Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Ancient England’s Map
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Ancient England’s Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Ancient England’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Ancient England’s Map

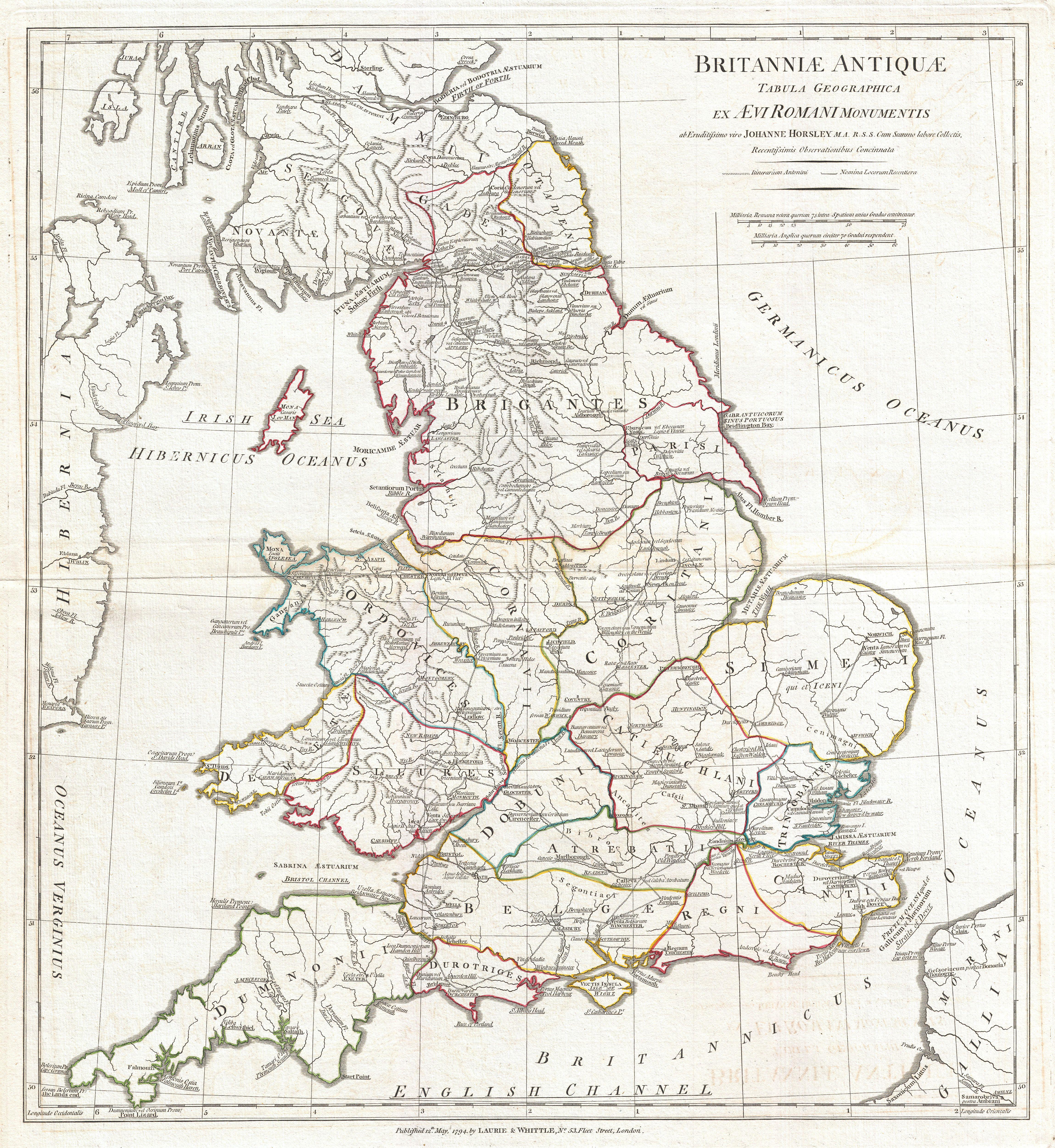
The landscape of England, as we know it today, is a product of millennia of history, shaped by natural forces and human endeavors. To truly understand the England of today, one must delve into its ancient past, a journey best undertaken through the lens of its ancient map. This map, a mosaic of archaeological evidence, linguistic analysis, and historical accounts, offers a fascinating glimpse into the lives, beliefs, and civilizations that once thrived on this land.
The Dawn of Civilization: The Neolithic and Bronze Age
The earliest traces of human presence in England date back to the Mesolithic period, around 10,000 BCE. However, it is the Neolithic period (c. 4000-2500 BCE) that marks the dawn of settled agriculture and the emergence of organized communities. This period saw the construction of megalithic monuments like Stonehenge and Avebury, testament to the ingenuity and spiritual beliefs of these early inhabitants. The Bronze Age (c. 2500-800 BCE) witnessed advancements in metalworking, leading to the production of tools, weapons, and decorative objects. The development of bronze metallurgy also facilitated trade networks, connecting communities across the British Isles.
The Iron Age: The Arrival of Celtic Tribes
The Iron Age (c. 800 BCE – 43 CE) saw the arrival of Celtic tribes, who brought with them a distinct culture and language. These tribes, known collectively as the Britons, established a complex social structure, practiced agriculture, and engaged in warfare. The ancient map reveals their presence through the discovery of hillforts, fortified settlements that provided protection and strategic advantage. The Iron Age also saw the development of a unique Celtic art style, evident in intricate carvings and metalwork, which continues to fascinate archaeologists and historians today.
The Roman Conquest and its Legacy
In 43 CE, the Roman Empire, under the Emperor Claudius, launched an invasion of Britain. Over the next four centuries, the Romans established a powerful presence in the island, building roads, fortresses, and towns. The Roman influence extended across the landscape, transforming the ancient map. The Romans introduced their own culture, language, and administrative structures, leaving an indelible mark on England’s history. The Roman conquest also led to the introduction of Christianity, which would later become the dominant religion of the land.
The Anglo-Saxon Period: A New Wave of Migrants
Following the withdrawal of the Romans in the 5th century CE, the Anglo-Saxons, Germanic tribes from mainland Europe, began migrating to Britain. This period, known as the Anglo-Saxon period (c. 410-1066 CE), saw the establishment of seven Anglo-Saxon kingdoms: Northumbria, Mercia, East Anglia, Essex, Sussex, Kent, and Wessex. The ancient map reveals the territorial boundaries of these kingdoms, highlighting the complex political landscape of the time. The Anglo-Saxons brought with them their own language, culture, and beliefs, which had a profound impact on the development of English society.
The Viking Age: Raiders and Settlers
From the 8th century onwards, Viking raiders from Scandinavia began to attack the coasts of Britain. These raids, initially focused on plunder, gradually evolved into settlements, establishing permanent communities across the land. The ancient map reveals the impact of the Viking presence, particularly in areas like East Anglia and the North, where Viking settlements and burial sites are found. The Vikings brought with them their own culture, language, and technology, influencing the development of Anglo-Saxon society and contributing to the rich tapestry of English history.
The Norman Conquest and the Rise of a New Nation
The Norman Conquest of 1066 CE, led by William the Conqueror, marked a turning point in English history. The Normans, a French-speaking people, brought with them their own culture, language, and administrative structures, leaving a lasting impact on the ancient map. The Normans established a new ruling class, built castles and fortified towns, and introduced the feudal system, which shaped the social and economic landscape of England for centuries to come.
The Ancient Map: A Window into the Past
The ancient map of England is not merely a static representation of geographical features. It is a dynamic tool, revealing the ebb and flow of civilizations, the evolution of cultures, and the interconnectedness of history. Each archaeological discovery, each linguistic analysis, and each historical account adds another layer to this intricate tapestry, allowing us to piece together the story of ancient England.
FAQs about the Ancient Map of England
1. What are the key features of the ancient map of England?
The ancient map of England encompasses a wide range of features, including:
- Archaeological sites: Megalithic monuments, hillforts, Roman towns and roads, Anglo-Saxon burial grounds, Viking settlements, Norman castles, and churches.
- Linguistic boundaries: Areas where different languages and dialects were spoken, reflecting the movement of different populations.
- Political divisions: The territories of different kingdoms and rulers, showcasing the changing power dynamics over time.
2. What is the significance of the ancient map of England?
The ancient map of England provides a vital framework for understanding the history of the land. It reveals the evolution of the landscape, the movement of populations, the development of cultures, and the impact of different civilizations. By studying the ancient map, we gain insights into the lives of our ancestors, their beliefs, and their contributions to the rich tapestry of English history.
3. How is the ancient map of England created?
The ancient map of England is a product of interdisciplinary research, combining evidence from:
- Archaeology: Excavation and analysis of archaeological sites, providing tangible evidence of past settlements and activities.
- Linguistics: Studying ancient languages and dialects, revealing the spread of different cultures and populations.
- Historical accounts: Examining written records, chronicles, and other historical sources, providing valuable insights into past events and societies.
4. How can the ancient map of England be used today?
The ancient map of England serves as a valuable resource for:
- Historical research: Providing context and understanding for historical events, cultures, and societies.
- Archaeological investigations: Guiding future excavations and research, revealing new insights into the past.
- Tourism and heritage preservation: Promoting awareness and appreciation of England’s rich history and cultural heritage.
5. What are some of the challenges in creating an accurate ancient map of England?
Creating an accurate ancient map of England presents several challenges:
- Limited archaeological evidence: Not all areas have been thoroughly excavated, leaving gaps in our understanding of past settlements and activities.
- Interpretation of evidence: Archaeological findings and historical accounts can be open to interpretation, requiring careful analysis and consideration of different perspectives.
- Changing landscapes: The landscape of England has changed significantly over time, due to natural processes and human intervention, making it difficult to accurately reconstruct the past.
Tips for Exploring the Ancient Map of England
- Visit archaeological sites: Immerse yourself in the history of England by visiting key archaeological sites like Stonehenge, Avebury, Hadrian’s Wall, and York Minster.
- Explore museums and archives: Discover artifacts, documents, and other resources that shed light on ancient England, including the British Museum, the National Archives, and local museums.
- Engage with historical accounts: Read historical texts, chronicles, and biographies to gain a deeper understanding of the people and events that shaped ancient England.
- Utilize online resources: Explore interactive maps, databases, and online resources that provide information about archaeological sites, historical events, and ancient cultures.
- Join historical societies and groups: Connect with fellow history enthusiasts, attend lectures and workshops, and participate in archaeological digs.
Conclusion
The ancient map of England is a testament to the rich and complex history of this land. It is a window into the past, revealing the lives, beliefs, and civilizations that have shaped the England we know today. By studying this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of history, the enduring legacy of our ancestors, and the importance of preserving our cultural heritage. Through continued research, exploration, and engagement, we can continue to unravel the tapestry of time and gain a deeper understanding of the ancient map of England, a treasure trove of stories waiting to be discovered.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Ancient England’s Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!