Unveiling the Taiga: A Comprehensive Guide to the World’s Largest Biome
Related Articles: Unveiling the Taiga: A Comprehensive Guide to the World’s Largest Biome
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Taiga: A Comprehensive Guide to the World’s Largest Biome. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Taiga: A Comprehensive Guide to the World’s Largest Biome

The taiga, often referred to as the boreal forest, is a vast and captivating biome that stretches across the northern hemisphere, encompassing vast swathes of land in North America, Europe, and Asia. Characterized by its distinctive coniferous forests, harsh climate, and unique biodiversity, the taiga plays a critical role in global ecosystems and provides a rich tapestry of ecological and cultural significance. Understanding the taiga requires a comprehensive exploration of its geographic distribution, defining characteristics, and the intricate web of life that thrives within it.
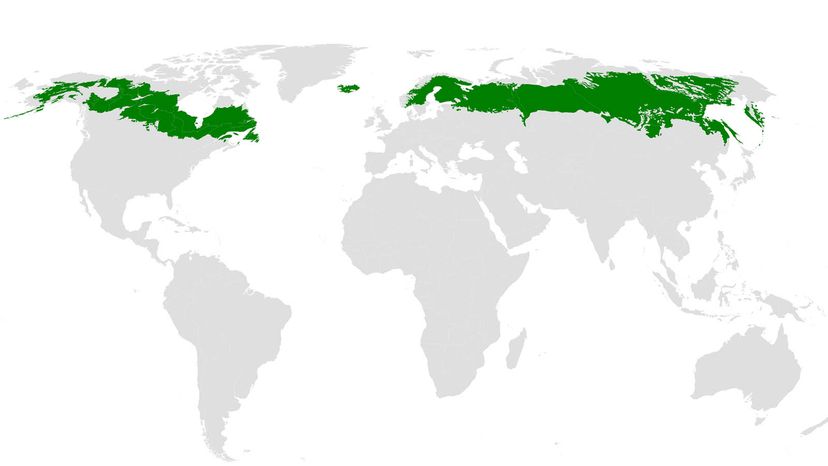
Mapping the Taiga: A Visual Representation of the World’s Largest Biome
A taiga biome map serves as a powerful tool for visualizing the global extent of this remarkable ecosystem. These maps depict the distribution of taiga forests across continents, highlighting their unique characteristics and geographical boundaries. By examining a taiga biome map, one can gain valuable insights into the following:
-
Global Distribution: Taiga biome maps clearly illustrate the vastness of this biome, spanning across North America, Europe, and Asia. This visual representation helps understand the global reach of this critical ecosystem and its significance in regulating climate and supporting biodiversity.
-
Specific Regions: Maps can pinpoint specific taiga regions, such as the Canadian Shield, the Siberian taiga, and the Scandinavian taiga. This allows for a focused analysis of the distinct ecological characteristics of each region and the unique flora and fauna they support.
-
Climate Influence: Taiga biome maps often incorporate climate data, showcasing the cold, snowy winters and short, cool summers that define this biome. This visual representation aids in understanding the influence of climate on vegetation patterns and the adaptations of taiga inhabitants.
-
Biodiversity Hotspots: By highlighting areas of high biodiversity within the taiga, maps can reveal critical zones for conservation efforts. These areas often harbor unique species and fragile ecosystems that require special attention to ensure their continued existence.
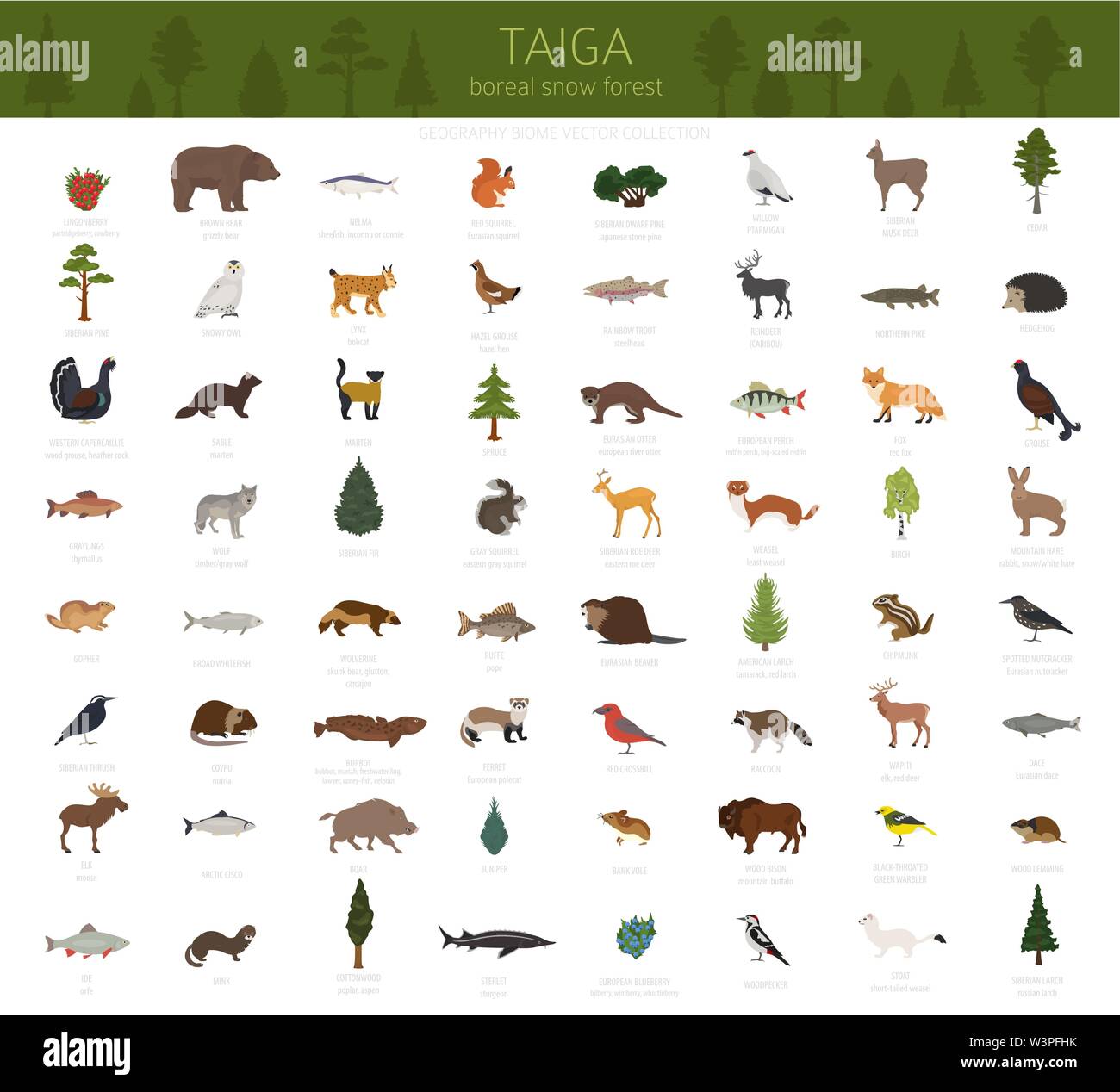
Unraveling the Taiga: Key Characteristics and Adaptations
The taiga is characterized by a specific set of environmental factors that shape its unique ecological profile. These factors include:
-
Climate: Taiga biomes are known for their long, cold winters with temperatures often dropping below freezing for months. Summers are short and cool, with average temperatures ranging from 30 to 50 degrees Fahrenheit.
-
Precipitation: Taiga regions receive moderate rainfall, primarily in the form of snow during the winter months. The total annual precipitation ranges from 15 to 40 inches, contributing to the abundance of water in the ecosystem.
-
Soil: Taiga soils are typically acidic and nutrient-poor due to slow decomposition rates in cold temperatures. The presence of permafrost, a layer of permanently frozen ground, further limits nutrient availability.
-
Vegetation: Coniferous trees, such as spruce, fir, and pine, dominate the taiga landscape. These trees are adapted to the harsh climate with needle-shaped leaves that minimize water loss during cold, dry periods.
-
Fauna: The taiga is home to a diverse array of animals, including large mammals like moose, elk, caribou, and wolves. Smaller mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians also thrive in this biome, adapting to the specific challenges of the taiga environment.
Navigating the Taiga: Adaptations and Survival Strategies
The harsh conditions of the taiga necessitate unique adaptations for survival. Plants and animals have evolved specific mechanisms to thrive in this challenging environment:
-
Plant Adaptations: Coniferous trees have evolved needle-shaped leaves that reduce water loss and resist freezing temperatures. Their dark green color absorbs maximum sunlight during the short growing season, enabling photosynthesis.
-
Animal Adaptations: Many taiga animals, like the snowshoe hare, have developed thick fur and large paws to navigate the snowy terrain. Some animals, such as the wood frog, have developed antifreeze proteins to survive freezing temperatures.
-
Migration and Hibernation: Many taiga animals migrate to warmer regions during the winter months to escape the harsh conditions. Others, like the ground squirrel, hibernate to conserve energy during the cold season.
The Taiga’s Importance: A Symphony of Ecological Benefits
The taiga biome plays a crucial role in global ecosystems, contributing significantly to:
-
Climate Regulation: Taiga forests act as massive carbon sinks, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This plays a vital role in mitigating climate change and regulating global temperatures.
-
Water Cycle: Taiga forests contribute significantly to the global water cycle, releasing water vapor into the atmosphere through transpiration. This contributes to the formation of clouds and precipitation, influencing regional and global weather patterns.
-
Biodiversity Hotspot: The taiga is home to a diverse array of species, including unique and endangered ones. This rich biodiversity contributes to the stability and resilience of the ecosystem.
-
Economic Importance: Taiga forests provide valuable timber resources and support various industries, including forestry, mining, and tourism. Sustainable management practices are essential to ensure the long-term economic and ecological benefits of these resources.
FAQs: Exploring the Taiga in Depth
1. What is the difference between a taiga and a tundra?
While both biomes are located in cold regions, the taiga is characterized by coniferous forests, while the tundra is a treeless biome with low-lying vegetation. The taiga experiences warmer temperatures and receives more precipitation than the tundra.
2. What are some of the challenges faced by animals in the taiga?
Animals in the taiga face challenges such as cold temperatures, limited food availability during winter, and the need to adapt to seasonal changes.
3. How does climate change impact the taiga?
Climate change is affecting the taiga in various ways, including rising temperatures, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risks of wildfires. These changes can disrupt the delicate balance of the ecosystem and threaten the survival of many species.
4. What are some of the conservation efforts focused on the taiga?
Conservation efforts in the taiga focus on protecting biodiversity, managing sustainable forestry practices, and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
5. What are some of the unique adaptations of plants in the taiga?
Taiga plants have adapted to the cold climate by developing needle-shaped leaves, deep root systems, and a thick layer of insulation.
Tips for Exploring the Taiga
-
Respect the environment: Leave no trace of your presence and avoid disturbing wildlife.
-
Dress appropriately: Wear warm clothing and layers to protect yourself from the cold.
-
Be aware of wildlife: Stay alert and maintain a safe distance from animals.
-
Pack essential supplies: Bring food, water, a map, and a compass.
-
Plan your trip carefully: Research the area and choose a suitable time of year for your visit.
Conclusion: A Vital Ecosystem for a Sustainable Future
The taiga biome is a testament to the resilience of life in extreme environments. Its vast expanse, unique adaptations, and critical ecological contributions highlight the importance of understanding and protecting this vital ecosystem. By appreciating the intricate web of life within the taiga and adopting sustainable practices, we can ensure its continued existence for generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Taiga: A Comprehensive Guide to the World’s Largest Biome. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!