Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Troy: A Journey Through Maps and History
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Troy: A Journey Through Maps and History
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Troy: A Journey Through Maps and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Troy: A Journey Through Maps and History
The city of Troy, immortalized in Homer’s epic poem "The Iliad," has captivated imaginations for millennia. While the legendary tale of the Trojan War may be shrouded in myth, the historical reality of a thriving Bronze Age city on the shores of the Aegean Sea is undeniable. Understanding the layout and geography of this ancient metropolis requires a deep dive into the world of ancient maps, the only surviving witnesses to its physical form.
The Quest for Troy: From Myth to Archaeology
For centuries, Troy remained a mythical entity, its location a subject of speculation and debate. The first tangible evidence of its existence emerged in the 19th century, when the German archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann began his excavations at Hisarlik, a hilltop site in northwestern Turkey. Schliemann’s work, fueled by a fervent belief in the historical truth of Homer’s account, unearthed a complex sequence of settlements, each representing a distinct period of occupation.
The Importance of Ancient Maps: Uncovering the Lost City
Ancient maps, while often lacking the precision and detail of modern cartography, provide invaluable insights into the physical characteristics of ancient cities. For Troy, these maps, combined with archaeological evidence, offer a glimpse into its strategic location, urban planning, and the evolution of its physical form over centuries.
Types of Ancient Maps: Illuminating the Past
Several types of ancient maps contribute to our understanding of ancient Troy:
- Textual Descriptions: Homer’s "Iliad" itself serves as a valuable source of information, offering vivid descriptions of the Trojan landscape, its fortifications, and key landmarks. These literary descriptions, while not precise maps, provide a sense of the city’s layout and its strategic importance.
- Relief Maps: Ancient civilizations, particularly the Greeks, created relief maps that depicted topographical features in three dimensions. While no specific relief maps of Troy have been discovered, the existence of similar maps for other cities suggests that such representations may have existed for Troy as well.
- Pictorial Maps: Ancient maps often took the form of pictorial representations, depicting key features of a city or region. While these maps are not precise in terms of scale or orientation, they offer valuable insights into the visual perception of the city by its inhabitants.
- Planimetric Maps: These maps, which depict the horizontal layout of a city, are rarer in ancient times. However, some evidence suggests that rudimentary planimetric maps may have existed, particularly for military purposes.
Reconstructing Troy: A Multi-Disciplinary Approach
The reconstruction of ancient Troy relies heavily on the integration of various sources of information:
- Archaeological Excavations: The ongoing excavations at Hisarlik have yielded a wealth of data, including the remains of buildings, fortifications, and artifacts. These findings offer a tangible representation of the city’s physical structure.
- Ancient Texts: Literary descriptions, like those found in Homer’s "Iliad," provide valuable information about the city’s layout, its strategic importance, and its cultural context.
- Comparative Studies: By comparing Troy with other ancient cities, archaeologists can gain insights into the city’s urban planning, its social organization, and its cultural practices.
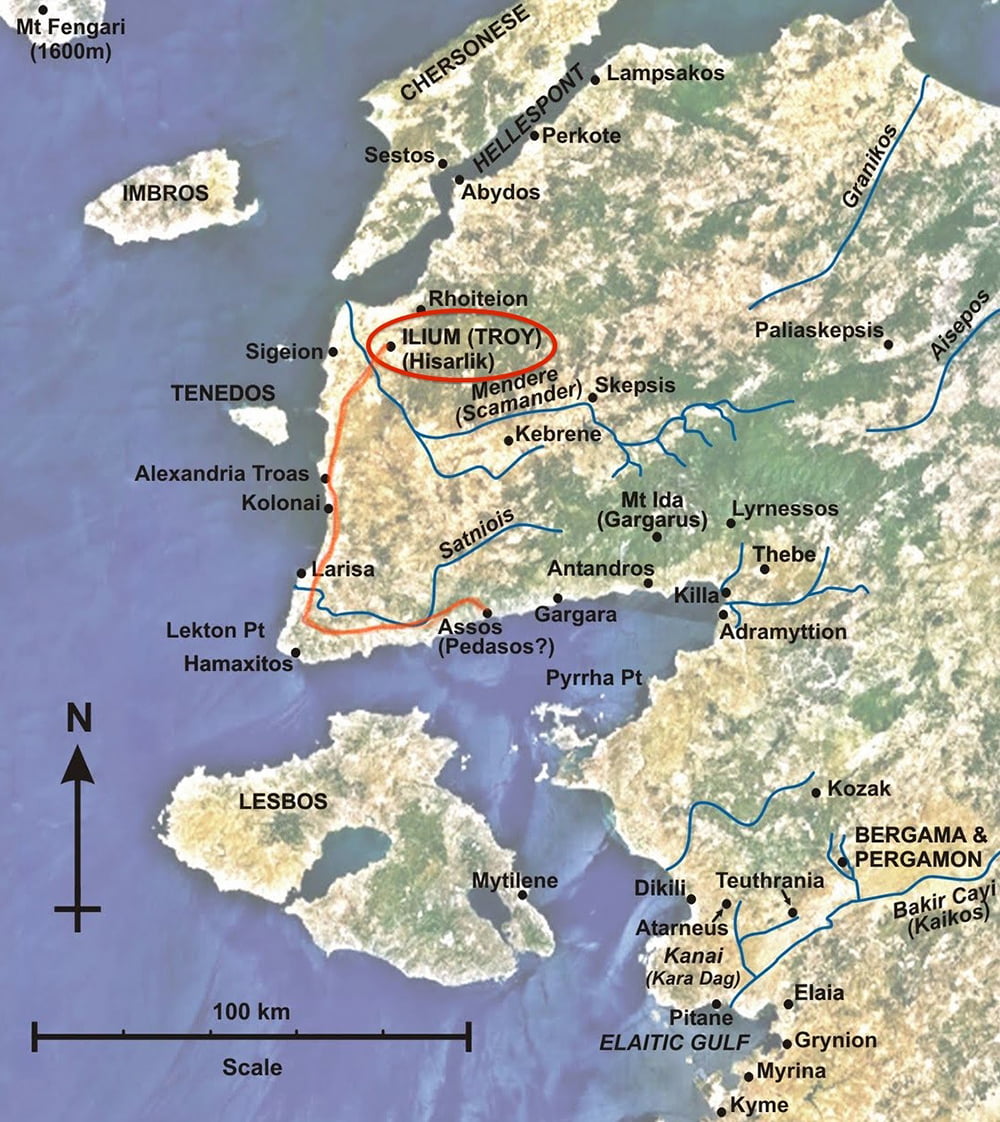
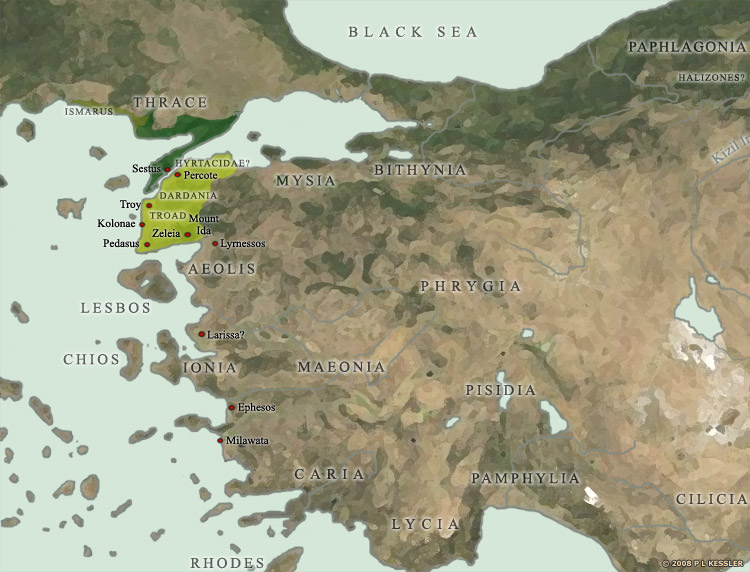
The Importance of Geographic Context: Strategic Location and Trade Networks
Troy’s strategic location at the entrance to the Dardanelles Strait, connecting the Aegean Sea to the Black Sea, played a pivotal role in its history. The city controlled a vital trade route, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas between different regions. This geographic advantage contributed to Troy’s wealth and its influence in the ancient world.
A Glimpse into the City’s Layout: From the Citadel to the Harbour
Based on archaeological evidence and textual descriptions, a picture of Troy’s layout emerges:
- The Citadel: The heart of the city, the citadel (or acropolis) was located on the highest point of the hilltop. This fortified area housed the palace, temples, and other important structures.
- The Lower City: The area surrounding the citadel was occupied by residential buildings, workshops, and commercial centers.
- The Harbour: Troy’s harbor, located on the shores of the Aegean Sea, provided access to the city’s trade routes and facilitated its connection with the wider Mediterranean world.
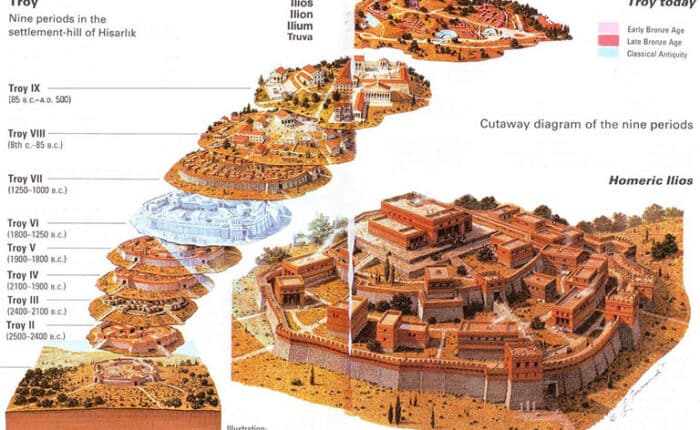
The Evolution of Troy: From the Early Bronze Age to the Late Bronze Age
Troy’s history spanned several centuries, witnessing a series of settlements and periods of occupation:
- Troy I-II: Dating back to the Early Bronze Age (3000-2500 BCE), these early settlements were relatively small and simple.
- Troy III-VI: These settlements, from the Middle Bronze Age (2500-1600 BCE), saw the growth of the city and the development of more complex urban structures.
- Troy VIIa: This period, dating back to the Late Bronze Age (1300-1200 BCE), is often associated with the legendary Trojan War. The city’s fortifications were expanded, and it reached its peak of prosperity.
- Troy VIIb-VIII: Following the destruction of Troy VIIa, the city was rebuilt and occupied for several centuries, but it never regained its former glory.
The Myth and the Reality: Reconciling the Tale of Troy
While the epic tale of the Trojan War may be a product of literary imagination, it reflects the reality of a powerful city that played a significant role in the ancient world. The archaeological evidence confirms the existence of a thriving Bronze Age city at Hisarlik, and the ancient maps, albeit incomplete, provide valuable insights into its physical form and its strategic importance.
FAQs
Q: What is the evidence for the existence of ancient Troy?
A: The primary evidence comes from archaeological excavations at Hisarlik, Turkey. The site has revealed a complex sequence of settlements, dating back to the Early Bronze Age, confirming the existence of a thriving city over centuries.
Q: How do ancient maps contribute to our understanding of ancient Troy?
A: Ancient maps, while often limited in detail, offer valuable insights into the city’s layout, its strategic location, and its connection to the wider Mediterranean world. They provide a visual perspective on the city’s physical characteristics and its relationship to its surrounding environment.
Q: What was the significance of Troy’s strategic location?
A: Troy’s location at the entrance to the Dardanelles Strait, connecting the Aegean Sea to the Black Sea, made it a vital control point for trade routes. This strategic advantage contributed to the city’s wealth and its influence in the ancient world.
Q: What are the key features of Troy’s layout?
A: Troy’s layout consisted of a fortified citadel, a lower city with residential and commercial areas, and a harbor on the shores of the Aegean Sea. These features reflect the city’s strategic importance and its role as a center of trade and administration.
Q: How does the story of the Trojan War relate to the archaeological evidence?
A: While the epic tale of the Trojan War may be a product of literary imagination, it reflects the reality of a powerful city that played a significant role in the ancient world. The archaeological evidence confirms the existence of a thriving Bronze Age city at Hisarlik, and the ancient maps, albeit incomplete, provide valuable insights into its physical form and its strategic importance.
Tips
- When studying ancient Troy, it is important to consider the multiple sources of information, including archaeological evidence, ancient texts, and ancient maps.
- By comparing Troy with other ancient cities, you can gain a deeper understanding of its urban planning, its social organization, and its cultural practices.
- Remember that ancient maps are not always precise or complete, but they offer valuable insights into the perception of the city by its inhabitants and its role in the wider Mediterranean world.
Conclusion
The study of ancient Troy offers a unique opportunity to explore the intersection of myth and history. While the legendary tale of the Trojan War may be a product of imagination, the archaeological evidence and the insights gleaned from ancient maps confirm the existence of a thriving Bronze Age city. By piecing together the fragments of the past, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and richness of ancient civilization.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Troy: A Journey Through Maps and History. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!