articles: Understanding the Flood Insurance Map: A Guide to Navigating Risk and Protection
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Flood Insurance Map: A Guide to Navigating Risk and Protection. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Flood Insurance Map: A Guide to Navigating Risk and Protection
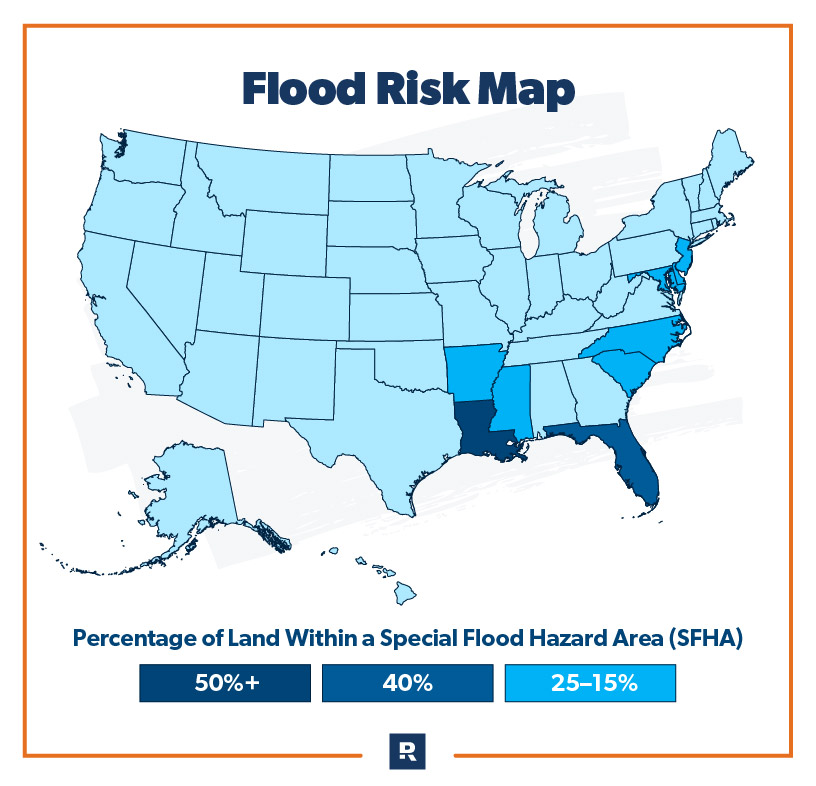
The potential for flooding is a significant concern for property owners across the United States. Flooding can occur due to various factors, including heavy rainfall, overflowing rivers, storm surges, and coastal erosion. To mitigate these risks and provide financial protection, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) developed the Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM). This comprehensive tool serves as a vital resource for individuals, communities, and policymakers, providing a visual representation of flood risk and informing crucial decisions regarding insurance, development, and emergency preparedness.
Delving into the Details of the FIRM
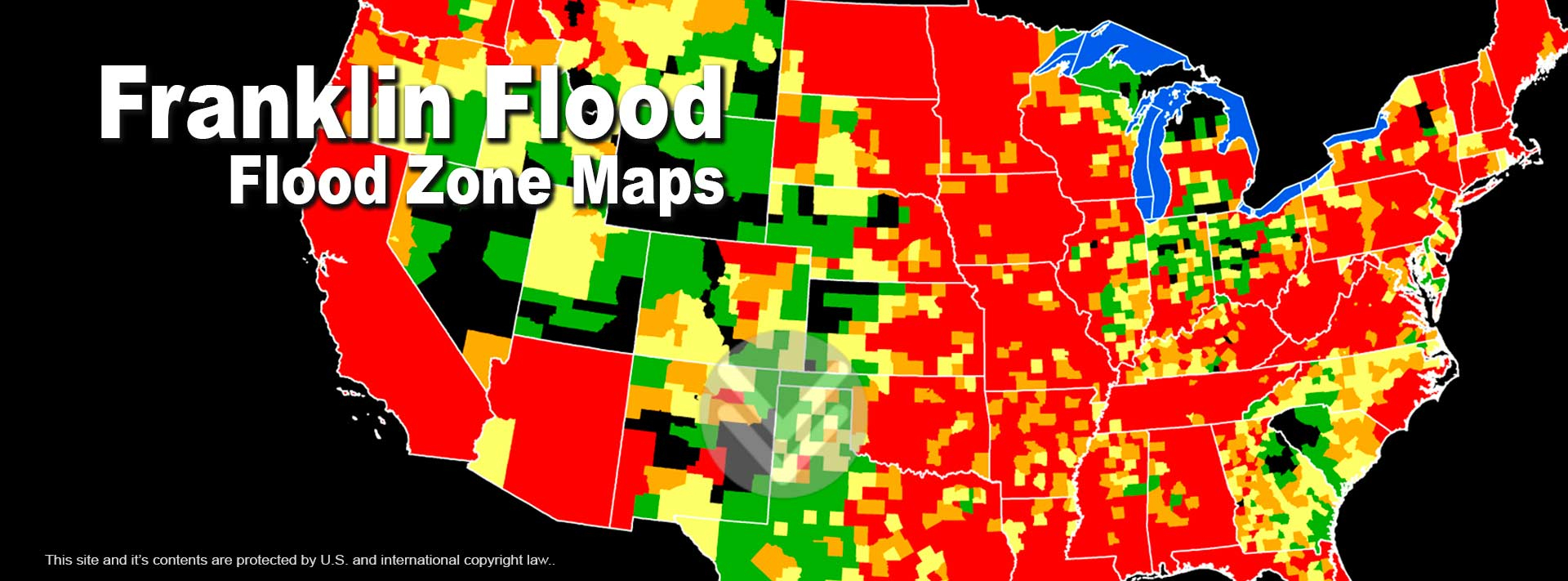
The FIRM is a specialized map that delineates areas susceptible to flooding. It categorizes land into different flood zones, each signifying a varying level of flood risk. These zones are designated using letters and numbers, with higher numerical values indicating a greater probability and severity of flooding.
Types of Flood Zones
-
Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs): These zones represent areas with a 1% or greater chance of flooding during any given year. They are further categorized into different types, including:
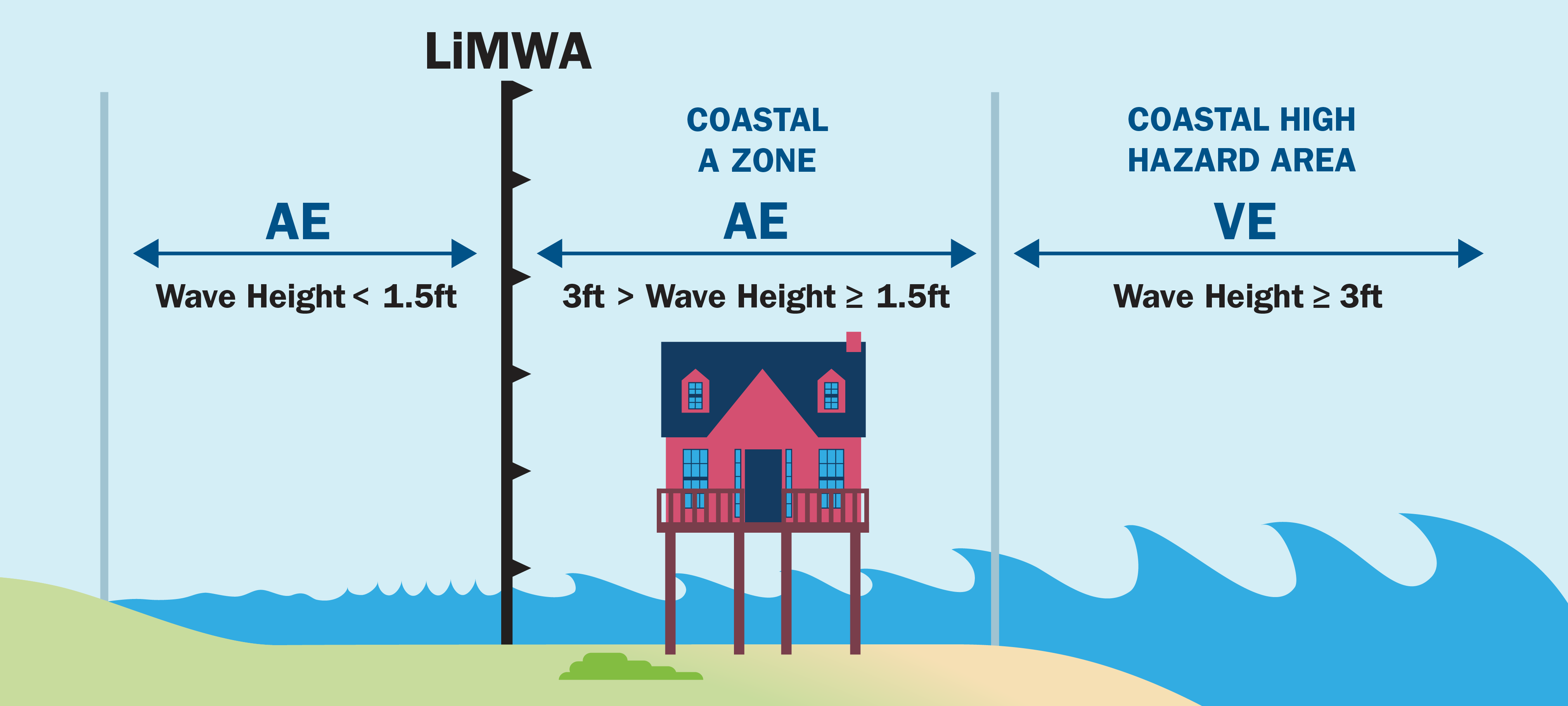
- Zone A: Areas with a 1% or greater chance of flooding, but where the depth and velocity of floodwaters are unknown.
- Zone AE: Areas with a 1% or greater chance of flooding, where the depth and velocity of floodwaters are known.
- Zone AO: Areas with a 1% or greater chance of flooding, where the depth of floodwaters is less than 1 foot, but the velocity of the floodwaters is significant.
- Zone AH: Areas with a 1% or greater chance of flooding, where the depth of floodwaters is greater than 1 foot and the velocity of the floodwaters is significant.
- Zone X: Areas with less than a 1% chance of flooding during any given year. These areas are typically considered to have a lower risk of flooding.
-
Other Flood Zones:
- Zone D: Areas where flood risk is undetermined or has not been fully assessed.
- Zone V: Areas subject to coastal flooding due to storm surge.
Understanding the Importance of the FIRM
The FIRM plays a crucial role in shaping various aspects of community development and individual preparedness. It serves as a foundation for:
- Flood Insurance Requirements: The FIRM determines whether flood insurance is required by lenders for properties located in SFHAs. This requirement is mandated by the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), ensuring that homeowners have adequate financial protection against potential flood losses.
- Community Planning and Development: The FIRM provides valuable data for municipalities and developers to make informed decisions regarding land use, zoning, and infrastructure development. By understanding flood risk, communities can develop strategies to minimize potential damage and protect residents.
- Emergency Response and Disaster Planning: The FIRM assists emergency responders in preparing for and responding to flood events. By identifying high-risk areas, emergency personnel can allocate resources effectively and implement targeted evacuation plans.
- Individual Awareness and Mitigation: The FIRM empowers individuals to understand the flood risks associated with their properties. This knowledge enables homeowners to take proactive measures to mitigate potential damage, such as elevating structures, installing flood barriers, and purchasing flood insurance.
Navigating the FIRM: Resources and Tools
The FIRM is accessible through various resources and tools, including:
- FEMA’s Website: The most comprehensive source for FIRM data, providing interactive maps, downloadable documents, and detailed information on flood risk.
- FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center: A dedicated team of experts who can assist with interpreting FIRM data and answering questions about flood risk.
- Local Government Offices: Many municipalities maintain copies of the FIRM for their respective jurisdictions.
- Insurance Agents: Insurance professionals can guide individuals through the FIRM and explain the implications of different flood zones.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the FIRM
Q: What is the difference between a flood zone and a flood plain?
A: A flood zone is a designated area on the FIRM map that represents a specific level of flood risk. A flood plain, on the other hand, is a natural area adjacent to a river, lake, or other water body that is prone to flooding.
Q: How often is the FIRM updated?
A: The FIRM is periodically updated to reflect changes in flood risk due to factors such as development, climate change, and new scientific data. Updates are typically conducted every 5-10 years.
Q: What happens if my property is located in a flood zone, but I don’t purchase flood insurance?
A: If your property is located in an SFHA and you do not have flood insurance, you may be ineligible for federal disaster assistance in the event of a flood.
Q: Can I appeal the FIRM’s designation of my property?
A: Yes, you can appeal the FIRM’s designation of your property if you believe it is inaccurate. FEMA provides a process for filing appeals, which requires submitting evidence to support your claim.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the FIRM
- Consult with a qualified professional: Seek guidance from a licensed surveyor, engineer, or insurance agent to interpret the FIRM accurately and understand its implications for your property.
- Review the FIRM regularly: The FIRM is periodically updated, so it’s essential to check for any changes that may impact your property’s flood risk.
- Consider mitigation measures: If your property is located in a flood zone, explore mitigation options such as elevating structures, installing flood barriers, or landscaping to reduce flood risk.
- Purchase flood insurance: Even if your property is not located in an SFHA, consider purchasing flood insurance as a precautionary measure.
Conclusion: The FIRM as a Vital Tool for Flood Risk Management
The FIRM plays a vital role in managing flood risk and protecting communities and individuals. By understanding its intricacies and utilizing its resources, homeowners, developers, and policymakers can make informed decisions that minimize flood damage and promote resilience. The FIRM serves as a critical tool for mitigating the financial and social impacts of flooding, ensuring a safer and more sustainable future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Flood Insurance Map: A Guide to Navigating Risk and Protection. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!