Unveiling Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps
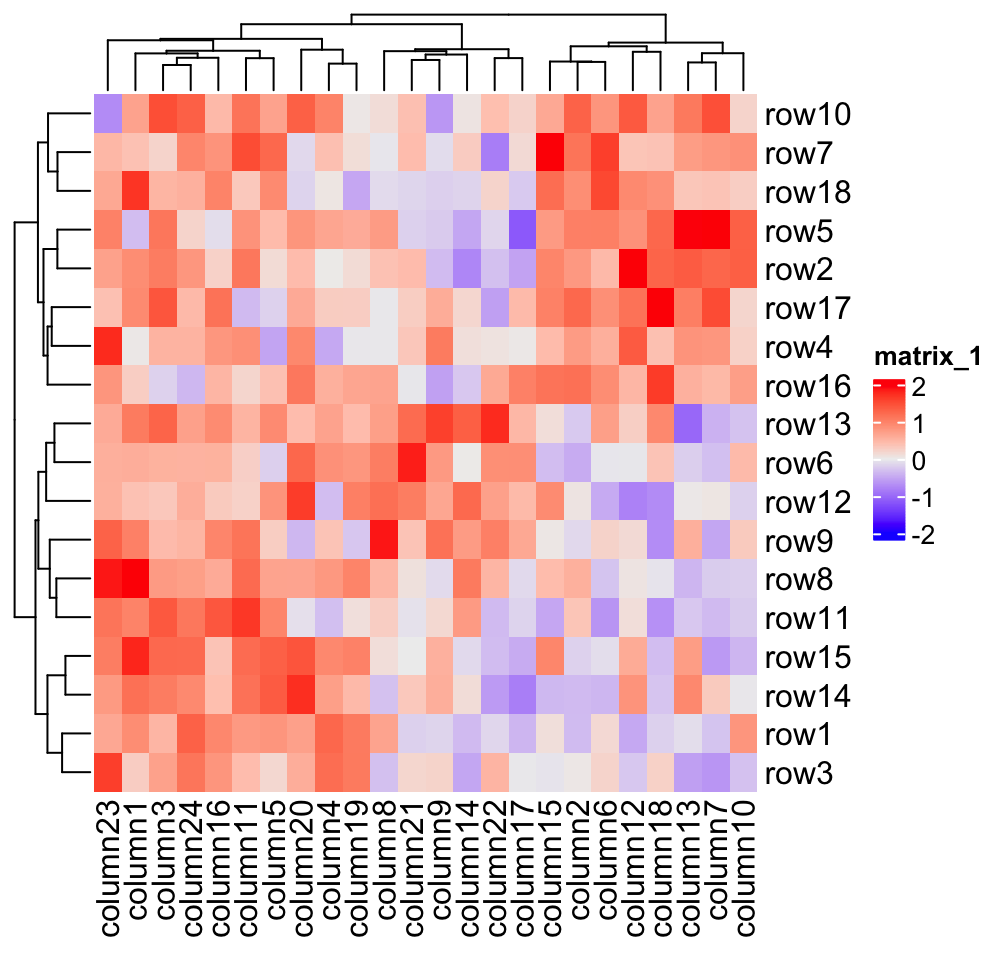
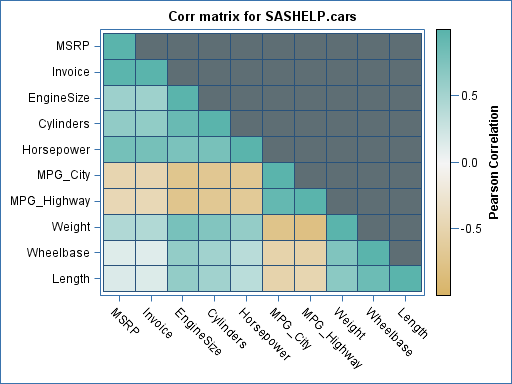
In the realm of data analysis, understanding the relationships between variables is paramount. A powerful visual tool that aids in this endeavor is the correlation heat map. This graphical representation provides a concise and intuitive overview of the strength and direction of correlations among multiple variables, offering invaluable insights into the underlying structure of data.
Understanding the Essence of Correlation
Correlation, in its simplest form, describes the degree to which two variables move together. A positive correlation indicates that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. Conversely, a negative correlation signifies that as one variable increases, the other tends to decrease. The strength of this relationship is measured by a correlation coefficient, which ranges from -1 to +1. A value of +1 represents a perfect positive correlation, -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, and 0 signifies no correlation.
Visualizing Relationships with a Heat Map
A correlation heat map utilizes a color gradient to depict the strength and direction of correlations between variables. Typically, a color scale ranging from blue (negative correlation) to red (positive correlation) is employed, with shades of purple representing weaker correlations. Each cell in the heat map represents the correlation between two specific variables, allowing for a rapid visual assessment of their relationship.
Benefits of Employing Correlation Heat Maps
- Immediate Insights: The visual nature of heat maps allows for quick identification of strong and weak correlations, providing an intuitive understanding of data relationships.
- Data Exploration: Heat maps facilitate the exploration of complex datasets, revealing potential patterns and hidden relationships that might be missed through traditional statistical methods.
- Hypothesis Generation: By highlighting significant correlations, heat maps can inspire hypotheses about the underlying mechanisms driving the observed relationships.
- Feature Selection: In machine learning, heat maps can assist in identifying features that are highly correlated with the target variable, aiding in the selection of relevant variables for model building.
- Outlier Detection: Deviations from expected patterns in the heat map can indicate potential outliers or anomalies in the data.
Constructing a Correlation Heat Map
Creating a correlation heat map involves the following steps:
- Data Preparation: Ensure that the data is clean and suitable for correlation analysis. This may involve handling missing values, transforming variables, and standardizing the data.
- Calculating Correlations: Calculate the correlation coefficients between all pairs of variables using appropriate methods, such as Pearson’s correlation coefficient or Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient.
- Visual Representation: Utilize a visualization library or software to generate the heat map. Choose a suitable color scale and ensure clear labeling of variables and correlation values.
Interpreting a Correlation Heat Map
Interpreting a correlation heat map requires a careful consideration of the following factors:
- Color Intensity: The intensity of the color indicates the strength of the correlation. Darker colors represent stronger correlations, while lighter colors indicate weaker correlations.
- Color Direction: The direction of the correlation is determined by the color hue. Red shades indicate positive correlations, while blue shades indicate negative correlations.
- Diagonal: The diagonal of the heat map represents the correlation of each variable with itself, which is always perfectly correlated (1).
- Clustering: Observe if any variables cluster together with similar correlation patterns, suggesting potential relationships between them.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Correlation Heat Maps
Q: What are the different types of correlation coefficients used in heat maps?
A: The most commonly used correlation coefficients are Pearson’s correlation coefficient, which measures linear relationships between continuous variables, and Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient, which assesses monotonic relationships between variables, regardless of their scale.
Q: How do I choose the appropriate correlation coefficient for my data?
A: The choice of correlation coefficient depends on the nature of your data and the type of relationship you are investigating. Pearson’s coefficient is suitable for linearly related continuous variables, while Spearman’s coefficient is appropriate for monotonic relationships, including ordinal variables.
Q: What are the limitations of correlation heat maps?
A: Correlation does not imply causation. Even if two variables are highly correlated, it does not necessarily mean that one causes the other. There may be other underlying factors influencing both variables. Additionally, heat maps only depict pairwise relationships, potentially missing complex interactions between multiple variables.
Q: How can I overcome the limitations of correlation heat maps?
A: To gain a deeper understanding of the relationships within your data, consider complementing correlation heat maps with other techniques such as scatter plots, partial correlation analysis, and causal inference methods.
Tips for Creating Effective Correlation Heat Maps
- Choose a Clear Color Scale: Select a color scale that provides a clear visual distinction between different correlation strengths and directions.
- Label Variables: Clearly label the variables on both axes of the heat map to ensure easy interpretation.
- Include Correlation Values: Display the numerical correlation values within each cell for precise understanding of the relationship.
- Use Appropriate Size and Resolution: Ensure that the heat map is large enough to display all variables clearly and with sufficient resolution for visual analysis.
- Consider Clustering: If applicable, cluster the variables based on their correlation patterns to enhance the visualization and highlight potential groupings.
Conclusion
Correlation heat maps offer a valuable tool for exploring and understanding relationships within data. By providing a visual representation of correlations between variables, they enable quick identification of significant relationships, facilitate hypothesis generation, and support feature selection in machine learning. While correlation does not imply causation, heat maps serve as a crucial starting point for further investigation and can guide the development of more complex models and analyses. By embracing the insights provided by correlation heat maps, data analysts can unlock the hidden patterns within their data and gain a deeper understanding of the underlying relationships driving their observations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Relationships: A Comprehensive Guide to Correlation Heat Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!