Unveiling Patterns: A Deep Dive into Google Maps Heatmaps
Related Articles: Unveiling Patterns: A Deep Dive into Google Maps Heatmaps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Patterns: A Deep Dive into Google Maps Heatmaps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Patterns: A Deep Dive into Google Maps Heatmaps
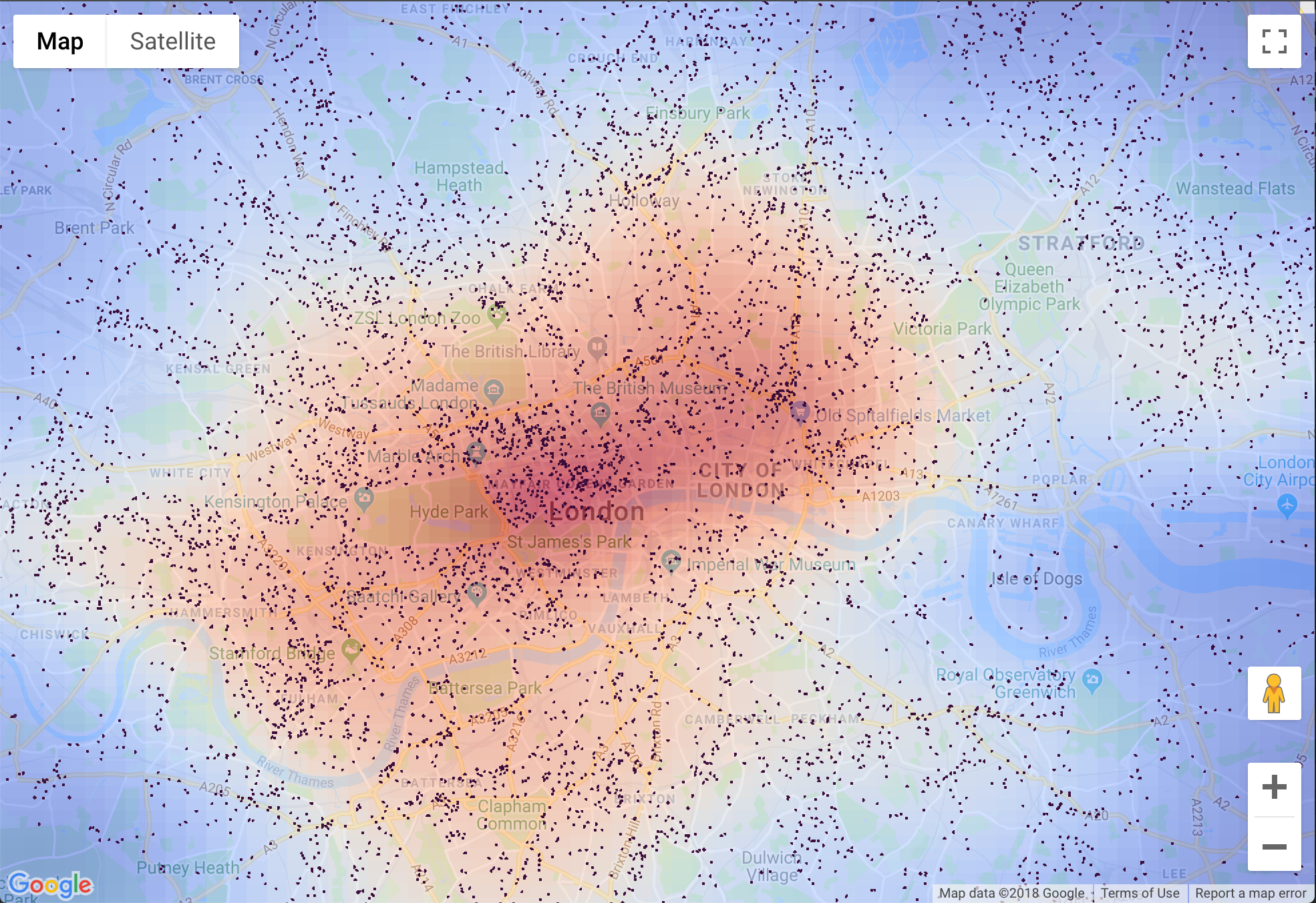
Google Maps, a ubiquitous tool for navigation and exploration, offers a powerful visualization tool known as the heatmap. This feature transforms raw data into a visually engaging representation, highlighting areas of high concentration and revealing underlying patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. Heatmaps are not merely aesthetic enhancements; they provide valuable insights across various domains, enabling data-driven decision-making and a deeper understanding of spatial phenomena.
Understanding the Essence of Heatmaps
Imagine a map where the density of points, representing specific data points, is visually translated into shades of color. The warmer the color, the higher the concentration of data in that particular area. This is the essence of a heatmap. It effectively aggregates data points, revealing areas of high activity or occurrence, allowing users to quickly identify trends and hotspots.
The Anatomy of a Google Maps Heatmap
A Google Maps heatmap is constructed using a specific set of parameters:
- Data Source: The foundation of a heatmap lies in the data it represents. This could be anything from crime incidents to restaurant reviews, traffic congestion to population density. The type of data dictates the insights derived from the heatmap.
- Weighting: Data points can be assigned different weights, signifying their relative importance. For instance, a major traffic incident might carry a higher weight than a minor one, resulting in a more intense color representation on the heatmap.
- Color Gradient: The choice of color gradient is crucial for visually representing the data effectively. Typically, a gradient ranging from blue (low concentration) to red (high concentration) is used, allowing for intuitive interpretation.
- Transparency: Adjusting the transparency of the heatmap allows users to see underlying geographical features or other data layers, ensuring a balanced visual representation.
- Radius: The radius parameter determines the area around each data point that contributes to the heatmap’s color intensity. A larger radius can smooth out data points, while a smaller radius provides a more granular view.
Applications of Google Maps Heatmaps
Heatmaps find diverse applications across various industries, offering valuable insights and informing strategic decisions:
- Urban Planning: Analyzing population density, crime rates, and traffic patterns helps urban planners understand the needs of different areas, optimize resource allocation, and improve infrastructure.
- Business Analytics: Businesses can leverage heatmaps to identify high-traffic areas, understand customer demographics, and optimize store locations or marketing campaigns.
- Healthcare: Heatmaps can visualize disease prevalence, hospital locations, and emergency service response times, aiding in resource allocation and public health initiatives.
- Environmental Studies: Mapping environmental hazards, pollution levels, and wildlife distribution using heatmaps contributes to effective conservation efforts and environmental management.
- Real Estate: Identifying areas with high property values, rental demand, or potential for development can be facilitated using heatmaps, informing real estate investments and market analysis.
- Transportation: Heatmaps visualize traffic congestion, identify areas with high pedestrian activity, and optimize public transportation routes, leading to improved mobility and reduced congestion.
- Social Sciences: Understanding human movement patterns, migration trends, and cultural hotspots can be achieved using heatmaps, providing valuable insights for social research and policy-making.
Building a Google Maps Heatmap: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a heatmap using Google Maps involves a few key steps:
- Data Preparation: Gather the data relevant to your analysis, ensuring it includes geographical coordinates (latitude and longitude) for each data point.
- Choosing a Platform: Utilize Google Maps’ Heatmap Layer API or a third-party tool like Google My Maps, which allows for creating and sharing custom heatmaps.
- Importing Data: Import the prepared data into the chosen platform, specifying the data fields representing geographical coordinates and any other relevant information.
- Customization: Configure the heatmap parameters, including color gradient, transparency, radius, and weighting, to best represent the data and convey the desired insights.
- Visualization and Analysis: Analyze the generated heatmap, identifying areas of high concentration, trends, and patterns. Use the insights to inform decisions and further explore the data.
FAQs on Google Maps Heatmaps
1. What types of data can be used to create a heatmap?
Any data that can be associated with geographical coordinates can be used to create a heatmap. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Location data: GPS coordinates from mobile devices, social media check-ins, or location-based services.
- Event data: Crime incidents, traffic accidents, or public gatherings.
- Business data: Customer locations, store sales, or marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Environmental data: Pollution levels, wildlife sightings, or natural disaster occurrences.
2. Can I create a heatmap from data that is not publicly available?
Yes, you can create a heatmap from private data, but it is essential to ensure compliance with privacy regulations and data security protocols.
3. How can I ensure the accuracy of my heatmap?
The accuracy of a heatmap depends on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. It is important to use reliable data sources and validate the results with other information.
4. What are some limitations of Google Maps heatmaps?
- Data bias: Heatmaps can be influenced by data biases, leading to inaccurate interpretations if the data is not representative of the entire population.
- Spatial resolution: The resolution of the heatmap is limited by the density of data points and the radius parameter.
- Oversimplification: Heatmaps provide a simplified representation of complex data, potentially overlooking nuances and specific details.
Tips for Effective Heatmap Creation
- Choose the right data: Select data that is relevant to your analysis and represents the phenomenon you wish to visualize.
- Consider data weighting: Assign different weights to data points based on their importance, ensuring that the heatmap accurately reflects the relative significance of each point.
- Experiment with color gradients: Explore different color gradients to find one that effectively conveys the data and enhances visual clarity.
- Adjust transparency: Experiment with transparency levels to balance the heatmap’s intensity with the visibility of underlying geographical features.
- Use multiple heatmaps: Create multiple heatmaps using different data sets or time periods to compare patterns and identify changes over time.
- Combine with other visualization tools: Integrate heatmaps with other visualization tools like charts and graphs to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the data.
Conclusion
Google Maps heatmaps are a powerful tool for visualizing data, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed. By understanding the principles behind their creation and application, users can leverage heatmaps to gain valuable insights across diverse domains, informing decision-making and driving progress. As data collection and analysis continue to evolve, heatmaps will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in unlocking the power of spatial data and shaping our understanding of the world around us.


:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9783709/DSCF2501.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Patterns: A Deep Dive into Google Maps Heatmaps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!