Understanding the Fuel Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Fuel Map: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Fuel Map: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Fuel Map: A Comprehensive Guide

In the realm of engine performance and optimization, the concept of a fuel map holds significant importance. It serves as a crucial tool for engineers and technicians, enabling them to fine-tune engine operation and achieve optimal efficiency. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of fuel maps, exploring their structure, function, and significance in modern automotive systems.
Defining the Fuel Map
A fuel map, also known as a fuel calibration table, is a multi-dimensional representation of an engine’s fuel injection strategy. It essentially acts as a blueprint outlining the precise amount of fuel required for each engine operating condition. These conditions encompass a wide range of parameters, including:
- Engine RPM (Revolutions Per Minute): Represents the speed at which the engine crankshaft rotates.
- Engine Load: Reflects the amount of power the engine is currently producing, typically measured as a percentage of its maximum output.
- Intake Manifold Pressure (MAP): Indicates the pressure within the intake manifold, which is directly related to engine load.
- Throttle Position: Represents the opening of the throttle valve, controlling the amount of air entering the engine.
- Air Temperature: Influences the density of air entering the engine, affecting combustion efficiency.
- Engine Coolant Temperature: Provides insight into the engine’s operating temperature, impacting fuel requirements.
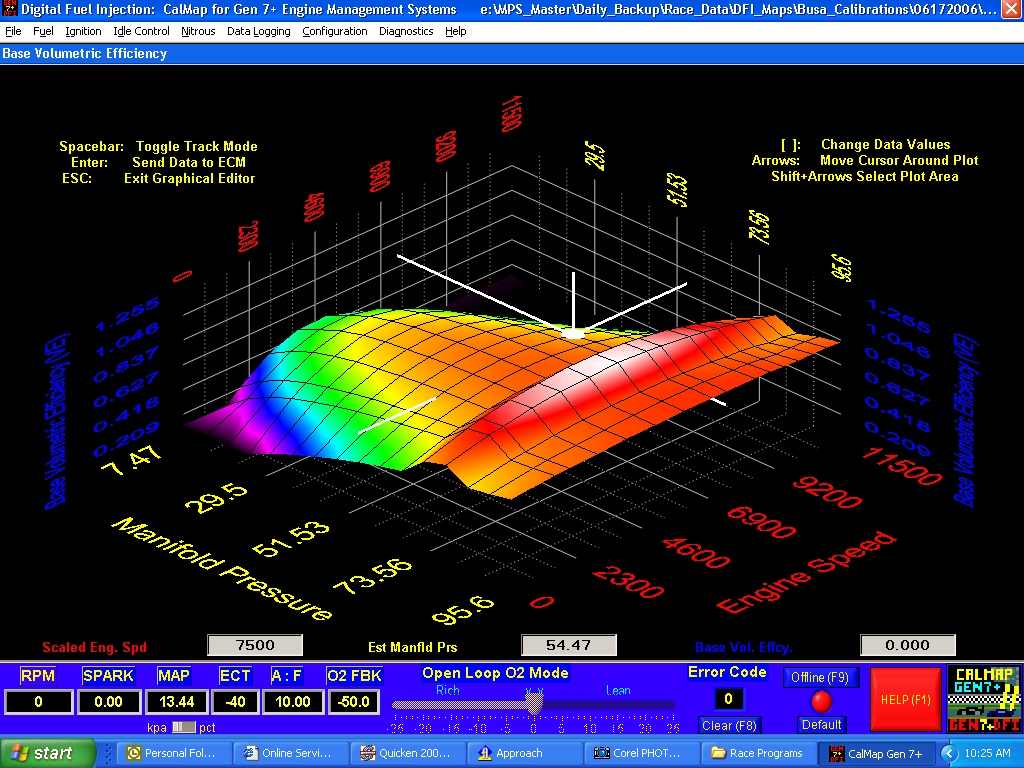
Fuel Map Structure: A Multidimensional Grid
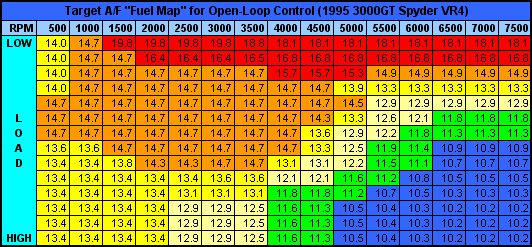
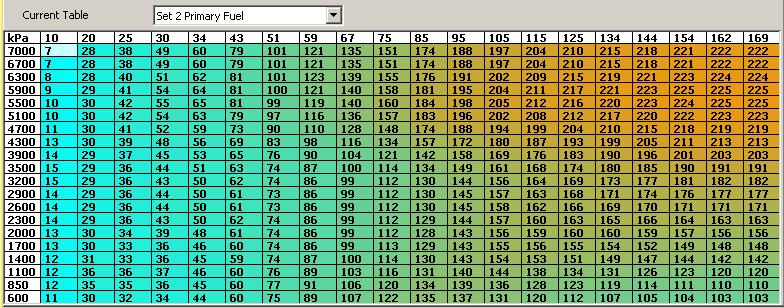
The fuel map is typically visualized as a grid, with engine RPM and engine load serving as the primary axes. Each cell within the grid represents a specific operating condition, and the corresponding value within the cell denotes the amount of fuel to be injected at that condition.
For example, a fuel map might specify a fuel injection duration of 10 milliseconds for an engine operating at 2000 RPM and 50% load. This means that the fuel injectors will remain open for 10 milliseconds during each engine cycle to deliver the appropriate fuel quantity.
Fuel Map Creation and Calibration
Fuel maps are meticulously crafted through a combination of testing and analysis. Engineers use sophisticated engine dynamometers to measure the engine’s performance under various operating conditions. This data is then used to create an initial fuel map, which is subsequently refined through a process known as calibration.
Calibration involves fine-tuning the fuel map to achieve optimal performance and emissions. This is typically done through a series of test drives and adjustments, with experienced technicians analyzing real-world data to optimize fuel injection parameters.
Fuel Map Benefits: Optimizing Performance and Efficiency
The use of fuel maps offers a multitude of benefits, contributing to enhanced engine performance and efficiency:
- Precise Fuel Delivery: By tailoring fuel injection to specific operating conditions, fuel maps ensure precise fuel delivery, optimizing combustion and reducing fuel consumption.
- Reduced Emissions: Fuel maps can be calibrated to minimize harmful emissions, such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, leading to cleaner and more environmentally friendly engines.
- Improved Power Output: By optimizing fuel delivery, fuel maps can enhance engine power output, enabling smoother acceleration and improved overall performance.
- Enhanced Driveability: Through precise fuel control, fuel maps contribute to smoother engine operation, reducing engine vibration and improving overall driveability.
- Increased Engine Durability: By ensuring optimal combustion, fuel maps help prevent engine damage caused by detonation or knocking, extending engine life.
Fuel Map Applications: A Wide Range of Engines
Fuel maps are employed across a wide range of engine types, including:
- Gasoline Engines: Fuel maps are essential for optimizing combustion and fuel economy in gasoline engines, particularly in modern vehicles equipped with advanced fuel injection systems.
- Diesel Engines: Fuel maps play a crucial role in diesel engines, ensuring efficient fuel delivery and minimizing emissions, especially in heavy-duty applications.
- Hybrid Engines: In hybrid vehicles, fuel maps are used in conjunction with electric motors to optimize fuel economy and performance, balancing the use of gasoline and electric power.
- Motorcycle Engines: Fuel maps are increasingly common in modern motorcycles, providing precise fuel control for improved performance and emissions.
Fuel Map Modifications: Unleashing Engine Potential
While fuel maps are designed to optimize engine performance, they can also be modified to achieve specific performance goals. This is often undertaken by experienced tuners who leverage their expertise to tailor fuel maps to individual driving preferences and engine upgrades.
Modifications to fuel maps can include:
- Performance Tuning: Increasing fuel delivery at higher RPMs and loads can boost engine power and torque, enhancing acceleration and overall performance.
- Economy Tuning: Adjusting fuel delivery to prioritize fuel economy can improve fuel consumption without compromising engine performance.
- Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Tuning: Modifying fuel maps to optimize EGR operation can reduce emissions and enhance fuel efficiency.
- Intake and Exhaust System Tuning: Adjusting fuel maps to accommodate modifications to the intake and exhaust systems can improve engine breathing and performance.
Fuel Map FAQs
Q: What is the difference between a fuel map and a spark map?
A: Both fuel maps and spark maps are essential components of engine control units (ECUs). While a fuel map dictates the amount of fuel injected, a spark map controls the timing of the spark plugs, determining when the air-fuel mixture is ignited. Both maps work in conjunction to optimize engine performance and efficiency.
Q: Can I modify my own fuel map?
A: While it is possible to modify fuel maps using specialized software and hardware, it is generally not recommended for novice users. Incorrect modifications can lead to engine damage, reduced performance, and increased emissions. Professional tuners with extensive knowledge and experience are best equipped to perform fuel map modifications.
Q: How often should I have my fuel map checked or updated?
A: Fuel map calibration should be performed whenever major engine modifications are made, such as intake or exhaust system upgrades, turbocharger installation, or engine rebuilds. Regular maintenance checks, including diagnostics and potential updates, can also be beneficial to ensure optimal engine performance and efficiency.
Q: Are fuel maps specific to each vehicle?
A: Yes, fuel maps are tailored to specific vehicle models and engine configurations. Factors such as engine displacement, compression ratio, and emissions regulations all influence the design and calibration of fuel maps.
Fuel Map Tips
- Consult a Professional: For any fuel map modifications, it is highly recommended to consult with a reputable and experienced tuner who can assess your specific needs and provide safe and effective solutions.
- Monitor Fuel Consumption: After any fuel map modifications, closely monitor your vehicle’s fuel consumption to ensure that the changes have not negatively impacted fuel efficiency.
- Regular Maintenance: Regular maintenance, including air filter replacement, spark plug inspection, and engine oil changes, can contribute to optimal engine performance and fuel economy.
- Avoid Aggressive Driving: Excessive acceleration and high-RPM driving can negatively impact fuel efficiency. Adopting a smooth and consistent driving style can help conserve fuel and extend engine life.
Conclusion
Fuel maps play a pivotal role in modern automotive systems, enabling precise fuel delivery and optimizing engine performance and efficiency. By understanding the structure, function, and benefits of fuel maps, drivers and technicians can gain valuable insights into engine operation and make informed decisions regarding fuel map modifications and maintenance. As technology continues to advance, fuel maps will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated, further enhancing engine performance and efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Fuel Map: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!