Unveiling the Taiga: A Map of the World’s Largest Biome
Related Articles: Unveiling the Taiga: A Map of the World’s Largest Biome
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Taiga: A Map of the World’s Largest Biome. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Taiga: A Map of the World’s Largest Biome

The taiga, often referred to as the boreal forest, stretches across vast swathes of the Northern Hemisphere, forming a continuous band of coniferous forests that encircles the globe. This immense biome, characterized by its harsh climate and unique ecosystem, plays a critical role in regulating global climate, providing vital resources, and harboring diverse wildlife. Understanding the taiga’s distribution and characteristics requires a comprehensive map, a visual representation that unveils the secrets of this vast and fascinating realm.
Mapping the Taiga: A Visual Representation of a Global Ecosystem
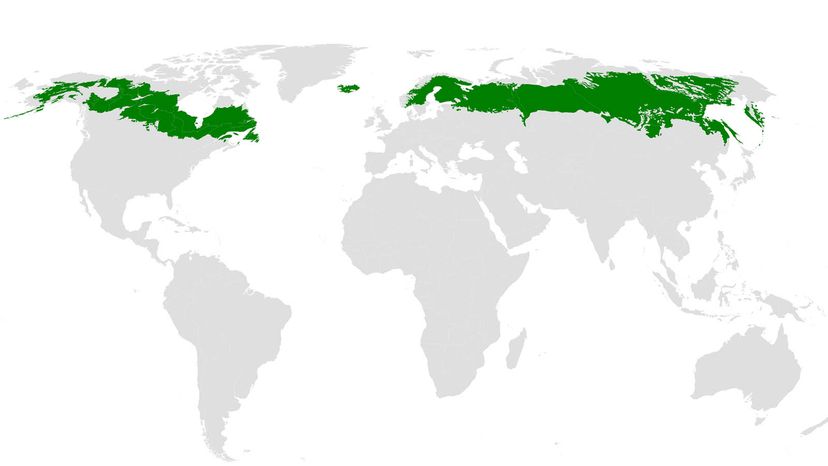
A taiga biome map is an essential tool for visualizing the distribution of this biome across the globe. It serves as a visual guide, highlighting the specific regions where taiga ecosystems thrive. These maps typically depict the taiga’s geographical boundaries, encompassing the dominant tree species, climate patterns, and the unique wildlife that call this biome home.
Essential Features of a Taiga Biome Map:
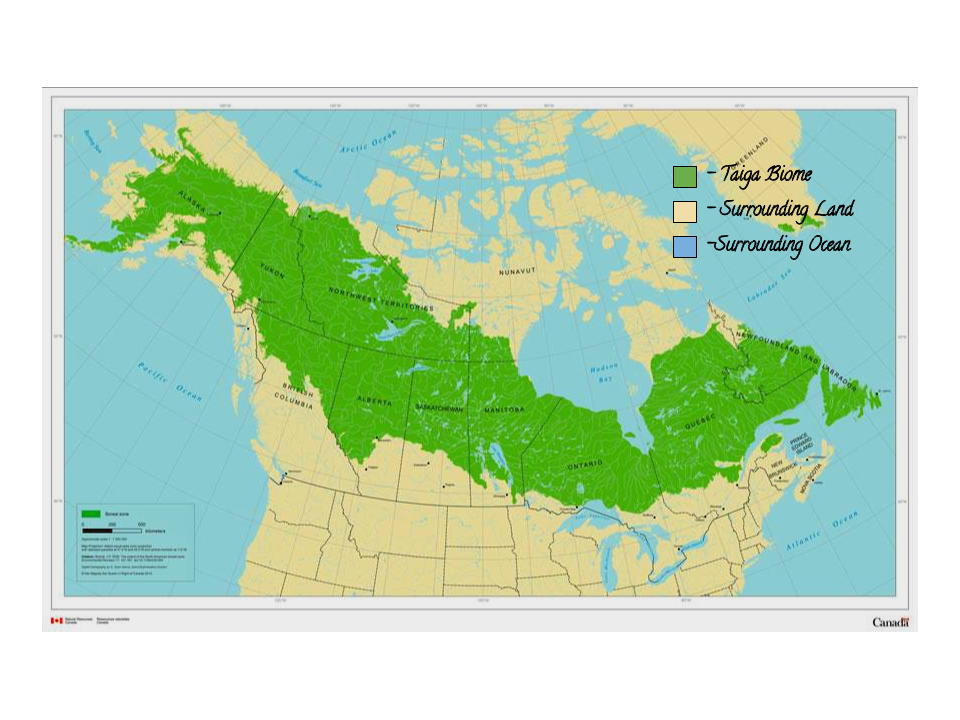
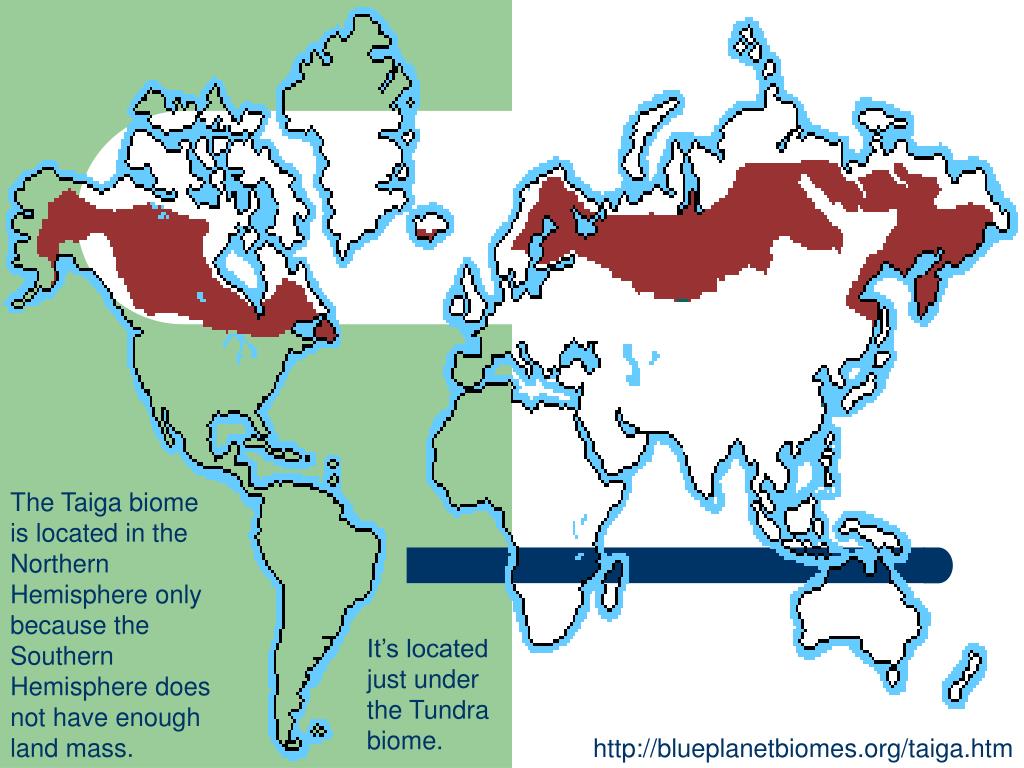
- Geographic Distribution: The map clearly outlines the taiga’s global distribution, showcasing its presence across northern continents. It indicates the specific countries and regions where taiga ecosystems are found, from the vast expanses of Siberia in Russia to the boreal forests of Canada and Alaska.
- Dominant Tree Species: The map identifies the key coniferous tree species that define the taiga, such as spruce, fir, pine, and larch. These trees are adapted to survive the harsh climate and play a crucial role in shaping the ecosystem’s structure and function.
- Climate Zones: The map represents the distinct climatic zones associated with the taiga. It highlights the long, cold winters, short, warm summers, and the significant precipitation that characterizes this biome.
- Wildlife Diversity: The map showcases the diverse wildlife found in the taiga, including iconic species like wolves, bears, moose, lynx, and numerous bird species. These animals have evolved unique adaptations to survive the challenging conditions of the taiga.
- Soil and Water Resources: The map provides insights into the soil types and water resources that support the taiga ecosystem. It highlights the presence of permafrost, a permanently frozen layer of soil, and the extensive network of rivers and lakes that characterize this biome.
The Importance of Taiga Biome Maps:
- Conservation and Management: Taiga biome maps are invaluable tools for conservation efforts. They enable scientists and policymakers to understand the spatial distribution of taiga ecosystems, identify areas under threat, and develop effective conservation strategies.
- Resource Management: The maps provide crucial information for sustainable resource management. They highlight areas with valuable timber resources, potential for renewable energy generation, and the distribution of key mineral deposits.
- Climate Change Research: Taiga biome maps are essential for studying the impacts of climate change on this sensitive ecosystem. They help scientists monitor changes in vegetation patterns, permafrost degradation, and the distribution of key species.
- Educational Purposes: Taiga biome maps serve as valuable educational resources, providing a visual representation of this unique ecosystem and its importance for the planet.
FAQs on Taiga Biome Maps:
Q: What are the primary uses of taiga biome maps?
A: Taiga biome maps serve various purposes, including conservation efforts, sustainable resource management, climate change research, and educational outreach. They provide essential information about the distribution, characteristics, and challenges facing this vital biome.
Q: How do taiga biome maps contribute to conservation efforts?
A: Taiga biome maps help identify areas of high ecological value, prioritize conservation efforts, and monitor the effectiveness of conservation strategies. They provide a clear understanding of the taiga’s spatial distribution, enabling targeted conservation interventions.
Q: What are the key factors influencing the distribution of taiga biomes?
A: The distribution of taiga biomes is primarily influenced by climate, specifically the long, cold winters, short, warm summers, and sufficient precipitation. Other factors include soil conditions, elevation, and the presence of suitable tree species.
Q: How do taiga biome maps help in understanding climate change impacts?
A: Taiga biome maps enable scientists to monitor changes in vegetation patterns, permafrost degradation, and the distribution of key species, providing insights into the effects of climate change on this sensitive ecosystem.
Q: What are some of the unique adaptations of wildlife found in the taiga?
A: Taiga wildlife has evolved unique adaptations to survive the harsh conditions, including thick fur for insulation, hibernation during winter, and specialized diets to utilize available resources.
Tips for Using Taiga Biome Maps:
- Focus on Key Features: Pay attention to the map’s representation of geographic distribution, dominant tree species, climate zones, wildlife diversity, and soil and water resources.
- Compare Different Maps: Consult multiple taiga biome maps to get a comprehensive understanding of the biome’s characteristics and variations.
- Consider Scale and Resolution: Choose maps with appropriate scales and resolutions for your specific needs, whether for regional analysis or detailed local studies.
- Integrate with Other Data: Combine taiga biome maps with other relevant data sources, such as climate models, species distribution maps, and land-use information, for a more comprehensive analysis.
- Engage with Experts: Consult with experts in taiga ecology and conservation for insights and guidance on interpreting and utilizing taiga biome maps.
Conclusion:
Taiga biome maps provide a powerful visual representation of this vast and essential biome. They are essential tools for understanding the taiga’s distribution, characteristics, and challenges, enabling effective conservation efforts, sustainable resource management, and informed decision-making regarding this critical ecosystem. By using taiga biome maps, scientists, policymakers, and educators can gain valuable insights into the taiga’s role in regulating global climate, providing vital resources, and sustaining diverse wildlife. As we face the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, these maps become increasingly important for safeguarding the future of this vital biome and the planet as a whole.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Taiga: A Map of the World’s Largest Biome. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!