Unveiling Hidden Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Hidden Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Hidden Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Hidden Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
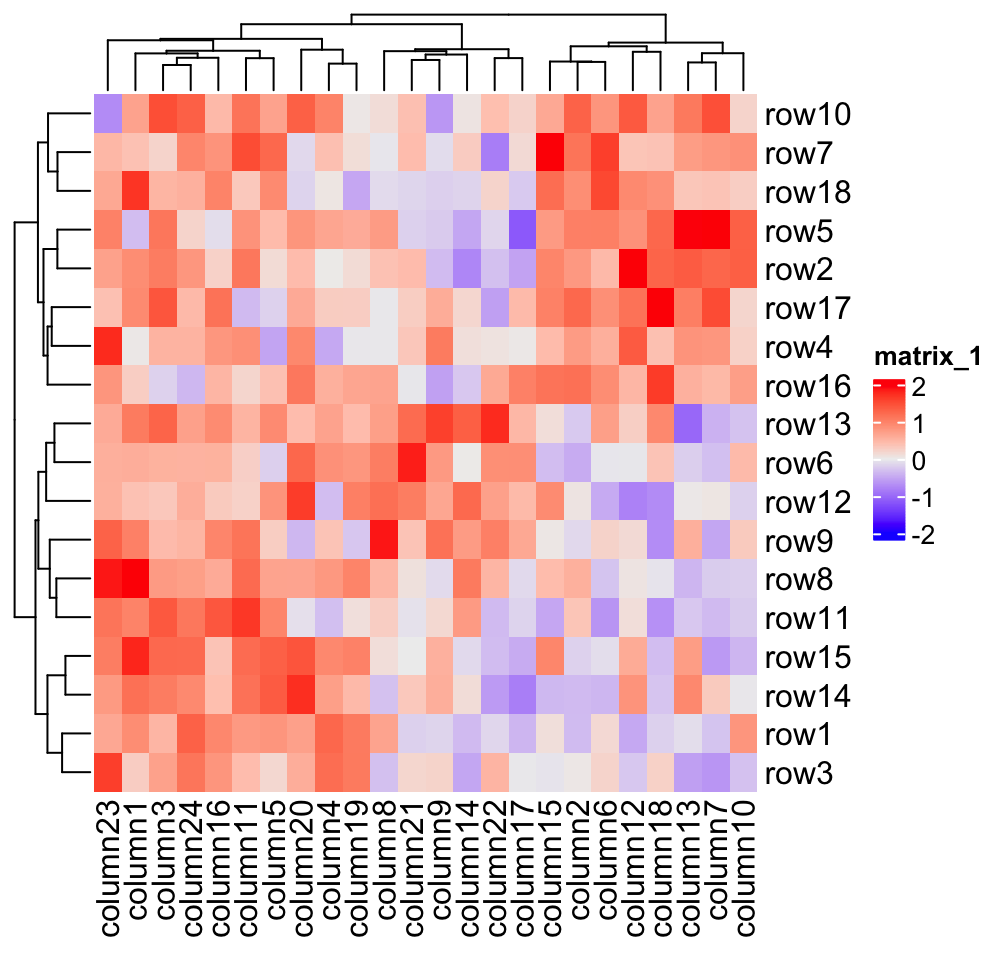
In the realm of data analysis, understanding the relationships between variables is paramount. This is where correlation heat maps emerge as powerful visual tools, offering a concise and insightful representation of the strength and direction of relationships within a dataset. This guide delves into the intricacies of correlation heat maps, illuminating their construction, interpretation, and wide-ranging applications.
The Essence of Correlation
Before embarking on the exploration of correlation heat maps, it is essential to grasp the concept of correlation itself. Correlation quantifies the strength and direction of the linear association between two variables. A positive correlation signifies that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. Conversely, a negative correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other tends to decrease. The strength of the correlation is measured by the correlation coefficient, which ranges from -1 to 1. A value of 1 represents a perfect positive correlation, -1 represents a perfect negative correlation, and 0 signifies no linear relationship.
Visualizing Relationships: The Correlation Heat Map
A correlation heat map, often referred to as a correlation matrix, is a graphical representation of the correlation coefficients between all pairs of variables in a dataset. This two-dimensional matrix visually displays the strength and direction of relationships, providing a holistic overview of the data’s interconnections. Each cell within the heat map represents the correlation between two variables, with the color intensity indicating the strength of the correlation. Typically, a color gradient is employed, where warmer colors represent stronger positive correlations, cooler colors represent stronger negative correlations, and neutral colors indicate weak or no correlation.
Decoding the Visual Landscape
Interpreting a correlation heat map involves identifying patterns and trends in the color distribution. By analyzing the color intensities and their arrangement, one can glean valuable insights into the relationships between variables. For instance, a block of bright red cells along the diagonal suggests a strong positive correlation between those variables. Conversely, a cluster of deep blue cells indicates a strong negative correlation.
Beyond the Visual: Statistical Significance
While the visual representation of correlations is insightful, it is crucial to consider the statistical significance of these relationships. A correlation coefficient alone does not guarantee a meaningful connection; it merely indicates the strength of the linear association. To assess the significance, statistical tests such as the Pearson correlation test are employed, which determine the probability of observing such a correlation by chance. This statistical validation helps ensure that the observed correlations are not mere random fluctuations in the data.
Constructing a Correlation Heat Map
Creating a correlation heat map typically involves the following steps:
-
Data Preparation: The initial step involves collecting and preparing the data, ensuring it is clean and suitable for correlation analysis. This may involve handling missing values, transforming variables, and standardizing the data if necessary.
-
Correlation Calculation: Once the data is ready, the correlation coefficients between all pairs of variables are calculated. This can be achieved using various statistical software packages or programming languages like Python or R.
-
Matrix Visualization: The calculated correlation coefficients are then arranged in a matrix form, with each row and column representing a variable. The matrix is then visualized using a color gradient to represent the strength and direction of correlations.
Applications of Correlation Heat Maps
Correlation heat maps find widespread application across diverse fields, providing valuable insights into complex data relationships. Some key applications include:
-
Financial Analysis: Identifying correlations between financial assets can help investors construct diversified portfolios and manage risk.
-
Healthcare Research: Understanding correlations between patient characteristics and disease outcomes can aid in developing targeted treatment strategies.
-
Marketing and Sales: Analyzing correlations between marketing campaigns and sales performance can optimize marketing strategies and improve ROI.
-
Social Sciences: Exploring correlations between social factors and human behavior can provide valuable insights into societal dynamics.
-
Environmental Studies: Investigating correlations between environmental variables and ecological changes can inform environmental policies and conservation efforts.
FAQs Regarding Correlation Heat Maps
Q: What are the limitations of correlation heat maps?
A: While correlation heat maps provide a valuable visual representation of relationships, they have limitations. They only capture linear relationships and may not reveal non-linear associations. Additionally, correlation does not imply causation; a strong correlation between two variables does not necessarily mean that one causes the other.
Q: How can I interpret a correlation heat map effectively?
A: Focus on the clusters of color intensity, identifying patterns and trends. Pay attention to the diagonal elements, as they represent the correlation of a variable with itself, which should always be 1. Consider the statistical significance of the correlations to ensure they are not random fluctuations.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using correlation heat maps?
A: Avoid drawing causal conclusions based solely on correlation. Ensure that the data is appropriately prepared and cleaned before performing correlation analysis. Be cautious of spurious correlations, which may arise from confounding factors not accounted for in the analysis.
Tips for Effective Correlation Heat Map Analysis
-
Use a clear and consistent color scheme. This enhances readability and aids in visual interpretation.
-
Label the rows and columns clearly. This ensures that the variables are easily identifiable.
-
Consider using a dendrogram or hierarchical clustering to group variables with strong correlations. This can reveal underlying structures in the data.
-
Use annotations to highlight specific correlations of interest. This can direct attention to key relationships.
Conclusion
Correlation heat maps serve as powerful visual tools for uncovering hidden relationships within datasets. By providing a concise and insightful representation of correlations, they empower data analysts to identify patterns, understand complex interactions, and make informed decisions. While it is crucial to acknowledge their limitations, correlation heat maps remain indispensable for exploring data relationships and gaining valuable insights across diverse fields.







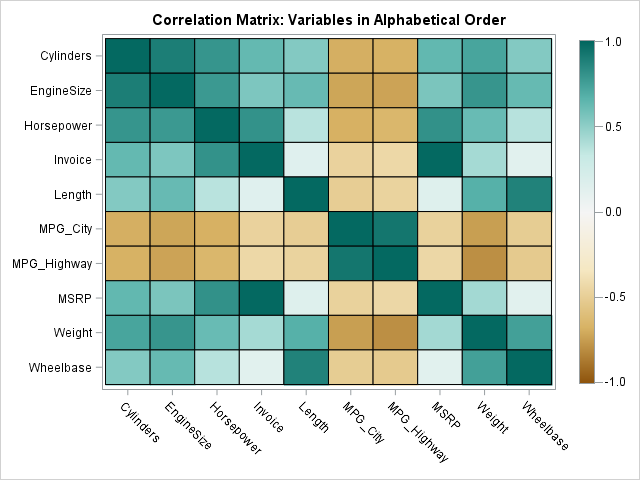
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Hidden Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!