Unveiling the Diversity of Russia’s Climate: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diversity of Russia’s Climate: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diversity of Russia’s Climate: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diversity of Russia’s Climate: A Geographical Exploration

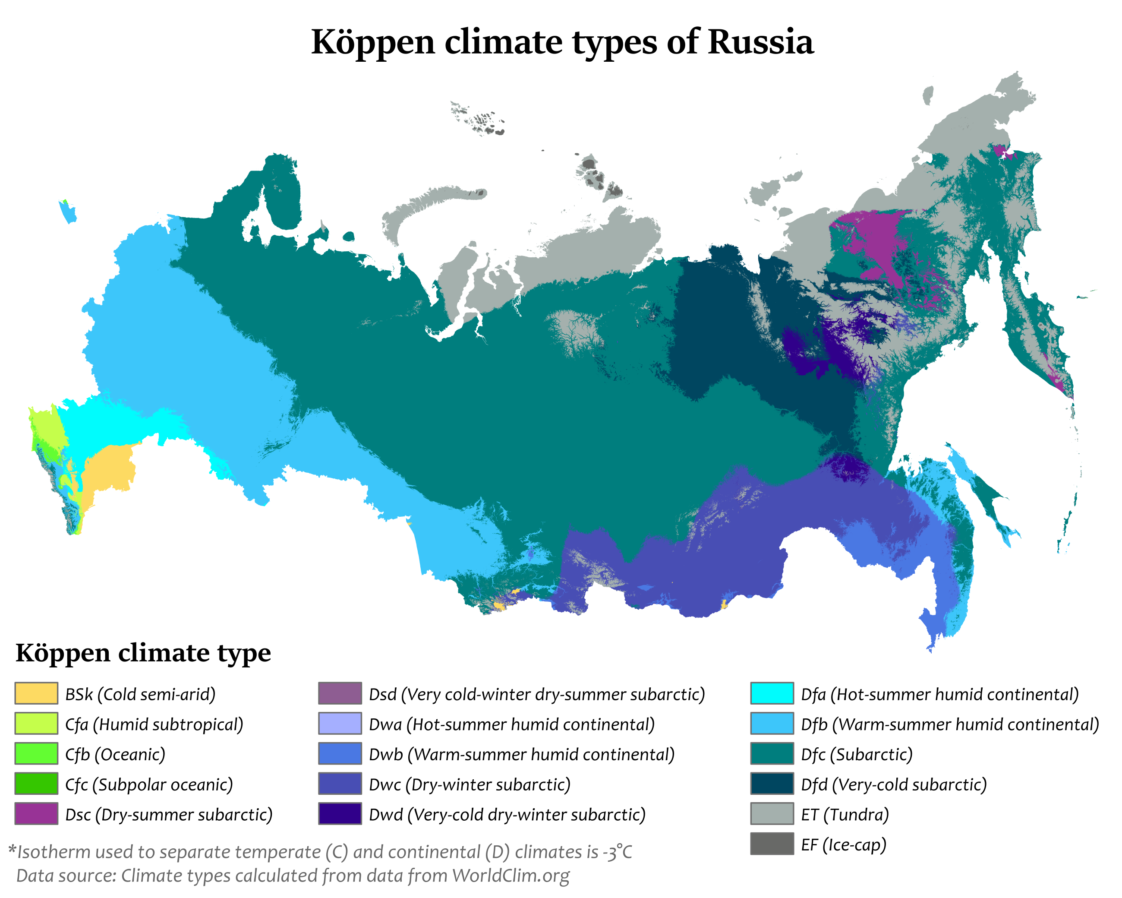
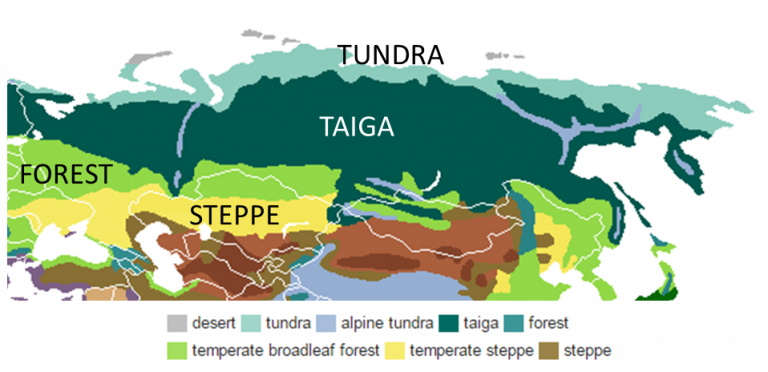
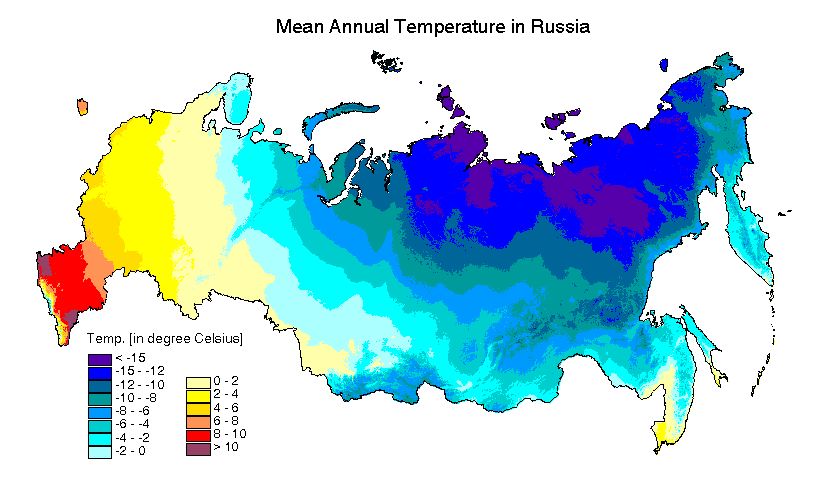
Russia, the largest country in the world, spans eleven time zones and boasts a remarkable diversity of landscapes, from the vast Siberian plains to the Caucasus Mountains. This vast geographical expanse also manifests in a wide range of climates, creating a complex and fascinating climatic tapestry. Understanding the intricacies of Russia’s climate map is crucial for comprehending the country’s natural resources, agriculture, transportation, and even its cultural identity.
A Journey Through Russia’s Climate Zones:
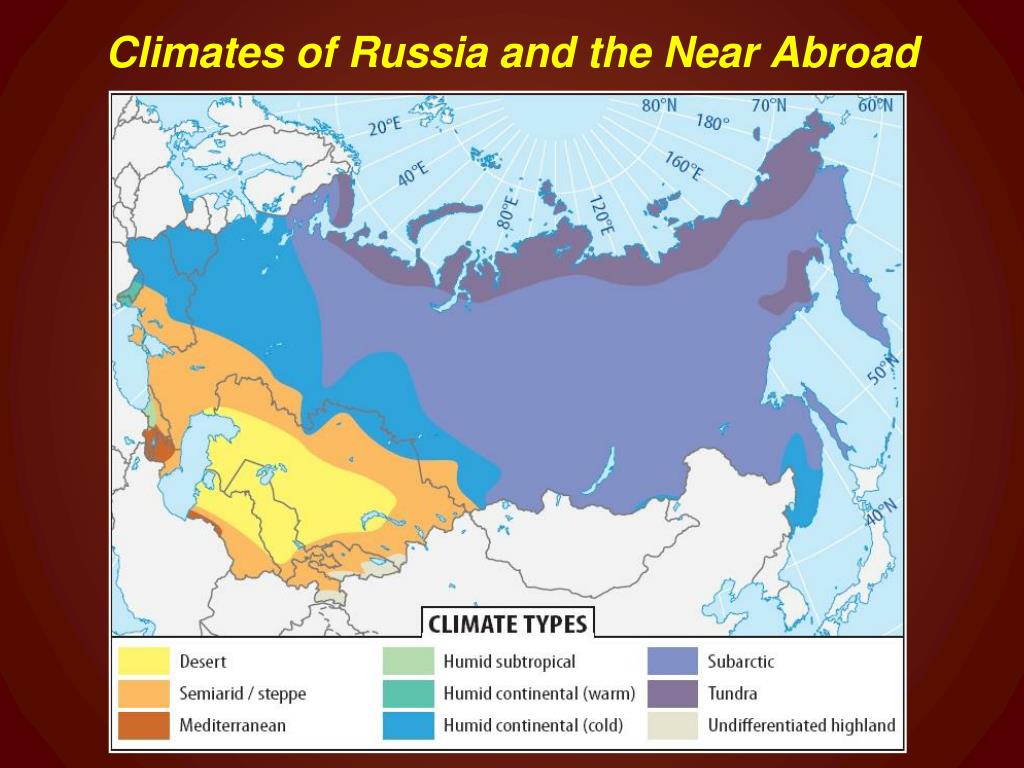
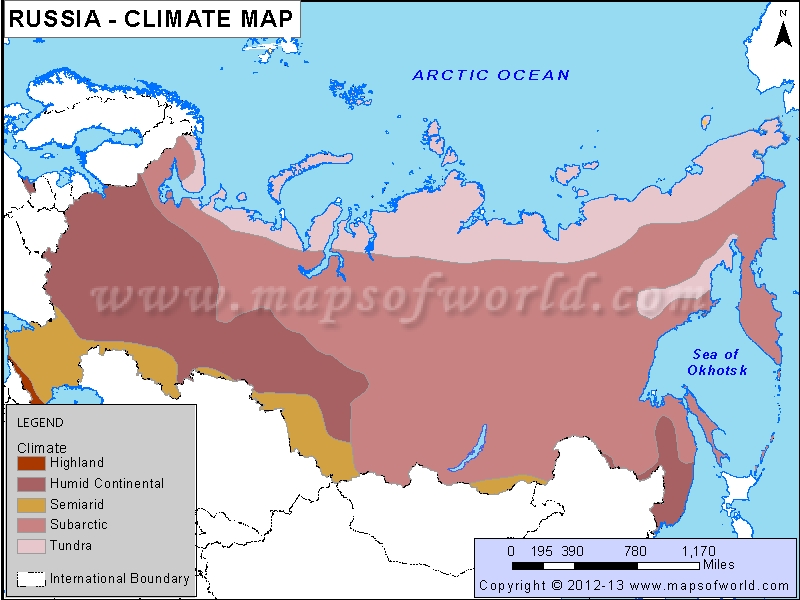
The Russian climate map is a visual representation of the country’s diverse climatic conditions, categorized into several distinct zones:
-
Arctic Climate: Encompassing the northernmost regions of Russia, including the Arctic Ocean and the vast Siberian tundra, this zone experiences extremely cold temperatures year-round, with average temperatures below freezing for most of the year. The winters are long and dark, while summers are short and cool. Precipitation is generally low, primarily in the form of snow.
-
Subarctic Climate: Located south of the Arctic zone, this region extends across northern Siberia and includes the vast taiga forests. While still experiencing long, cold winters, the summers are slightly warmer and longer than in the Arctic zone. Precipitation is slightly higher, with snow being the dominant form.
-
Humid Continental Climate: This zone dominates the European part of Russia, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains. Characterized by distinct seasons, this climate experiences hot, humid summers and cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is relatively high throughout the year.
-
Steppe Climate: Found in the southern part of Russia, this zone is characterized by dry, semi-arid conditions with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters. Precipitation is low, with most of it occurring in the spring and early summer.
-
Monsoon Climate: This unique climate is found in the far eastern region of Russia, along the Pacific coast. Characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons, this zone experiences warm, humid summers with heavy rainfall, and cold, dry winters.
Beyond the Zones: Understanding the Nuances:
While the climate map provides a general overview, it is essential to recognize that these zones are not uniform. Within each zone, variations in elevation, proximity to water bodies, and local topography create microclimates with unique characteristics. For instance, the mountainous regions of the Caucasus and Altai experience a distinct alpine climate with colder temperatures and heavier snowfall compared to the surrounding lowlands.
The Significance of the Russian Climate Map:
The Russian climate map holds immense significance for various aspects of the country’s life:
-
Agriculture: Understanding the climate zones is crucial for determining the suitability of different crops and livestock. For example, the fertile black soil regions of the European part of Russia are ideal for growing wheat and other grains, while the drier steppe regions are better suited for livestock grazing.
-
Transportation: The harsh winter conditions in many parts of Russia pose significant challenges to transportation infrastructure. The climate map helps in planning and designing roads, railways, and air routes to ensure smooth operations throughout the year.
-
Energy Production: Russia is rich in energy resources, particularly oil and gas. The climate map plays a vital role in identifying potential energy reserves and planning infrastructure development.
-
Human Health: The climate map is crucial for understanding the prevalence of various diseases and planning public health initiatives. For example, the cold winters in the northern regions increase the risk of respiratory illnesses, while the hot summers in the south pose a risk of heatstroke.
-
Tourism: The diverse climate zones of Russia offer a wide range of tourist attractions, from the snow-covered mountains of the Caucasus to the beaches of the Black Sea. The climate map helps tourists plan their trips based on their preferred weather conditions.
FAQs About the Russian Climate Map:
- Why is Russia’s climate so diverse?
Russia’s vast geographical expanse, spanning several latitudes and longitudes, is the primary reason for its diverse climate. The country’s location in the northern hemisphere, with a large portion lying within the Arctic Circle, results in long, cold winters and short, cool summers. The presence of large mountain ranges like the Ural Mountains and the Caucasus Mountains further influences regional climates, creating microclimates with unique characteristics.
- What are the main challenges posed by Russia’s climate?
Russia’s climate poses several challenges, including:
* **Extreme temperatures:** The extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can be detrimental to human health, infrastructure, and agriculture.
* **Severe winters:** Long, cold winters with heavy snowfall disrupt transportation, energy production, and everyday life.
* **Drought:** The steppe regions of southern Russia are prone to drought, impacting agriculture and water resources.
* **Flooding:** Heavy rainfall and melting snow can lead to flooding in various parts of the country, causing damage to infrastructure and property.- How is climate change impacting Russia’s climate?
Climate change is expected to have significant impacts on Russia’s climate, including:
* **Rising temperatures:** Average temperatures are projected to rise significantly, leading to longer summers and shorter winters.
* **Increased precipitation:** Some regions are expected to experience increased precipitation, leading to more frequent and intense flooding.
* **Permafrost thaw:** The thawing of permafrost in the Arctic region poses significant risks to infrastructure and ecosystems.Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the Russian Climate Map:
- Consult reliable sources: Use reputable sources like the Russian Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring (Roshydromet) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) for accurate climate data.
- Focus on regional variations: Remember that the climate map provides a general overview, and regional variations within each zone can be significant.
- Consider specific activities: When planning activities, consider the climate conditions specific to the location and time of year.
- Stay informed about climate change: Keep abreast of the latest research and projections on climate change impacts in Russia to prepare for future challenges.
Conclusion:
The Russian climate map is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse climatic conditions and their implications for various aspects of life. From agriculture and transportation to energy production and tourism, the climate map plays a crucial role in shaping Russia’s development and resilience. As climate change continues to reshape the world, understanding the nuances of Russia’s climate is more important than ever, enabling us to navigate the challenges and harness the opportunities presented by this vast and dynamic land.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diversity of Russia’s Climate: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!